人脸口罩检测(含运行代码+数据集)
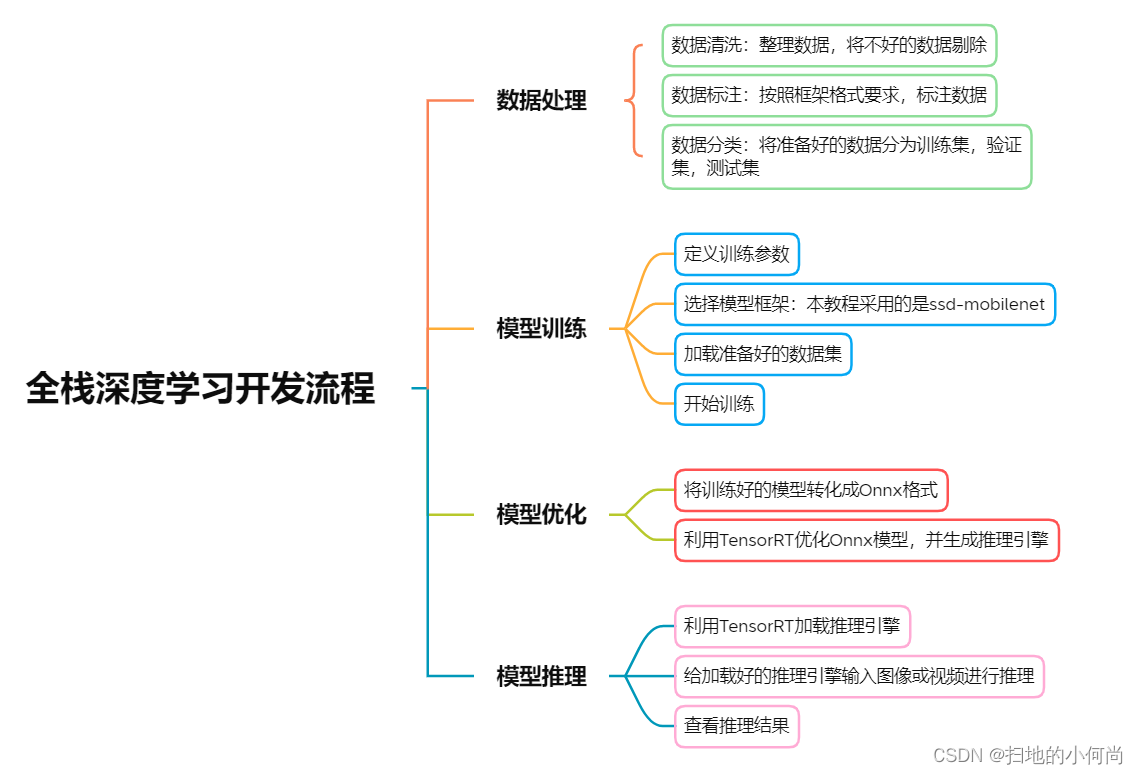
- 本教程目的为让开发者了解深度学习中的完整流程,这包括:
1.数据集导入及预处理流程
2.网络模型选择及参数设置流程
3.模型训练及导出流程
4.模型加载/优化并得出推断结果
项目源码以及数据集下载:
https://download.csdn.net/download/kunhe0512/85360655
-
本教程采用了以下主要的软硬件环境:
1.NVIDIA Xavier NX
2.Jetpack 4.6
3.TensorRT 8.0.1
4.Pytorch 1.10.0
5.Python 3.6.9
6.Opencv 4.1.1 -
实验内容:
- 本教程的实验内容是利用深度学习的方法,完成口罩检测的任务。
- 检测目标类别为:Background,face,mask,mask_weared_incorrect
- 在实验过程中,采用了OpenImages CVS格式的数据集和SSD-mobilenet的模型。
- 本实验利用Pytorch进行模型训练,将训练好的模型转化为ONNX格式,最后利用TensorRT进行推理
- 更多精彩内容,请扫描下方二维码来加入NVIDIA开发者计划

开始实验
1.导入需要的工具库
#1
import os
import sys
sys.executable
import logging
import argparse
import itertools
import torch
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader, ConcatDataset
from torch.optim.lr_scheduler import CosineAnnealingLR, MultiStepLR
from vision.utils.misc import str2bool, Timer, freeze_net_layers, store_labels
from vision.ssd.ssd import MatchPrior
from vision.ssd.vgg_ssd import create_vgg_ssd
from vision.ssd.mobilenetv1_ssd import create_mobilenetv1_ssd
from vision.ssd.mobilenetv1_ssd_lite import create_mobilenetv1_ssd_lite
from vision.ssd.mobilenet_v2_ssd_lite import create_mobilenetv2_ssd_lite
from vision.ssd.squeezenet_ssd_lite import create_squeezenet_ssd_lite
from vision.datasets.voc_dataset import VOCDataset
from vision.datasets.open_images import OpenImagesDataset
from vision.nn.multibox_loss import MultiboxLoss
from vision.ssd.config import vgg_ssd_config
from vision.ssd.config import mobilenetv1_ssd_config
from vision.ssd.config import squeezenet_ssd_config
from vision.ssd.data_preprocessing import TrainAugmentation, TestTransform
2.使用GPU完成训练
#2
DEVICE = torch.device("cuda:0")
torch.backends.cudnn.benchmark = True
3.设定训练方法
#3
def train(loader, net, criterion, optimizer, device, debug_steps=100, epoch=-1):
net.train(True)
running_loss = 0.0
running_regression_loss = 0.0
running_classification_loss = 0.0
for i, data in enumerate(loader):
images, boxes, labels = data
images = images.to(device)
boxes = boxes.to(device)
labels = labels.to(device)
optimizer.zero_grad()
confidence, locations = net(images)
regression_loss, classification_loss = criterion(confidence, locations, labels, boxes) # TODO CHANGE BOXES
loss = regression_loss + classification_loss
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
running_loss += loss.item()
running_regression_loss += regression_loss.item()
running_classification_loss += classification_loss.item()
if i and i % debug_steps == 0:
avg_loss = running_loss / debug_steps
avg_reg_loss = running_regression_loss / debug_steps
avg_clf_loss = running_classification_loss / debug_steps
print(
f"Epoch: {epoch}, Step: {i}/{len(loader)}, " +
f"Avg Loss: {avg_loss:.4f}, " +
f"Avg Regression Loss {avg_reg_loss:.4f}, " +
f"Avg Classification Loss: {avg_clf_loss:.4f}"
)
running_loss = 0.0
running_regression_loss = 0.0
running_classification_loss = 0.0
4.设定测试方法
#4
def test(loader, net, criterion, device):
net.eval()
running_loss = 0.0
running_regression_loss = 0.0
running_classification_loss = 0.0
num = 0
for _, data in enumerate(loader):
images, boxes, labels = data
images = images.to(device)
boxes = boxes.to(device)
labels = labels.to(device)
num += 1
with torch.no_grad():
confidence, locations = net(images)
regression_loss, classification_loss = criterion(confidence, locations, labels, boxes)
loss = regression_loss + classification_loss
running_loss += loss.item()
running_regression_loss += regression_loss.item()
running_classification_loss += classification_loss.item()
return running_loss / num, running_regression_loss / num, running_classification_loss / num
5.设定训练参数
#5
net_name = "mb1-ssd"
datasets = []
datasets_path = ["data/mask"]
model_dir = "models/mask/"
voc_or_open_images = "open_images"
batch_size = 4
num_epochs = 6
validation_epochs = 2
num_workers = 2
lr = 0.01
base_net_lr = 0.001
extra_layers_lr = 0.01
momentum=0.9
weight_decay=5e-4
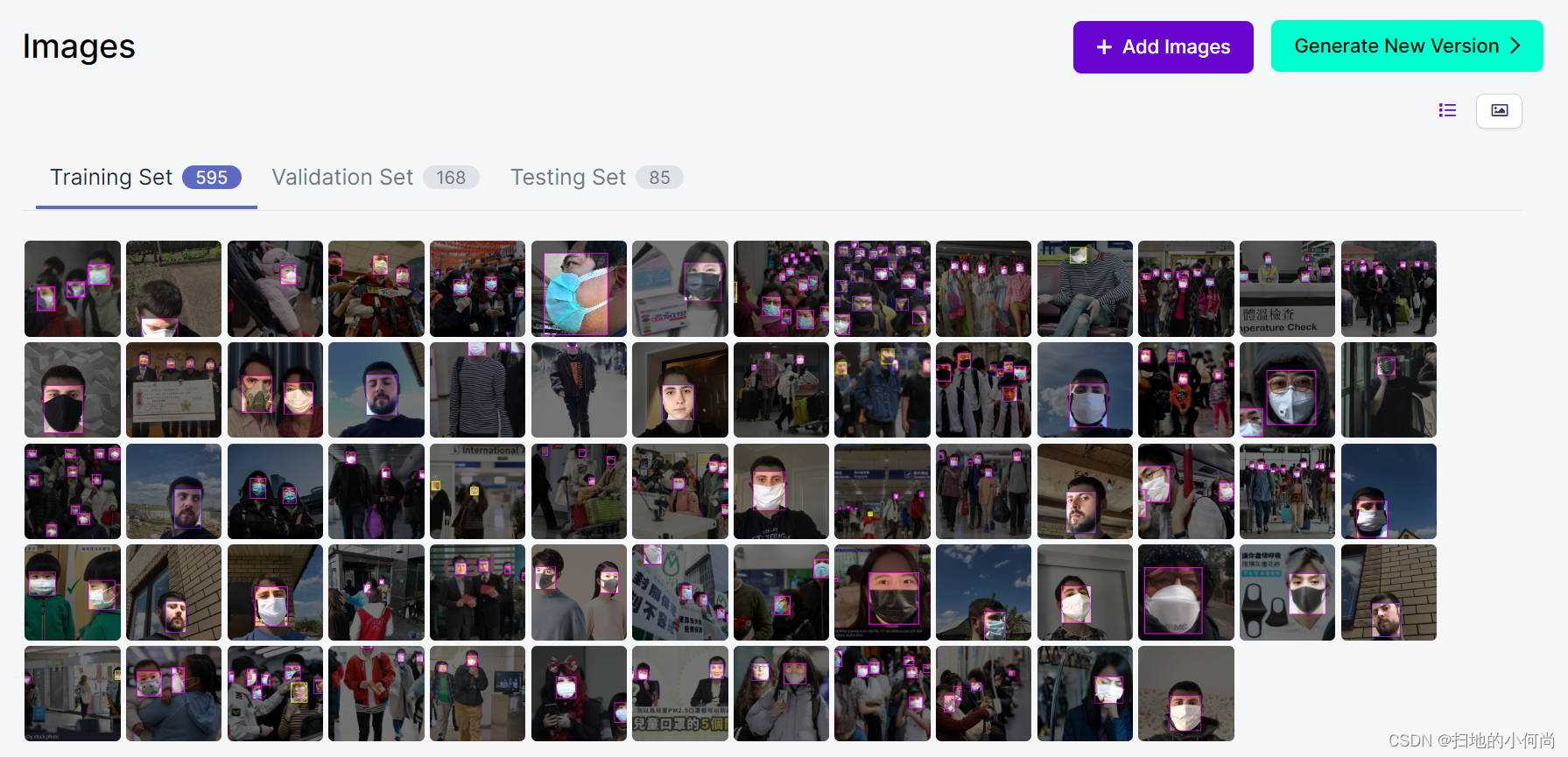
6.加载数据集
#6
timer = Timer()
create_net = create_mobilenetv1_ssd
config = mobilenetv1_ssd_config
# create data transforms for train/test/val
train_transform = TrainAugmentation(config.image_size, config.image_mean, config.image_std)
target_transform = MatchPrior(config.priors, config.center_variance,
config.size_variance, 0.5)
test_transform = TestTransform(config.image_size, config.image_mean, config.image_std)
# load datasets (could be multiple)
print("Prepare training datasets.")
for dataset_path in datasets_path:
if voc_or_open_images == 'voc':
dataset = VOCDataset(dataset_path, transform=train_transform,target_transform=target_transform)
label_file = os.path.join(model_dir, "labels.txt")
store_labels(label_file, dataset.class_names)
num_classes = len(dataset.class_names)
elif voc_or_open_images == 'open_images':
dataset = OpenImagesDataset(dataset_path,transform=train_transform, target_transform=target_transform,dataset_type="train", balance_data=False)
label_file = os.path.join(model_dir, "labels.txt")
store_labels(label_file, dataset.class_names)
print(dataset)
num_classes = len(dataset.class_names)
else:
raise ValueError(f"Dataset type is not supported.")
datasets.append(dataset)
7.将加载好的数据集分割为训练集和验证集
#7
# create training dataset
print(f"Stored labels into file {label_file}.")
train_dataset = ConcatDataset(datasets)
print("Train dataset size: {}".format(len(train_dataset)))
train_loader = DataLoader(train_dataset, batch_size,num_workers=num_workers,shuffle=True)
# create validation dataset
print("Prepare Validation datasets.")
if voc_or_open_images == "voc":
val_dataset = VOCDataset(dataset_path, transform=test_transform,target_transform=target_transform, is_test=True)
elif voc_or_open_images == 'open_images':
val_dataset = OpenImagesDataset(dataset_path,transform=test_transform, target_transform=target_transform,dataset_type="test")
print(val_dataset)
print("Validation dataset size: {}".format(len(val_dataset)))
val_loader = DataLoader(val_dataset, batch_size,num_workers = num_workers,shuffle=False)
8.创建网络模型
#8
# create the network
print("Build network.")
net = create_net(num_classes)
min_loss = -10000.0
last_epoch = -1
params = [
{'params': net.base_net.parameters(), 'lr': base_net_lr},
{'params': itertools.chain(
net.source_layer_add_ons.parameters(),
net.extras.parameters()
), 'lr': extra_layers_lr},
{'params': itertools.chain(
net.regression_headers.parameters(),
net.classification_headers.parameters()
)}
]
9.定义是否使用预训练模型或者
- 我们这里设计了三种模式:
1.重头开始训练,只需将你的模型路径赋值给base_net: base_net = “path/to/the/basic/model”
2.使用之前训练一半中间断开没训练完的模型继续训练,只需将模型路径赋值给resume:resume = “path/to/the/resume/model”
3.利用我们已经准好的预训练模型,只需将模型路径赋值给pretrained_ssd: pretrained_ssd = “path/to/the/pretrained_ssd/model” - 如果不太明白想选择什么模型,可以将resume,base_net和pretrained_ssd都赋值None,将会自动从头开始训练
#9
# load a previous model checkpoint (if requested)
timer.start("Load Model")
resume=None
base_net = None
pretrained_ssd = "models/face-mask-pretrain-model.pth"
if resume:
print(f"Resume from the model {resume}")
net.load(resume)
elif base_net:
print(f"Init from base net {base_net}")
net.init_from_base_net(base_net)
elif pretrained_ssd:
print(f"Init from pretrained ssd {pretrained_ssd}")
net.init_from_pretrained_ssd(pretrained_ssd)
print(f'Took {timer.end("Load Model"):.2f} seconds to load the model.')
10.开始训练模型
#10
# move the model to GPU
net.to(DEVICE)
# define loss function and optimizer
criterion = MultiboxLoss(config.priors, iou_threshold=0.5, neg_pos_ratio=3,center_variance=0.1, size_variance=0.2, device=DEVICE)
optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(params, lr=lr, momentum=0.9, weight_decay=weight_decay)
print(f"Learning rate: {lr}, Base net learning rate: {base_net_lr}, "+ f"Extra Layers learning rate: {extra_layers_lr}.")
# set learning rate policy
print("Uses CosineAnnealingLR scheduler.")
scheduler = CosineAnnealingLR(optimizer, 100, last_epoch=last_epoch)
# train for the desired number of epochs
print(f"Start training from epoch {last_epoch + 1}.")
for epoch in range(last_epoch + 1, num_epochs):
scheduler.step()
train(train_loader, net, criterion, optimizer,device=DEVICE, debug_steps=10, epoch=epoch)
if epoch % validation_epochs == 0 or epoch == num_epochs - 1:
val_loss, val_regression_loss, val_classification_loss = test(val_loader, net, criterion, DEVICE)
print(
f"Epoch: {epoch}, " +
f"Validation Loss: {val_loss:.4f}, " +
f"Validation Regression Loss {val_regression_loss:.4f}, " +
f"Validation Classification Loss: {val_classification_loss:.4f}"
)
model_path = os.path.join(model_dir, f"{net_name}-Epoch-{epoch}-Loss-{val_loss}.pth")
net.save(model_path)
print(f"Saved model {model_path}")
print("Task done, exiting program.")
11.将训练好的模型转化成ONNX格式
#11
!python3 onnx_export.py --model-dir=models/mask
12.将转化好的ONNX格式利用TensorRT进行优化,生成TensorRT推理引擎
这里注意,需要安装Onnx2TensorRT
#12
!onnx2trt models/mask/ssd-mobilenet.onnx -o models/TRT_ssd_mobilenet_v1_face2.bin
13.加载引擎推理时所需要的工具库
#13
import sys
import time
import argparse
import cv2
import pycuda.autoinit
import numpy as np
from utils.ssd_classes import get_cls_dict
from utils.camera import add_camera_args, Camera
from utils.display import open_window, set_display, show_fps
from utils.visualization import BBoxVisualization
import ctypes
import tensorrt as trt
import pycuda.driver as cuda
14.设计引擎输入输出的预处理方法和后处理方法
#14
def do_nms(det, boxes, confs, clss):
drop = False
if len(boxes) <= 0:
boxes.append((det[0],det[1],det[2],det[3]))
confs.append(det[4])
clss.append(det[5])
return boxes, confs, clss
for i in range(0,len(boxes)):
bbox = boxes[i]
xx1 = np.maximum(det[0], bbox[0])
yy1 = np.maximum(det[1], bbox[1])
xx2 = np.minimum(det[2], bbox[2])
yy2 = np.minimum(det[3], bbox[3])
w = np.maximum(0.0, xx2-xx1+1)
h = np.maximum(0.0, yy2-yy1+1)
area_det = (det[2]-det[0]+1)*(det[3]-det[1]+1)
area_bbox = (bbox[2]-bbox[0]+1)*(bbox[3]-bbox[1]+1)
inter = w*h
ovr = inter / (area_det + area_bbox - inter)
if ovr > 0.6 and not drop:
if det[4] > confs[i]:
boxes[i] = ((det[0],det[1],det[2],det[3]))
confs[i] = det[4]
clss[i] = det[5]
drop = True
if not drop:
boxes.append((det[0],det[1],det[2],det[3]))
confs.append(det[4])
clss.append(det[5])
return boxes, confs, clss
def _preprocess_trt(img, shape=(300, 300)):
"""Preprocess an image before TRT SSD inferencing."""
img = cv2.resize(img, shape)
img = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
img = img.transpose((2, 0, 1)).astype(np.float32)
img *= (2.0/255.0)
img -= 1.0
return img
def _postprocess_trt(img, output, conf_th, output_layout):
"""Postprocess TRT SSD output."""
img_h, img_w, _ = img.shape
boxes, confs, clss, results = [], [], [],[]
#print(((len(output[1]))/4+1))
#print("len(outputs[0]): "+str(len(output[0]))+" len(outputs[1]): "+str(len(output[1])))
for n in range(0, int((len(output[1]))/4)):
maxScore = -1000.0000
maxClass = 0
for m in range(0, 4):
score = output[0][n*4+m]
#print(score)
if score < conf_th:
continue
if m <= 0:
continue
if( score > maxScore):
maxScore = score
maxClass = m
#if(maxClass < 0):
# continue
index = int(n)
if maxScore < conf_th:
continue
#print(str(output[1][n*4+0])+" "+str(output[1][n*4+1])+" "+str(output[1][n*4+2])+" "+str(output[1][n*4+3]))
x1 = int(output[1][n*4+0] * img_w)
y1 = int(output[1][n*4+1] * img_h)
x2 = int(output[1][n*4+2] * img_w)
y2 = int(output[1][n*4+3] * img_h)
det = [x1,y1,x2,y2,maxScore,maxClass,n]
boxes, confs, clss = do_nms(det, boxes, confs, clss)
return boxes, confs, clss
15.定义SSD-mobilenet v1模型的推理引擎的加载
- 当我们已经优化好了引擎的时候,我们可以将优化好的引擎以文件的形式写到硬盘上,我们称之为序列化文件(serialized file)或PLAN文件
- 我们下次想直接使用优化好的引擎的时候,我们可以通过读取硬盘上的序列化文件,并利用 deserialize_cuda_engine() 方法进行反序列化,生成可执行的引擎
- 利用序列化文件生成可执行引擎可以为我们节省大量的时间
- 不同平台(软件或硬件平台)上生成的引擎的序列化文件不能直接通用,相同平台(软件且硬件平台)或同一台设备上生成的引擎序列化文件可以直接用
#15
class TrtSSD(object):
"""TrtSSD class encapsulates things needed to run TRT SSD."""
#加载自定义组建,这里如果TensorRT版本小于7.0需要额外生成flattenconcat的自定义组件库
def _load_plugins(self):
trt.init_libnvinfer_plugins(self.trt_logger, '')
#加载通过Transfer Learning Toolkit生成的推理引擎
def _load_engine(self):
TRTbin = 'models/TRT_%s.bin' % self.model
with open(TRTbin, 'rb') as f, trt.Runtime(self.trt_logger) as runtime:
return runtime.deserialize_cuda_engine(f.read())
#通过加载的引擎,生成可执行的上下文
def _create_context(self):
for binding in self.engine:
size = trt.volume(self.engine.get_binding_shape(binding)) * \
self.engine.max_batch_size
##注意:这里的host_mem需要时用pagelocked memory,以免内存被释放
host_mem = cuda.pagelocked_empty(size, np.float32)
cuda_mem = cuda.mem_alloc(host_mem.nbytes)
self.bindings.append(int(cuda_mem))
if self.engine.binding_is_input(binding):
self.host_inputs.append(host_mem)
self.cuda_inputs.append(cuda_mem)
else:
self.host_outputs.append(host_mem)
self.cuda_outputs.append(cuda_mem)
return self.engine.create_execution_context()
#初始化引擎
def __init__(self, model, input_shape, output_layout=7):
"""Initialize TensorRT plugins, engine and conetxt."""
self.model = model
self.input_shape = input_shape
self.output_layout = output_layout
self.trt_logger = trt.Logger(trt.Logger.INFO)
self._load_plugins()
self.engine = self._load_engine()
self.host_inputs = []
self.cuda_inputs = []
self.host_outputs = []
self.cuda_outputs = []
self.bindings = []
self.stream = cuda.Stream()
self.context = self._create_context()
#释放引擎,释放GPU显存,释放CUDA流
def __del__(self):
"""Free CUDA memories."""
del self.stream
del self.cuda_outputs
del self.cuda_inputs
#利用生成的可执行上下文执行推理
def detect(self, img, conf_th=0.3):
"""Detect objects in the input image."""
img_resized = _preprocess_trt(img, self.input_shape)
np.copyto(self.host_inputs[0], img_resized.ravel())
#将处理好的图片从CPU内存中复制到GPU显存
cuda.memcpy_htod_async(
self.cuda_inputs[0], self.host_inputs[0], self.stream)
#开始执行推理任务
self.context.execute_async(
batch_size=1,
bindings=self.bindings,
stream_handle=self.stream.handle)
#将推理结果输出从GPU显存复制到CPU内存
cuda.memcpy_dtoh_async(
self.host_outputs[1], self.cuda_outputs[1], self.stream)
cuda.memcpy_dtoh_async(
self.host_outputs[0], self.cuda_outputs[0], self.stream)
self.stream.synchronize()
output = self.host_outputs
#print("len(outputs[0]): "+str(len(self.host_outputs[0]))+" len(outputs[1]): "+str(len(self.host_outputs[1])))
#for x in self.host_outputs[0]:
# print(str(x),end=' ')
#for x in self.host_outputs[1]:
# print(str(x),end=' ')
return _postprocess_trt(img, output, conf_th, self.output_layout)
16.设置模型库
- 1.这里定义了多个模型库,我们选用的是人脸口罩检测,也就是最后一个ssd_mobilenet_v1_face2
- 2.这里还定义了我们模型的输入(300,300)
#16
INPUT_HW = (300, 300)
SUPPORTED_MODELS = [
'ssd_mobilenet_v1_coco',
'ssd_mobilenet_v1_egohands',
'ssd_mobilenet_v2_coco',
'ssd_mobilenet_v2_egohands',
'ssd_mobilenet_v2_face',
'ssd_resnet18_5th',
'ssd_mobilenet_v1_face2',
'ssd_mobilenet_v1_fruit'
]
17.开始定义方法来读取数据并将输出可视化的画到图像上
- detect_one()方法是检测单张图片,detect_video()方法是检测视频
- 注意:这里打印的fps值是包括将图像写到结果视频中的时间,如果取消将视频写到结果视频的功能,速度会有大幅度提升
#17-1
def detect_video(video, trt_ssd, conf_th, vis,result_file_name):
full_scrn = False
fps = 0.0
tic = time.time()
frame_width = int(video.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_WIDTH))
frame_height = int(video.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_HEIGHT))
fps = video.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FPS)
#print(str(frame_width)+str(frame_height))
##定义输入编码
fourcc = cv2.VideoWriter_fourcc('M', 'P', '4', 'V')
videoWriter = cv2.VideoWriter('result.AVI', fourcc, fps, (frame_width,frame_height))
##开始循环检测,并将结果写到result.mp4中
while True:
ret,img = video.read()
if img is not None:
boxes, confs, clss = trt_ssd.detect(img, conf_th)
#print("boxes,confs,clss: "+ str(boxes)+" "+ str(confs)+" "+str(clss))
img = vis.draw_bboxes(img, boxes, confs, clss)
videoWriter.write(img)
toc = time.time()
curr_fps = 1.0 / (toc - tic)
fps = curr_fps if fps == 0.0 else (fps*0.95 + curr_fps*0.05)
tic = toc
print("\rfps: "+str(fps),end="")
else:
break
#17-2
def detect_one(img, trt_ssd, conf_th, vis):
full_scrn = False
tic = time.clock()
##开始检测,并将结果写到result.jpg中
boxes, confs, clss = trt_ssd.detect(img, conf_th)
toc = time.clock()
curr_fps = (toc - tic)
#print("boxes: "+str(boxes))
#print("clss: "+str(clss))
#print("confs: "+str(confs))
img = vis.draw_bboxes(img, boxes, confs, clss)
cv2.imwrite("result.jpg",img)
print("time: "+str(curr_fps)+"(sec)")
18.定义main()函数,检测单张图片**
- 您可以自行上传图像到当前文件夹,并将filename请改成您要测试的图片的名字
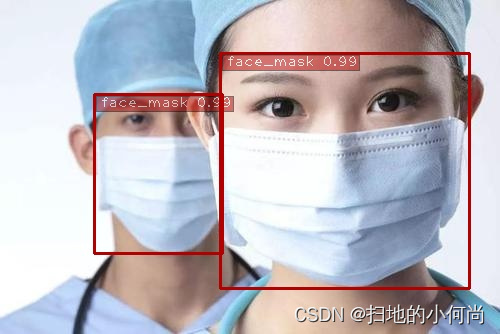
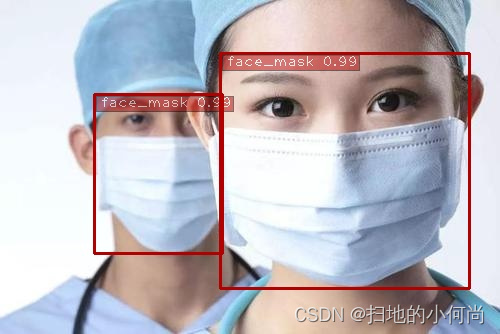
- face指的是没有戴口罩的人脸,face_mask指的是带了口罩的人脸,mask_weared_incorrect指的是带了口罩但是带的不规范的人脸
#18-1
def main_one():
filename = "mask.jpg"
result_file_name = str(filename)
img = cv2.imread(filename)
cls_dict = get_cls_dict("ssd_mobilenet_v1_face2".split('_')[-1])
model_name ="ssd_mobilenet_v1_face2"
trt_ssd = TrtSSD(model_name, INPUT_HW)
vis = BBoxVisualization(cls_dict)
print("start detection!")
detect_one(img, trt_ssd, conf_th=0.5, vis=vis)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
print("finish!")
#18-2
from IPython.display import Image
main_one()
Image("result.jpg")
19.定义main()函数,检测视频
- 您可以自行上传视频到当前文件夹,并将filename请改成您要测试的视频的名字
- 检测视频部分由于要将检测的结果写到硬盘上,所以时间会加倍,如果要得到和单张检测相似的数据,可以将读写的语句注释掉
- face指的是没有戴口罩的人脸,face_mask指的是带了口罩的人脸,mask_weared_incorrect指的是带了口罩但是带的不规范的人脸)
#19-1
def main_loop():
filename = "face_mask_test_video.mp4"
result_file_name = str(filename)
video = cv2.VideoCapture(filename)
cls_dict = get_cls_dict("ssd_mobilenet_v1_face2".split('_')[-1])
model_name ="ssd_mobilenet_v1_face2"
trt_ssd = TrtSSD(model_name, INPUT_HW)
vis = BBoxVisualization(cls_dict)
print("start detection!")
detect_video(video, trt_ssd, conf_th=0.8, vis=vis, result_file_name=result_file_name)
video.release()
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
print("\nfinish!")
#19-2
main_loop()
20.将生成的视频转码,以便能够在Jupyter Notebook中查看
- 这里采用的是利用GPU加速的转码技术,将输出的视频转换到MP4格式,比单纯使用CPU进行转码的速度有大幅度提升
#20
!rm result-ffmpeg4.mp4
!ffmpeg -i result.AVI -vcodec libx264 -f mp4 result-ffmpeg4.mp4
21.查看结果视频
#21
from IPython.display import Video
Video("result-ffmpeg4.mp4")
文章出处登录后可见!
已经登录?立即刷新
