逻辑回归预测考试是否通过
免责声明:本文为课程学习记录,如有侵权,请联系我删除。
注:本篇文章基于sklearn库,这里我们应该掌握的基础知识有:logistic回归。
目标:基于数据集建立逻辑回归模型,给定两个分数,预测第三个分数能否通过;建立二阶边界以提高模型的准确性。
# 加载数据
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
data = pd.read_csv('examdata.csv')
data.head()
| Exam1 | Exam2 | Pass | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 34.623660 | 78.024693 | 0 |
| 1 | 30.286711 | 43.894998 | 0 |
| 2 | 35.847409 | 72.902198 | 0 |
| 3 | 60.182599 | 86.308552 | 1 |
| 4 | 79.032736 | 75.344376 | 1 |
# 可视化数据
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
fig1 = plt.figure()
plt.figure(figsize=(8,8))
plt.scatter(data.loc[:,'Exam1'],data.loc[:,'Exam2'])
plt.title('Exam1 VS Exam2')
plt.xlabel('Exam1')
plt.ylabel('Exam2')
plt.show()
<Figure size 432x288 with 0 Axes>
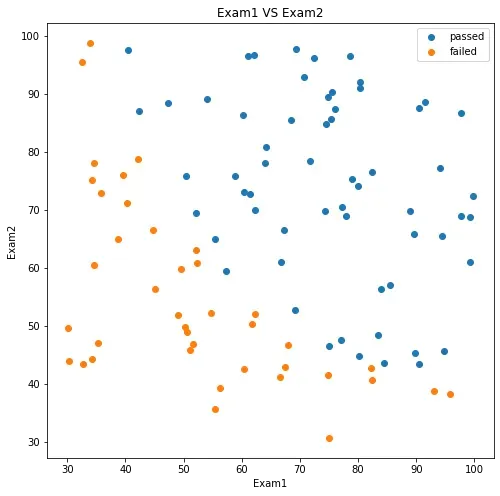
#添加标签
mask = data.loc[:,'Pass']==1
fig2 = plt.figure()
plt.figure(figsize=(8,8))
passed = plt.scatter(data.loc[:,'Exam1'][mask],data.loc[:,'Exam2'][mask])
failed = plt.scatter(data.loc[:,'Exam1'][~mask],data.loc[:,'Exam2'][~mask])
plt.title('Exam1 VS Exam2')
plt.xlabel('Exam1')
plt.ylabel('Exam2')
plt.legend((passed,failed),('passed','failed'))
plt.show()
# 对变量进行数据赋值
x = data.drop(['Pass'],axis=1)
#x.head()
y = data.loc[:,'Pass']
#y.head()
x1 = data.loc[:,'Exam1']
#x1.head()
x2 = data.loc[:,'Exam2']
#x2.head()
# 建立并训练模型
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
LR = LogisticRegression()
LR.fit(x,y)
LogisticRegression()
# 显示预测结果
y_predict = LR.predict(x)
print(y_predict)
[0 0 0 1 1 0 1 0 1 1 1 0 1 1 0 1 0 0 1 1 0 1 0 0 1 1 1 1 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 0 1
1 0 0 1 0 1 1 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 1 0 1 1 1
1 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 1 0 1 1 0 1 1 0 1 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 0 1]
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score
accuracy = accuracy_score(y,y_predict)
print(accuracy)
0.89
# 进行结果测试
y_test = LR.predict([[70,65]])
#print(y_test)
print('passed' if y_test==1 else 'failed')
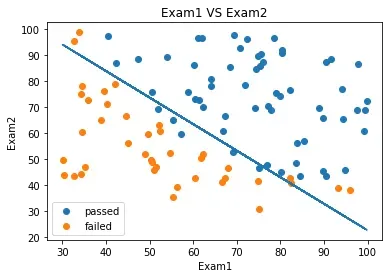
#画出直线
theta0 = LR.intercept_ #截距
theta1,theta2 = LR.coef_[0][0],LR.coef_[0][1]
print(theta0,theta1,theta2)
[-25.05219314] 0.20535491217790372 0.20058380395469036
边界函数为:
x2_new = -(theta0+theta1*x1)/theta2
print(x2_new)
0 89.449169
1 93.889277
2 88.196312
3 63.282281
4 43.983773
...
95 39.421346
96 81.629448
97 23.219064
98 68.240049
99 48.341870
Name: Exam1, Length: 100, dtype: float64
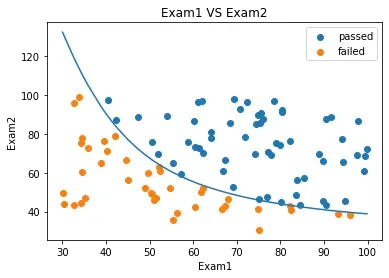
fig3 = plt.figure()
passed = plt.scatter(data.loc[:,'Exam1'][mask],data.loc[:,'Exam2'][mask])
failed = plt.scatter(data.loc[:,'Exam1'][~mask],data.loc[:,'Exam2'][~mask])
plt.plot(x1,x2_new)
plt.title('Exam1 VS Exam2')
plt.xlabel('Exam1')
plt.ylabel('Exam2')
plt.legend((passed,failed),('passed','failed'))
plt.show()
二阶边界函数:
#创建新的数据集
x1_2 = x1*x1
x2_2 = x2*x2
x1_x2 = x1*x2
#print(x1,x1_2)
x_new = {'x1':x1,'x2':x2,'x1_2':x1_2,'x2_2':x2_2,'x1_x2':x1_x2}
x_new = pd.DataFrame(x_new)
print(x_new)
x1 x2 x1_2 x2_2 x1_x2
0 34.623660 78.024693 1198.797805 6087.852690 2701.500406
1 30.286711 43.894998 917.284849 1926.770807 1329.435094
2 35.847409 72.902198 1285.036716 5314.730478 2613.354893
3 60.182599 86.308552 3621.945269 7449.166166 5194.273015
4 79.032736 75.344376 6246.173368 5676.775061 5954.672216
.. ... ... ... ... ...
95 83.489163 48.380286 6970.440295 2340.652054 4039.229555
96 42.261701 87.103851 1786.051355 7587.080849 3681.156888
97 99.315009 68.775409 9863.470975 4730.056948 6830.430397
98 55.340018 64.931938 3062.517544 4216.156574 3593.334590
99 74.775893 89.529813 5591.434174 8015.587398 6694.671710
[100 rows x 5 columns]
LR2 = LogisticRegression()
LR2.fit(x_new,y)
LogisticRegression()
y2_predict = LR2.predict(x_new)
accuracy2 = accuracy_score(y,y2_predict)
print(accuracy2)
1.0
LR2.coef_
array([[-8.95942818e-01, -1.40029397e+00, -2.29434572e-04,
3.93039312e-03, 3.61578676e-02]])
x1_new = x1.sort_values()#排序,原因是让后面画图按照次序画图以防止画图很凌乱无序。
print(x1,x1_new)
0 34.623660
1 30.286711
2 35.847409
3 60.182599
4 79.032736
...
95 83.489163
96 42.261701
97 99.315009
98 55.340018
99 74.775893
Name: Exam1, Length: 100, dtype: float64 63 30.058822
1 30.286711
57 32.577200
70 32.722833
36 33.915500
...
56 97.645634
47 97.771599
51 99.272527
97 99.315009
75 99.827858
Name: Exam1, Length: 100, dtype: float64
theta0 = LR2.intercept_
theta1 = LR2.coef_[0][0]
theta2 = LR2.coef_[0][1]
theta3 = LR2.coef_[0][2]
theta4 = LR2.coef_[0][3]
theta5 = LR2.coef_[0][4]
a = theta4
b = theta2+theta5*x1_new
c = theta0+theta1*x1_new+theta3*x1_new*x1_new
x2_new_boundary = (-b+(np.sqrt(b*b-4*a*c)))/(2*a)
plt.plot(x1_new,x2_new_boundary)
[<matplotlib.lines.Line2D at 0x1ce77b30b50>]
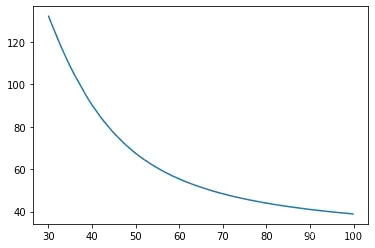
fig4 = plt.figure()
passed = plt.scatter(data.loc[:,'Exam1'][mask],data.loc[:,'Exam2'][mask])
failed = plt.scatter(data.loc[:,'Exam1'][~mask],data.loc[:,'Exam2'][~mask])
plt.plot(x1_new,x2_new_boundary)
plt.title('Exam1 VS Exam2')
plt.xlabel('Exam1')
plt.ylabel('Exam2')
plt.legend((passed,failed),('passed','failed'))
plt.show()
如果想要进行本例子实战的数据链接如下:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1dPKCOMse7Ai1WkrJs64xBw
提取码:1234,支持flare老师课程!
文章出处登录后可见!
已经登录?立即刷新
