1.创新点
提出了一种聚合全局信息的,新颖的基于 anchor 的注意力机制。
提出了一种基于 anchor 的单阶段车道检测模型,称为 LaneATT。它的架构允许使用轻量级 backbone CNN,同时保持高精度。
基于 anchor 的特征池化通过使用 anchor 本身来实现单级检测器,可以潜在地探索所有特征图,从而能够使用更轻量级的 backbone 和更小的感受野。
2.解决了哪些问题
一种车道检测方法,在大型复杂数据集上比现有最先进的实时方法更准确。
与大多数其他模型相比,该模型能够实现更快的训练和推理时间(达到 250 FPS,并且乘加运算 (MAC) 比之前最先进的模型少了一个数量级)。
3.原理和算法步骤
LaneATT 是一种基于 anchor 的单阶段模型,RGB 图像 作为输入,输出是车道边界线。
作为主干的 CNN 会生成一个特征图,然后将其池化以提取每个 anchor 的特征。这些特征会和由注意力模块提取的一组全局特征相结合。最后,组合特征被传递到全连接层以预测最终输出车道。
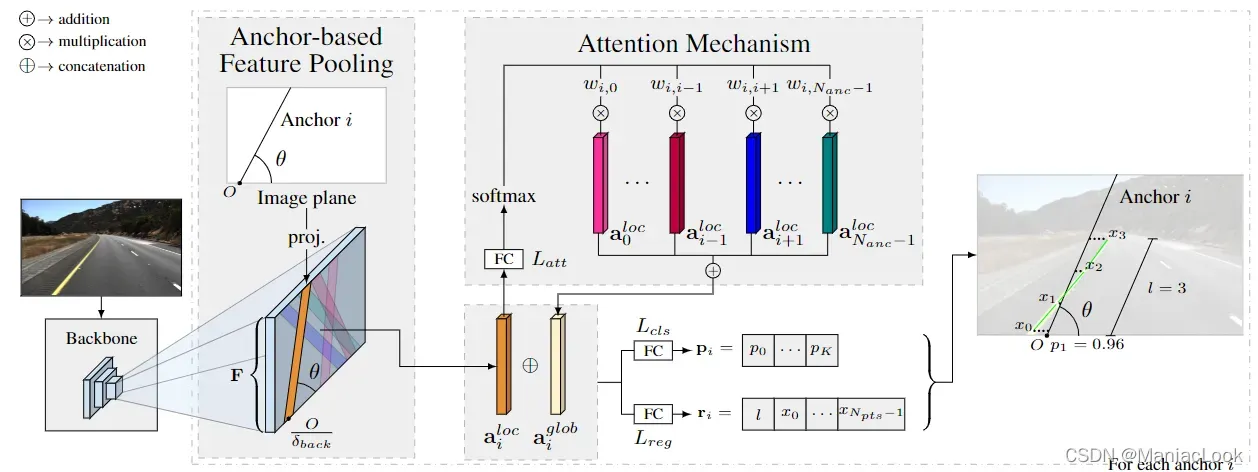
3.1.车道和 anchor 表示
车道由等距 y 坐标 和
x 坐标 。
基于锚的检测时使用线,由 (i) 位于图像边界之一的原点 (其中
) 和 (ii) 方向
θ 形成。使用起始索引 s 和结束索引 e 来定义 X 的有效连续序列。
3.2.主干网络
用如 resnet 的通用 CNN 输出特征图 ,再用
1 x 1 卷积对 进行降维,生成通道缩减的特征图
。
3.3.基于 anchor 的特征池化
锚定义了将用于各个建议的 F 点。由于锚被建模为线,因此给定锚的兴趣点是那些与锚的虚拟线相交的点。对于每个 ,将有一个对应的
x 坐标,
其中 和
θ 分别是锚线的原点和斜率, 是主干的全局步长。因此,每个锚
i 将有其对应的特征向量 (列向量表示法)从
F 中池化,该 F 带有局部特征信息(局部特征)。如果锚的一部分在 F 的边界之外,则 是零填充的。
3.4.注意力机制
注意力机制结构由一个全连接层 组成,它处理一个局部特征向量
,并为每个锚
j, 输出一个概率(权重)
。
之后,这些权重与局部特征相结合,产生相同维度的全局特征向量:
是锚的数量。
是包含局部特征向量(作为行)的矩阵,
是权重矩阵,
有公式 (2) 定义。因此,全局特征可以计算为:
和
具有相同的维度,即
。
3.5.proposal 预测
为每个 anchor 预测一个 lane proposal,由三个主要部分组成:(i)K + 1 个概率(K 个 lane types 和一个用于“背景”或无效 proposal 的类别);(ii) 偏移量(预测和
anchor 之间的水平距离),以及 (iii) proposal 的长度 l(有效偏移的数量)。proposal 的起始索引 (s) 直接由锚原点的 y 坐标确定(,参见第
3.1 节)。因此,结束索引可以确定为 。
为了生成最终 proposal,通过连接 和
来聚合局部和全局信息,产生一个增强的特征向量
。这个增强的向量被馈送到两个并行的全连接层,一个用于分类(
),一个用于回归(
),它们会产生最终的
proposal。 预测
(第 i 项),
预测
(第 ii 项和第 iii 项)。
3.6.NMS
两条车道 和
之间的距离是根据它们共同的有效索引(或
y 坐标)计算的。让 和
定义这些公共索引的范围。因此,车道距离度量定义为
3.7.模型训练
在训练期间,公式(5)中的距离度量也用于定义正锚和负锚。首先,该指标用于测量每个锚(未在 NMS 中过滤的锚)与真实车道之间的距离。随后,距离(公式 5)低于阈值 的锚被认为是正,而距离大于
的锚被认为是负。距离在这些阈值之间的锚(及其相关提案)将被忽略。留下的
用于定义的多任务损失:
其中 ,
是锚
i 的分类和回归输出,而 和
是锚
i 的分类和回归目标。回归损失仅使用长度 l 和对应于 proposal 和 ground-truth 共有的索引的 x 坐标值来计算。 x 坐标的公共索引(在 s' 和 e' 之间)的选择类似于车道距离(公式 (5)),但使用 而不是
,其中
和
分别是
proposal 及其对应的 ground-truth 的结束索引。如果使用 proposal 中预测的结束索引 ,则训练可能会因收敛到退化解而变得不稳定(例如,
可能收敛到零)。函数
和
分别是
Focal Loss [14] 和 Smooth L1。如果锚 i 被认为是负,则其对应的 等于 0。因子
λ 用于平衡损失分量。
3.8.anchor 过滤以提高速度效率
为了选择在训练和测试阶段将忽略哪些锚,该方法测量了训练集中每个锚被标记为正的次数(与训练中的标准相同)。最后,仅保留前 个标记的锚以供进一步处理(也在测试期间用)。
版权声明:本文为博主ManiacLook原创文章,版权归属原作者,如果侵权,请联系我们删除!
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/ManiacLook/article/details/122560253
