基于知识图谱的智能问答
- 1.问答系统的简单介绍
- 1.1 问答系统的目标
- 1.2问答系统框架
- 2. 项目介绍
- 2.1数据集介绍
- 2.2 问题分类
- 2.3 技术方案
- 2.3.1 数据准备
- 2.3.2 数据导入neo4j
- 3 模型
- 3.1 JointBERT(分类、实体识别)
- 3.1.1 数据集构造
- 3.1.2 模型
- 3.2 GraphSAGE(图网络完成属性预测)
- 3.2.1 数据集构造
- 3.2.3 模型
- 4. KBQA
- 5. 问题与总结
1.问答系统的简单介绍
1.1 问答系统的目标
- 将数据导入到neo4j数据库
- 完成图神经网络并嵌入到问答系统
- 给定一个自然语言的问题
完成三元组的提取
能回答任意问题的智能系统收益小于9968614的公司有哪些
王青多大
沈阳惠天热电股份有限公司有可能失信吗
1.2问答系统框架
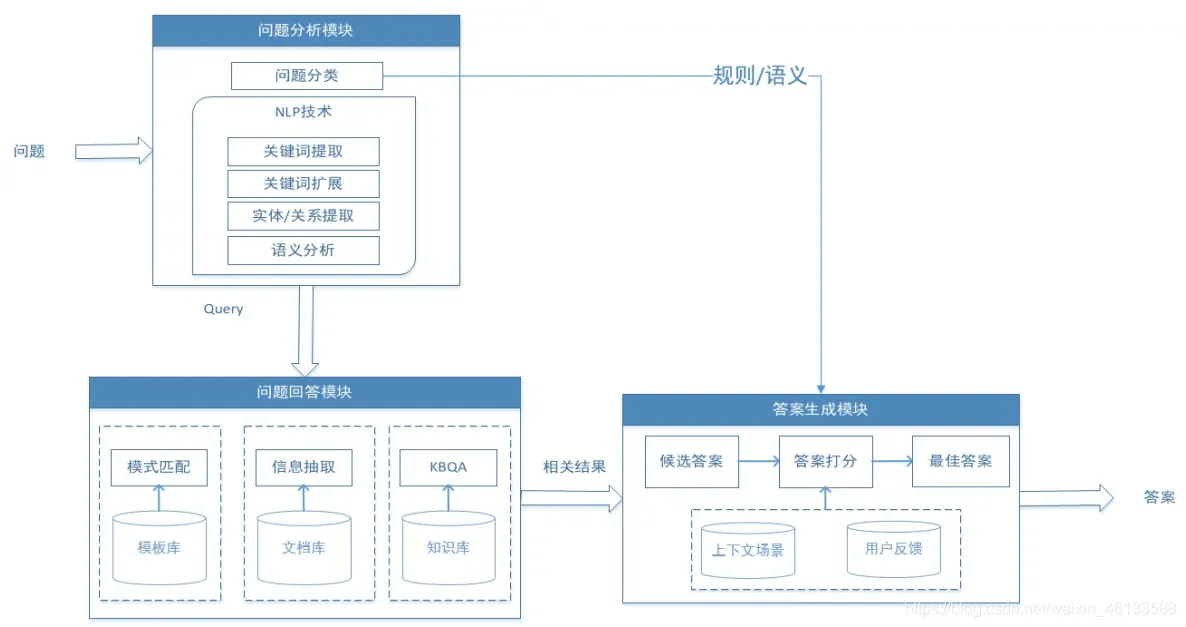
- 1- 问题分析模块
问题分析模块主要负责对用户的问题进行处理,如 王青多大
问题分类:分析出这个问题是由实体查询属性
⽣成查询关键词(提问关键词,扩展关键词,…)
确定提问答案类型(PER, LOC, ORG, TIM, NUM, …)
确定提问的句法、命名实体、语义表示等等。 - 2- 问题回答模块(信息检索)
总的⽬标:如何根据问题的分析结果去缩⼩答案可能存在的范围。这个过程包含
2.1.信息抽取
⽅法描述:从问句中提取关键词语,⽤信息检索的⽅法找出包含候选答案的段落或句⼦,然后基于问答
类型⽤信息抽取的⽅法从备选答案集中提取出最佳答案。
检索过程:段落或者句⼦级排序,利⽤不同类型关键词的加权组合
答案抽取过程:根据问答类型从排序后的段落或句⼦中抽取答案
2.2.模式匹配
基本思想:对于某些提问类型(某⼈的出⽣⽇期、原名、别称等),问句和包含答案的句⼦之间存在⼀
定的答案模式,该⽅法在信息检索的基础上根据这种模式找出答案。因此如何⾃动获取某些类型提问的
尽可能多的答案模式是其中的关键技术。
举个例⼦:
问题⽂本:1968年的今天,加州斯坦福研究所的道格·恩格勒巴特发明了世界上第⼀只⿏标。最初恩格
勒巴特给⿏标 起的名字叫“显示位置纵横显示器”最初的⿏标不过是⼀个⽊盒拖着⼀根绳⼦。但⼀个“⿏
标”(Mouse)的⼩名却⻛靡天下。就是这⽆名⿏辈,竟让世界发⽣了天翻地覆的变化。……
如下给出了⼀个发明家(INVENTOR)型问题的的答案模式及其答案匹配过程:
问题:⿏标是谁发明的?
先由问题解析问题类型< Question Type>和问题词< Q_tag>,这个⽅法略过。
问题类型< Question Type>:发明家(INVENTOR)
问题词< Q_tag>:⿏标
我们要求的是答案< A>,然后根据候选句的评分,进⾏排序,返回前n句中匹配到的答案项。
1.0 < A> 发明 < Q_tag>
1.0 < Q_tag> 被 < A> 发明
0.83 < A> 的 发明 < Q_tag>
0.79 < A> < Q_tag> 的 发明者
0.50 < A> (< Q_tag>)
……
匹配到的模式:1.0 < A> 发明 < Q_tag>
匹配到的答案:道格·恩格勒巴特(如上⽂本⿊体加粗⽂字) - 2.3- 问答
给定⾃然语⾔问题,通过对问题进⾏语义理解和解析,利⽤知识库进⾏查询、推理得出答案。 其特点
是,回答的答案是知识库中的实体。 KBQA问答是我们本项⽬的重点,具体的下个章节论述。 - 3- 答案⽣成模块
总的⽬标:如何从可能存在答案的信息块中抽取答案。
⼀般搜索引擎返回的是⼀堆⽹⻚,⽽问答系统需要返回的是简短的答案。这样,通过信息检索模块
搜索出来的相关⽂档就要提交给答案抽取模块来提炼答案。答案可以是⼀句话,或者是⼏句话,也
可以是⼏个词或者短语。对于那些问时间地点的问题,就可以⽤很短的语句来回答,⽽对于询问原
因、事件的问题就需要较⻓的语句才能回答。⽐如对于问题“9.11事件的是怎么回事?”就不可能⽤
⼀句话就能回答的。所以答案的抽取还需要依据问题的类型。
最后是⽤户⾏为反馈,就是怎么样根据⽤户的结果去指导我们去做更好对话模型的理解。
2. 项目介绍
2.1数据集介绍
数据中包含公司的主键、名称、分红方式、所处行业、债券类型等,也包含公司主要职位的人物名称,还有公司与公司之间的关系。
经过分析之后,我们建立的图谱中内容如下
- 实体:公司、人物、行业、分红方式、违规类型、债券类型。
- 公司的属性:名称、收益。
- 人物的属性:名称、年龄。
- 其他实体的属性只有:名称。
- 公司与公司之间的关系有:供应商、客户、公担保。
- 人物与公司之间的关系有:监事、董事。
- 公司与行业的关系:属于。
- 公司与分红方式的关系:属于。
- 其他类似。
- 将属性公司的所处行业属性按照关系来处理,便于之后进行查询。
2.2 问题分类
KBQA问题可以分为事实类问题、是非类问题、对比类问题、原因方法类问题等。我们这里只回答事实类问题。
- 事实类问题又分为:查询实体、查询属性、查询关系。
- 查询实体:收益大于1000的公司有哪些;王青多大
- 查询属性:沈阳惠天热电股份有限公司的分红方式什么
- 查询关系:沈阳惠天热电股份有限公司的供应商; 沈阳惠天热电股份有限公司的供应商的供应商
- 引入图神经网络完成属性预测:沈阳惠天热电股份有限公司有可能失信吗
其中查询关系又分为一跳和多跳。
项目目标1:能够识别这4类问题,给出正确答案。
项目目标2:引入召回、排序功能,彻底解决名称不匹配的可能性
项目目标3:引入生成式聊天机器人
2.3 技术方案
- 1 输入问句
- 2 通过联合模型JointBERT完成问句分类,实体识别,属性识别
- 3 如果需要预测,则调用图神经网络完成属性预测
- 4 输出答案
我们已知关系有:董事、理事、违规类型、供应商、客户等9种。
对于一跳关系查询:秦皇岛兴龙房地产集团有限公司的董事,这个处理和查询属性类似:使用AC自动机匹配得到关系,使用模板:match (s:company)-[p:{p}]->(o) where s.name=’{subject}’ return o.name 查询。
对于多跳关系查询:秦皇岛兴龙房地产集团有限公司的供应商的分红方式。这就要求先找到 ”秦皇岛兴龙房地产集团有限公司的供应商“查询得到答案: 重庆广建装饰股份有限公司。然后将问题替换为”重庆广建装饰股份有限公司的分红方式“。对于该问题要先分类,然后再按照不同类型问题的模板去查询。当前对于这个问题应该属于第三类查询关系,并且是一跳关系。按照模板处理。
2.3.1 数据准备
原始数据存在excel中,是以属性的方式存储的。将其拆分为公司、人物、行业等excel。
2.3.2 数据导入neo4j
#######################
# 导入节点
######################
def import_company():
# 组件-公司名-有无失信行为
df = pd.read_csv('company_data/公司.csv')
# 提取组件和公司名
eid = df['eid'].values
name = df['companyname'].values
nodes = []
data = list(zip(eid, name))
for eid, name in tqdm(data):
# 加入了额外属性, 收入profit
# 这个例子中是随机数
profit = np.random.randint(100000, 100000000, 1)[0]
# 创建节点, 并加入属性,如再加入公司人数
# node = Node('company', name=name, profit=int(profit), eid=eid, people_num=1000)
node = Node('company', name=name, profit=int(profit), eid=eid)
nodes.append(node)
graph.create(Subgraph(nodes))
3 模型
3.1 JointBERT(分类、实体识别)
采用JointBERT的思想:
使用[CLS]完成意图识别、使用last_hidden_state完成实体识别、使用[CLS]+[SEP]完成属性识别
3.1.1 数据集构造
创建意图识别(4类)、实体识别(BIO标记法)、属性识别(多分类)的数据集
| 问题 | BIO | 意图 | 属性 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 收益小于5684719的公司有哪些 | O O O O O O O O O B-LOC I-LOC O O O | 0 | profit |
| 景明琪多大 | B-LOC I-LOC I-LOC O O | 1 | age |
| 诸城外贸有限责任公司的债券类型是啥 | B-LOC I-LOC I-LOC I-LOC I-LOC I-LOC I-LOC I-LOC I-LOC I-LOC O O O O O O O | 2 | other |
| 中铁高新工业股份有限公司有可能失信吗 | B-LOC I-LOC I-LOC I-LOC I-LOC I-LOC I-LOC I-LOC I-LOC I-LOC I-LOC I-LOC O O O O O O | 3 | other |
| … | … | … | … |
3.1.2 模型
class JointBERT(BertPreTrainedModel):
def __init__(self, config, args, intent_label_lst, slot_label_lst, attribute_label_lst):
super(JointBERT, self).__init__(config)
self.args = args
self.num_intent_labels = len(intent_label_lst)
self.num_slot_labels = len(slot_label_lst)
self.num_attribute_labels = len(attribute_label_lst)
self.bert = BertModel(config=config) # Load pretrained bert
self.intent_classifier = IntentClassifier(config.hidden_size, self.num_intent_labels, args.dropout_rate)
self.slot_classifier = SlotClassifier(config.hidden_size, self.num_slot_labels, args.dropout_rate)
self.attribute_classifier = ObjectClassifier(config.hidden_size, self.num_attribute_labels, args.dropout_rate)
if args.use_crf:
self.crf = CRF(num_tags=self.num_slot_labels, batch_first=True)
def forward(self, input_ids, attention_mask, token_type_ids, intent_label_ids, attribute_label_ids=None, slot_labels_ids=None):
outputs = self.bert(input_ids, attention_mask=attention_mask, token_type_ids=token_type_ids) # sequence_output, pooled_output, (hidden_states), (attentions)
# last_hidden_state: [batch_size, seq_len, hidden_size]
sequence_output = outputs[0] # [last_hidden_state]
# pooler_output: [batch_size, hidden_size]
pooled_output = outputs[1] # [CLS]
slot_logits = self.slot_classifier(sequence_output) # [batch_size, seq_len, hidden_size] --> [batch_size, seq_len, num_slot]
intent_logits = self.intent_classifier(pooled_output) # [batch_size, hidden_size] --> [batch_size, num_intent]
# total_loss = intent_loss + self.args.slot_loss_coef * slot_loss
total_loss = 0
# 1. Intent Softmax
if intent_label_ids is not None:
if self.num_intent_labels == 1:
intent_loss_fct = nn.MSELoss()
intent_loss = intent_loss_fct(intent_logits.view(-1), intent_label_ids.view(-1))
else:
intent_loss_fct = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
intent_loss = intent_loss_fct(intent_logits.view(-1, self.num_intent_labels), intent_label_ids.view(-1))
total_loss += intent_loss
# 2. Slot Softmax
if slot_labels_ids is not None:
if self.args.use_crf:
slot_loss = self.crf(slot_logits, slot_labels_ids, mask=attention_mask.byte(), reduction='mean')
slot_loss = -1 * slot_loss # negative log-likelihood
else:
slot_loss_fct = nn.CrossEntropyLoss(ignore_index=self.args.ignore_index)
# Only keep active parts of the loss
if attention_mask is not None:
active_loss = attention_mask.view(-1) == 1
active_logits = slot_logits.view(-1, self.num_slot_labels)[active_loss]
active_labels = slot_labels_ids.view(-1)[active_loss]
slot_loss = slot_loss_fct(active_logits, active_labels)
else:
slot_loss = slot_loss_fct(slot_logits.view(-1, self.num_slot_labels), slot_labels_ids.view(-1))
total_loss += self.args.slot_loss_coef * slot_loss
# 3. Object
# 为了导入subject 的信息,先做一次预测,求取出 subject token ---> word_embedding ---> plus to sequence_output
if attribute_label_ids is not None:
# slot_preds_ids: [batch_size, seq_len, num_slot_labels]
slot_preds_ids = slot_logits.detach().cpu().numpy()
slot_preds_ids = np.argmax(slot_preds_ids, axis=2)
# 将slot_preds_ids 转换为 subject_preds_ids
subject_preds_ids = slots_ids_2_subject_ids(slot_preds_ids)
# subject_input_index = [[input_ids[batch][start:end+1] for start, end in line] for batch, line in enumerate(subject_preds_ids)]
attribute_logits = self.attribute_classifier(sequence_output)
# compute Object loss
if attribute_label_ids is not None:
if self.num_attribute_labels == 1:
attribute_loss_fct = nn.MSELoss()
attribute_loss = attribute_loss_fct(attribute_logits.view(-1), attribute_label_ids.view(-1))
else:
attribute_loss_fct = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
attribute_loss = attribute_loss_fct(attribute_logits.view(-1, self.num_attribute_labels), attribute_label_ids.view(-1))
total_loss += attribute_loss
outputs = ((intent_logits, slot_logits, attribute_logits),) + outputs[2:] # add hidden states and attention if they are here
outputs = (total_loss,) + outputs
# outputs: (total_loss), ( (last_hidden_state, pooler_output), (outputs[2:]) )
return outputs # (loss), logits, (hidden_states), (attentions) # Logits is a tuple of intent and slot logits
3.2 GraphSAGE(图网络完成属性预测)
仅可预测公司实体是否可能存在失信
3.2.1 数据集构造
| eid | companyname | industry | assign | violations | bond | dishonesty_y |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 06fc37e2-8bf5-4e36-adc2-387f6a96a4ad | 江苏联赢激光有限公司 | 不分配 | 信息披露虚假或严重误导性陈述 | 1 | ||
| 003ffe3f-d012-40b6-9cd6-ba94cf235ae2 | 重庆江骏房地产开发有限公司 | 寿险公司 | 业绩预测结果不准确或不及时 | 企业债 | 0 | |
| … | … | … | … | … | … | … |
3.2.3 模型
GraphSAGE 是Graph SAmple and aggreGatE的缩写,其运行流程如上图所示,可以分为三个步骤
对图中每个顶点邻居顶点进行采样
根据聚合函数从聚合邻居顶点蕴含的信息
得到图中各顶点的向量表示供下游任务
class GraphSAGE_MODEL(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self, args, in_channels=31, hidden_channels=64):
super(GraphSAGE_MODEL, self).__init__()
# in_channels # 初始特征的维度
# out_channels # 分类
self.args = args
self.out_channels = args.num_classes
self.conv1 = SAGEConv(in_channels, hidden_channels)
self.conv2 = SAGEConv(hidden_channels, hidden_channels)
self.conv3 = SAGEConv(hidden_channels, hidden_channels)
self.lin = torch.nn.Linear(3 * hidden_channels, self.out_channels)
# 每层的聚合方式
def set_aggr(self, aggr):
self.conv1.aggr = aggr
self.conv2.aggr = aggr
self.conv3.aggr = aggr
def forward(self, data):
x0, edge_index, edge_weight = data.x, data.edge_index, data.edge_attr
x1 = F.relu(self.conv1(x0, edge_index, edge_weight))
x1 = F.dropout(x1, p=0.2, training=self.training)
x2 = F.relu(self.conv2(x1, edge_index, edge_weight))
x2 = F.dropout(x2, p=0.2, training=self.training)
x3 = F.relu(self.conv3(x2, edge_index, edge_weight))
x3 = F.dropout(x3, p=0.2, training=self.training)
x = torch.cat([x1, x2, x3], dim=-1)
x = self.lin(x)
return x
4. KBQA
主要包含内容:
- 调用训练好的ner_bert 模型(文本分类、实体提取、属性名提取),完成文本分类
- 属性查实体
# 属性 查 实体 op, num = get_op(text) cypher = f'match (n:{subject_type}) where n.{attribute}{op}{num} return n.name' print(cypher) res = graph.run(cypher).to_ndarray() - 实体查属性
# 实体 查 属性 cypher = f'''match (n:{subject_type}) where n.name='{subject}' return n.{attribute}''' print(cypher) res = graph.run(cypher).to_ndarray() - 实体、关系查询实体(多跳问答)
# 实体、关系 查询实体 # 实体 subject # 关系抽取 这里 可用 spo 方法, 同时抽取 ner 和 relation predicate = [] for end_index, original_value in ac_relation.iter(text): start_index = end_index - len(original_value) + 1 print('关系:', (start_index, end_index, original_value)) assert text[start_index:start_index + len(original_value)] == original_value predicate.append(original_value) for i, p in enumerate(predicate): cypher = f'''match (s:company)-[p:`{p}`]->(o) where s.name='{subject}' return o.name''' print(cypher) res = graph.run(cypher).to_ndarray() object = res[0][0] if i == len(predicate) - 1: break new_index = text.index(p) + len(p) new_question = object + str(text[new_index:]) print('new question:', new_question) res = kbqa(new_question) break - 预测是否可能失信
- 调用图神经网络
# 预测是否可能失信 assert subject_type == "company", "Subject not a company if you want to pre_dishonesty" from utils import pre_dishonesty res = pre_dishonesty(args, subject)
- 调用图神经网络
- 属性查实体
5. 问题与总结
1、仅限于提问已经存在与知识库的问题
1、提取的实体(slot_pred –> subject)来自输入语句txt, 有可能导致和数据库中实体名称不能匹配,如公司名字应该说全名
2、三任务联合训练在简单数据集(如本项目,以公司为主题的数据集)上能达到很好的效果,这是因为数据集简单,提问简单,但是如果是复杂数据集,其可能存在其他的问题
3、GNN模块存在较大的问题
a) 数据集的制作存在问题,OneHot编码的方式简单的使用了pd.get_dummies,考虑能否往embedding反向转变
b) 准确率有待提高
结果
text:收益小于9968614的公司有哪些
question type: 0
match (n:company) where n.profit<9968614.0 return n.name
[[‘广东欧昊集团有限公司’]
[‘浙江天工建设集团有限公司’]
…]text:绍兴仁昌酱园有限公司的收入
question type: 1
match (n:company) where n.name=‘绍兴仁昌酱园有限公司’ return n.profit
[[16399117]]text:沈阳惠天热电股份有限公司的分红方式什么
question type: 2
match (s:company)-[p:分红方式]->(o) where s.name=‘沈阳惠天热电股份有限公司’ return o.name
[[‘现金分红’]]text:沈阳惠天热电股份有限公司有可能失信吗
question type: 3
the node: 沈阳惠天热电股份有限公司, –> 0
展望
1、引入召回、排序功能,彻底解决名称不匹配的可能性
2、引入生成式聊天机器人
文章出处登录后可见!