
🎉个人名片:
🐼作者简介:一名乐于分享在学习道路上收获的大二在校生
🐻❄个人主页🎉:GOTXX
🐼个人WeChat:ILXOXVJE
🐼本文由GOTXX原创,首发CSDN🎉🎉🎉
🕊系列专栏:零基础学习C语言—– 数据结构的学习之路
🐓每日一句:如果没有特别幸运,那就请特别努力!🎉🎉🎉
————————————————
🎉文章简介:
本篇文章对 树的相关概念及结构,二叉树(堆)的概念及结构,二叉树顺序结构及实现的相关知识详细讲解!二叉树链式结构 在下一章讲解!
如果您觉得文章不错,期待你的一键三连哦,你的鼓励是我创作动力的源泉,让我们一起加油,一起奔跑,让我们顶峰相见!!!🎉🎉🎉
目录
一.树的概念及结构
1.1树的概念
相关概念:
1.2树的表示
二.二叉树的概念及结构
2.1二叉树的概念
二叉树:
2.2两个特殊的二叉树
满二叉树:
完全二叉树:
三.二叉树顺序结构及实现
3.1二叉树顺序结构
堆在存储的分类:大根堆,小根堆
3.2二叉树(堆)顺序结构的实现
这里重点分析向上/向下调整的函数
向上调整:
向下调整:
完整代码:Heap.h Heap.c
一.树的概念及结构
1.1树的概念
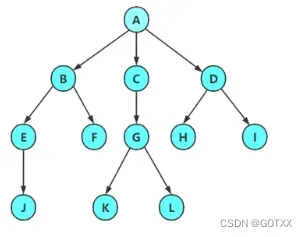
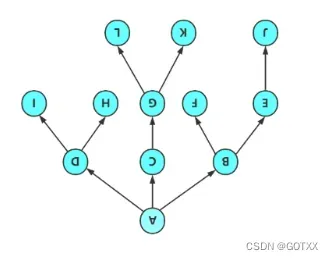
树是一种非线性的数据结构,它是由k个节点(k>=0)组成的具有层次关系的一个集合,如图一所示,把上图倒过来,如图二所示,看起来像一棵树,所以被叫作树;
类似于树的特点,把最上面的那个结点(A)叫作根结点;
除了根结点,其余的结点又可以分为若干个类似于树的子树,如下图:
所以树是递归定义的;
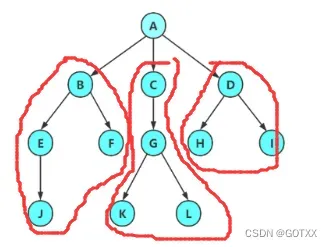
相关概念:
1.结点的度:及该结点含有子树的个数(有几个孩子),如上图:1的度为3,2的度为1,4的度为2;
2.叶结点(终端结点):度为0的结点,如上图的3,5,6,7;
3.分枝结点(非终端结点):根结点与叶结点以外的结点,如2,4;
4.双亲结点(父结点):一个结点含有子结点,该结点称为子结点的父结点,如1是2,3,4的父结点,4是6,7的父结点;
5.孩子结点(子结点):如5是2的子结点,4是1的子结点;
6.兄弟结点:有相同父结点的结点称为兄弟结点,如6,7的父结点都是4,所以6,7是兄弟结点;
7.树的度:一棵树中,最大的结点的度称为树的度,如上面的树的度是3(因为1的度最大,为3);
8.结点的层次:根为第一层,往下一次类推;
9.树的高度(深度):如上图,树的高度为3;
10.森林:有许多互不相交的树组成的集合;
11.度为0的结点个数为N0,度为2的节点个数为N2;则有N0=N2+1;
1.2树的表示
最常见的是孩子兄弟表示法

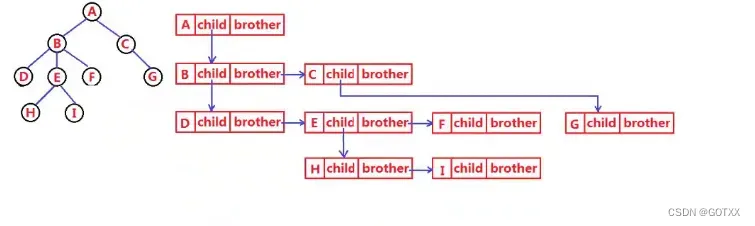
双亲表示法(一般使用结构体数组):只存储双亲的下标或指针;
例如:
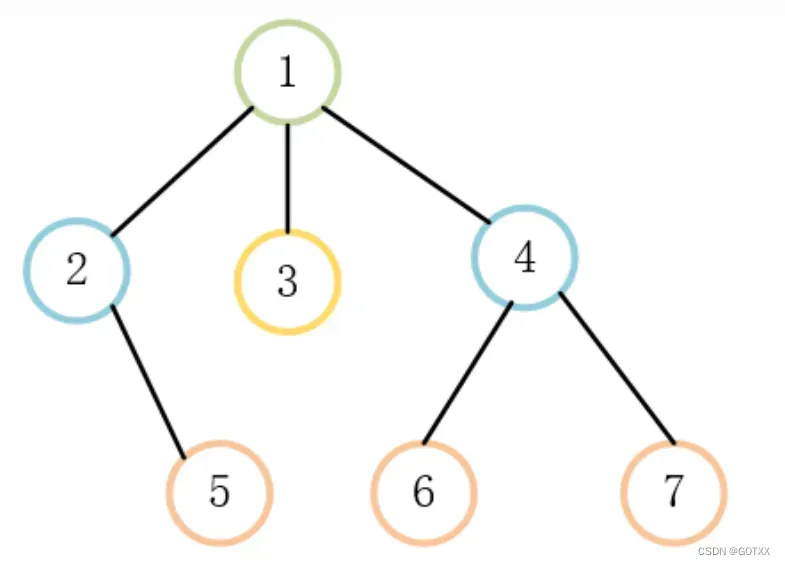
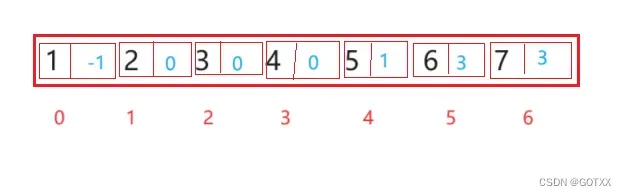
上面这个树用双亲表示法表示:
蓝色:存储的该结点的父结点的下标或指针;
没有父亲就存储-1(-1不是个有效的下标);
二.二叉树的概念及结构
2.1二叉树的概念
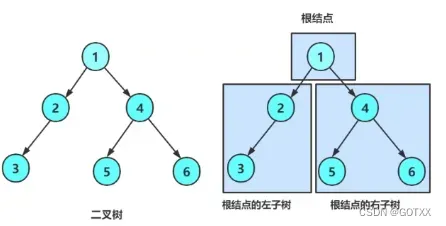
二叉树:
1.不存在度大于2的结点的树;最多两个,可以是1个或则0个;
度为0(空树);
2.二叉树的子树 有左右子树之分,次序不能颠倒,所以二叉树是有序的;
2.2两个特殊的二叉树
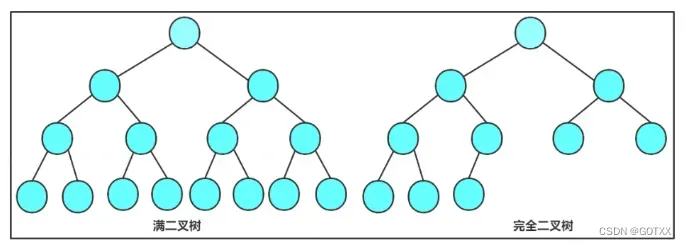
满二叉树:
一个二叉树,如果每一层的结点数都达到最大值,这个数就是满二叉树;
假设一个满二叉树有h层,则该二叉树的总的结点为2^h-1;
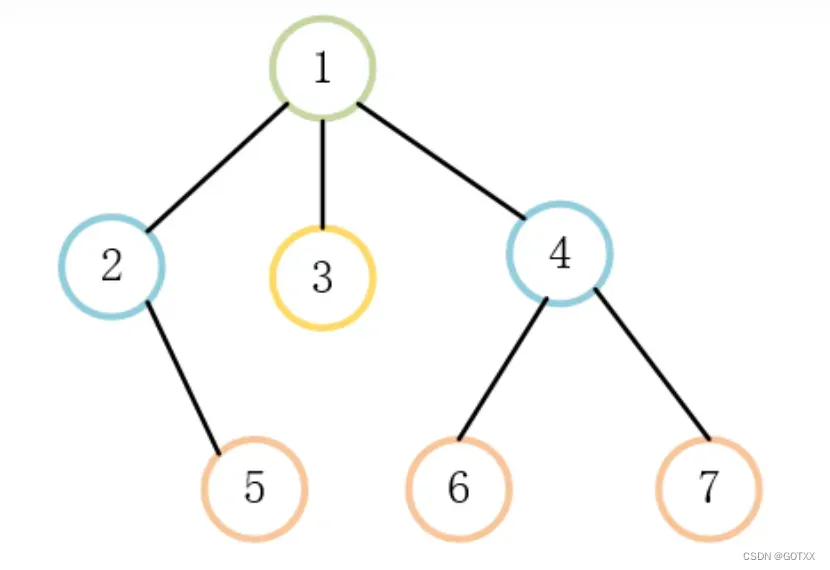
完全二叉树:
是一个深度为k的有n个节点的二叉树,对树中的节点按从上至下、从左到右的顺序进行编号,如果编号为i1≤i≤n的结点与满二叉树中编号为i的结点在二叉树中的位置相同;
三.二叉树顺序结构及实现
3.1二叉树顺序结构
根据完全二叉树的特点,可以得出这样的结论:
如果完全二叉树用数组存储,那么可以得到任意一个父结点,可以通过下标找到孩子,通过孩子下标也可以找到父结点的下标;
规律如下:
liftchild = perent*2+1;
rightchild = parent*2+2;
parent = (child-1)/2;
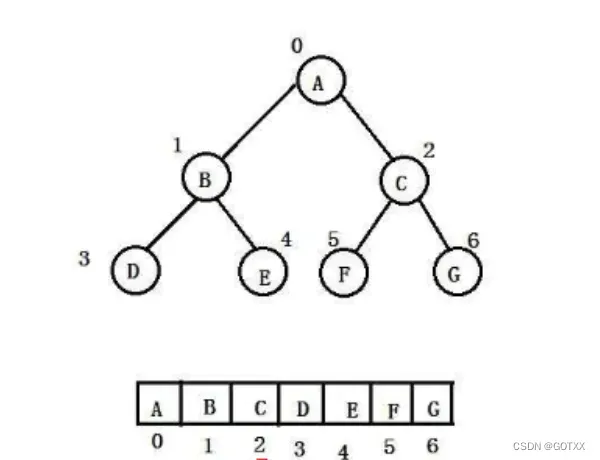
堆在存储的分类:大根堆,小根堆

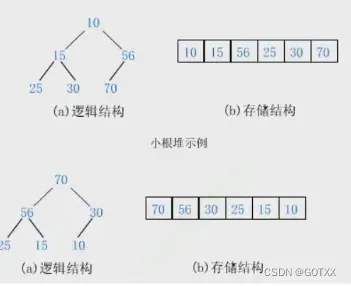
3.2二叉树(堆)顺序结构的实现
这里重点分析向上/向下调整的函数
向上调整:
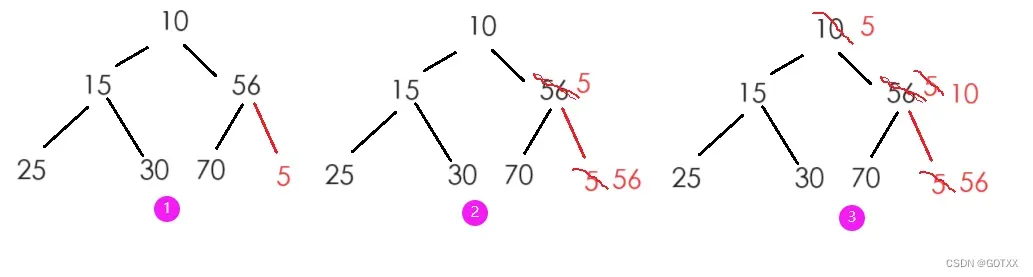
思想:将插入的数据尾插到数组里面,根据父结点与孩子结点下标的关系向上比较做调整,如果父亲结点的数据大于(小于)孩子结点,就交换:如图:
实现代码:
//交换函数
void Swap(HPDataType* x, HPDataType* y)
{
HPDataType tmp = *x;
*x = *y;
*y = tmp;
}
//向上调整
void Adjustup(HPDataType* a, int child)
{
assert(a);
int parent = (child - 1) / 2;
while (child>0)
{
if (a[parent] > a[child])
{
Swap(&a[parent], &a[child]);
child = parent;
parent = (parent - 1) / 2;
}
else
{
break;
}
}
}向下调整:
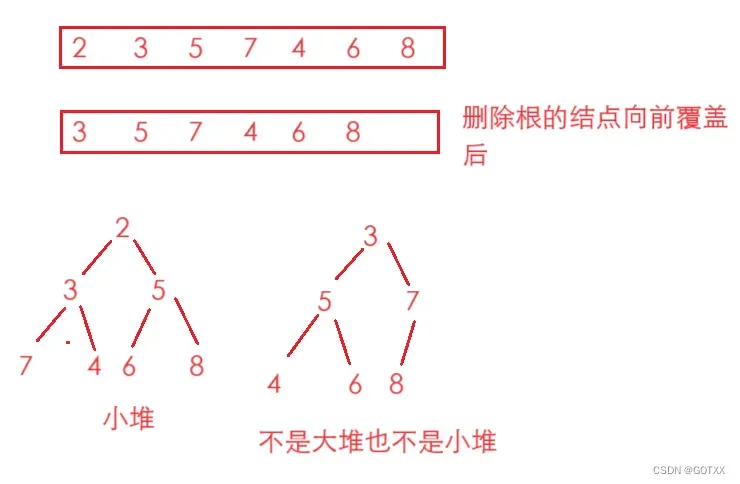
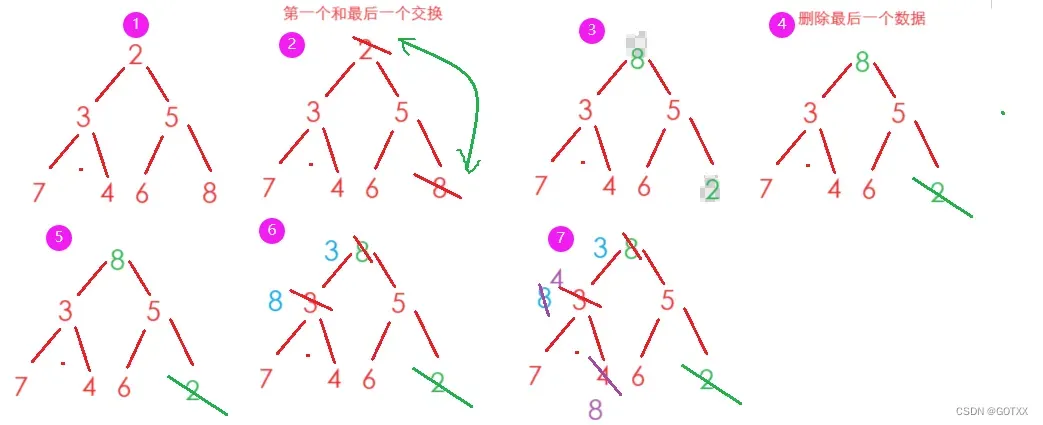
思想:如果我们要删除堆顶(根)的结点,如果直接删除,然后向前覆盖,堆的顺序就会改变,不再是大堆(小堆),如图,这里就需要用到向下调整,先将最后一个数据与第一个数据交换,再将最后一个数据删除,这样保证了除了根,下面的结点都是大堆(小堆);
然后再用根和两个孩子中较小的一个交换,一次向下重复以上动作,图解如下:
实现代码:
//向下调整
void Adjustdown(HPDataType* a, int parent,int n)
{
assert(a);
int child = parent * 2 + 1;
while (child<n)
{
//假设左孩子小
if (child+1<n && a[child] > a[child + 1]) //假设错误,修正
{
child = child + 1;
}
if (a[child] < a[parent])
{
Swap(&a[parent], &a[child]);
parent = child;
child = child * 2 + 1;
}
else
{
break;
}
}
}
完整代码:Heap.h Heap.c
Heap.h
#pragma once
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <assert.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
#include<string.h>
#define HPDataType int
typedef struct Heap
{
//存储数据的数组
HPDataType* a;
int size;
int capacity;
}Heap;
//初始化函数,两种
//先不开空间,使用的时候再开
void HeapInit(Heap* php);
//已经有一个数组的数据,先开空间,把一个数组的数据放到堆数组里面
void HeapInitArray(Heap* php,int* a,int n);
//摧毁函数,防止内存泄露
void HeapDestory(Heap* php);
//打印函数
void HeapPrintf(Heap* php);
//向上调整函数
void Adjustup(HPDataType* a, int child);
//向下调整函数
void Adjustdown(HPDataType* a, int child,int n);
//向堆里面插入数据的函数
void HeapPush(Heap* php, HPDataType x);
//把堆里面的根结点Pop出去的函数
void HeapPop(Heap* php);
//取出根结点数据的函数
HPDataType HeapTop(Heap* php);
//判断堆是否为空的函数
bool HeapEmpty(Heap* php);
Heap.c
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include "Heap.h"
void HeapInit(Heap* php)
{
assert(php);
php->a = NULL;
php->capacity = 0;
php->size = 0;
}
void HeapInitArray(Heap* php,int* a,int n)
{
assert(a);
assert(php);
php->a = (HPDataType*)malloc( n * sizeof(int));
if (php->a == NULL)
{
perror("malloc fail");
exit(-1);
}
memcpy(php->a, a, n * sizeof(int));
//向上调整建堆
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++)
{
Adjustup(php->a, i);
}
php->size = n;
php->capacity = n;
}
void HeapDestory(Heap* php)
{
assert(php);
php->a = NULL;
php->capacity = php->size = 0;
}
void HeapPrintf(Heap* php)
{
assert(php);
for (int i = 0; i < php->size; i++)
{
printf("%d ",php->a[i]);
}
printf("\n");
}
//交换函数
void Swap(HPDataType* x, HPDataType* y)
{
HPDataType tmp = *x;
*x = *y;
*y = tmp;
}
//向上调整函数
void Adjustup(HPDataType* a, int child)
{
assert(a);
int parent = (child - 1) / 2;
while (child>0)
{
if (a[parent] > a[child])
{
Swap(&a[parent], &a[child]);
child = parent;
parent = (parent - 1) / 2;
}
else
{
break;
}
}
}
//向下调整函数
void Adjustdown(HPDataType* a, int parent,int n)
{
assert(a);
int child = parent * 2 + 1;
while (child<n)
{
//假设左孩子小
if (child+1<n && a[child] > a[child + 1])
{
child = child + 1;
}
if (a[child] < a[parent])
{
Swap(&a[parent], &a[child]);
parent = child;
child = child * 2 + 1;
}
else
{
break;
}
}
}
//插入函数
void HeapPush(Heap* php, HPDataType x)
{
assert(php);
if (php->capacity == php->size)
{
int newcapacity = php->capacity == 0 ? 4 : 2 * php->capacity;
HPDataType* tmp = (HPDataType*)realloc(php->a, newcapacity * sizeof(HPDataType));
if (tmp == NULL)
{
perror("realloc fail");
exit(-1);
}
php->a=tmp;
php->capacity = newcapacity;
}
php->a[php->size] = x;
php->size++;
Adjustup(php->a,php->size-1);
}
//删除堆顶结点
void HeapPop(Heap* php)
{
assert(php);
Swap(&php->a[0], &php->a[php->size - 1]);
php->size--;
Adjustdown(php->a, 0,php->size);
}
//取出堆顶数据的函数
HPDataType HeapTop(Heap* php)
{
assert(php);
return php->a[0];
}
//判空函数
bool HeapEmpty(Heap* php)
{
assert(php);
return php->size;
}
文章出处登录后可见!
