JavaScript请求数据有4种主流方式,分别是Ajax、fetch、jQuery和axios。
一、Ajax、fetch、jQuery和axios的详细解释:
1、 Ajax
Ajax(Asynchronous JavaScript and XML)是一种使用JavaScript在用户的浏览器上发送请求的技术,可以在不重新加载整个网页的情况下从服务器获取数据。它允许网页在后台与服务器进行少量数据交换,从而实现网页的异步更新。这意味着可以在不干扰用户浏览体验的情况下,从服务器获取数据并更新网页的部分内容。
2、fetch
fetch API是现代浏览器提供的一种用于发起网络请求的新方法。它返回一个Promise对象,可以用来替代传统的XMLHttpRequest。fetch API提供了一个更现代、更强大的方式来处理网络请求,并支持包括CORS在内的更多功能。
3、jQuery
jQuery是一种流行的JavaScript库,旨在简化HTML文档遍历和操作、事件处理、动画和Ajax操作。它提供了一组简单易用的API,使得JavaScript编程更为简单、快速和有趣。jQuery大大简化了跨浏览器的DOM操作、事件处理和动画效果,同时它也提供了一些工具函数,使得JavaScript编程更加高效。
4、axios
axios是一个基于Promise的HTTP客户端,用于浏览器和node.js。它提供了一种简单且灵活的方式来进行HTTP请求,包括XMLHttpRequests和HTTP请求。axios返回的是一个包含响应数据的Promise对象,这使得异步处理更加简单和直观。axios还支持拦截请求和响应、转换请求和响应数据、取消请求等功能,使得HTTP请求的管理更加方便。
二、Ajax、fetch、jQuery和axios的主要区别:
1、Ajax 数据请求:
原生js提供的(内置),核心使用XMLHttpRequest对象,多个请求之间如果有先后关系的话,就会出现回调地狱。
2、fetch 数据请求:
原生js提供的(内置),和ajax同级,使用promise形式,关注分离思想,但兼容性不太好,所以用的不是很多。
3、jquery数据请求:
第三方库提供的,封装原生的ajax请求,使用回调形式,可能出现回调地狱。
4、axios数据请求:
第三方库提供的,封装原生的ajax请求,使用promise的形式,并且可以在请求和响应阶段进行拦截。
三、Ajax、fetch、jQuery和axios的代码详解:
在测试Ajax、fetch、jQuery和axios的示例代码之前,这里使用nodejs写一个简单的web服务器(server.js)做响应。
启动命令:node server.js
ajax的get请求示例:http://127.0.0.1:8000/ajax_get.html
ajax的post请求示例:http://127.0.0.1:8000/ajax_post.html
fetch的get请求示例:http://127.0.0.1:8000/fetch_get.html
fetch的post请求示例:http://127.0.0.1:8000/fetch_post.html
jQuery的get请求示例:http://127.0.0.1:8000/jQuery_get.html
jQuery的post请求示例:http://127.0.0.1:8000/jQuery_post.html
axios的get请求示例:http://127.0.0.1:8000/axios_get.html
axios的post请求示例:http://127.0.0.1:8000/axios_post.html
axios请求(高级用法)示例:http://127.0.0.1:8000/axios_other.html
axios请求(实例用法)示例:http://127.0.0.1:8000/axios_instance.html代码如下:
const http = require('http');
const path = require('path');
const url = require('url')
const fs = require('fs');
const server = http.createServer()
server.on('request',(req,res)=>{
const urlObj = url.parse(req.url, true);
if(urlObj.pathname === '/test'){
if(req.method === 'GET'){
const str = JSON.stringify(urlObj.query);
res.end(str);
}
if(req.method === 'POST'){
let params = '';
req.on('data', chunk=>{
params += chunk;
});
req.on('end', ()=>{
res.end(params);
});
}
}else{
fs.readFile(path.join(__dirname, urlObj.pathname), 'utf8', function(err, dataStr){
if(err){
return console.log(err.message)
}
res.setHeader('Content-type', 'text/html; charset=utf-8');
res.end(dataStr);
})
}
})
server.listen(8000, ()=>{
console.log('server running at http://127.0.0.1:8000')
})
1、Ajax请求
Ajax使用五个步骤:
步骤1:创建一个XMLHttpRequest对象
var xmlhttp=new XMLHttpRequest();
步骤2:设置请求方式和请求地址(使用open(method,url,async)方法)
method:请求方式,get或者post。(默认为get)
url:请求路径,文件在服务器上的位置
async:是否为异步请求。(默认为true,异步请求)
步骤3:发送send() 请求
若为post方式时需要使用setRequestHeader()来添加http头
步骤4:监听状态的变化
每当readyState状态改变时,就会触发 onreadystatechange事件,执行回调函数。readyState存有XMLHttpRequest的5种状态。从 0 到 4 发生变化。
0: 请求未初始化
1: 服务器连接已建立
2: 请求已接收
3: 请求处理中
4: 请求已完成,且响应已就绪
步骤5:处理返回的结果
根据请求服务器返回状态码(status),大于200,小于300,或等于304,则表示请求成功, 否则服务器请求失败。获取服务器中响应,使用XMLHttpRequest对象的responseText或responseXML属性。
responseText:获得字符串形式的响应数据。
responseXML:获得 XML 形式的响应数据。
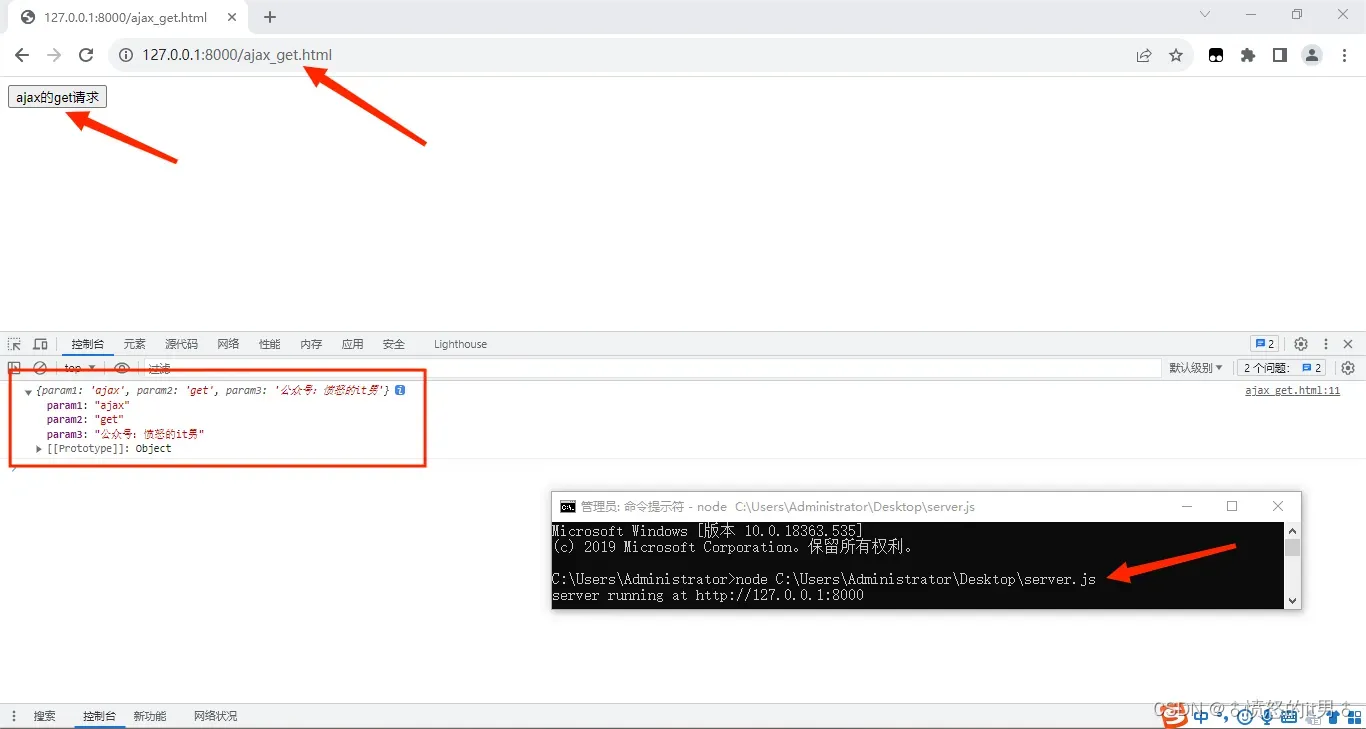
ajax的get请求示例代码:
<button>ajax的get请求</button>
<script>
const btn = document.querySelector("button");
btn.onclick = function () {
var xmlhttp = new XMLHttpRequest();
xmlhttp.open("GET", "http://127.0.0.1:8000/test?param1=ajax¶m2=get¶m3=公众号:愤怒的it男", true);
xmlhttp.send();
xmlhttp.onreadystatechange = function () {
if (xmlhttp.readyState === 4) {
if (xmlhttp.status >= 200 && xmlhttp.status < 300 || xmlhttp.status === 304) {
console.log(JSON.parse(xmlhttp.responseText));
} else {
console.log("没有接收到服务器的数据");
}
}
}
}
</script>ajax的post请求示例代码:
<button>ajax的post请求</button>
<script>
const btn = document.querySelector("button");
btn.onclick = function () {
var xmlhttp=new XMLHttpRequest();
xmlhttp.open("POST","http://127.0.0.1:8000/test",true);
xmlhttp.setRequestHeader("Content-Type","application/x-www-form-urlencoded");
xmlhttp.send(JSON.stringify({'param1':'ajax','param2':'post','param3':'公众号:愤怒的it男'}));
xmlhttp.onreadystatechange=function () {
if (xmlhttp.readyState === 4) {
if (xmlhttp.status>=200 && xmlhttp.status<300 ||xmlhttp.status===304 ){
console.log(JSON.parse(xmlhttp.responseText));
}else{
console.log("没有接收到服务器的数据");
}
}
}
}
</script>2、fetch请求
(1)POST请求的2种内容类型:
//如果是application/x-www-form-urlencoded,body请求体内容为FormData对象:
var formData = new FormData()
formData.append('param1','fetch')
formData.append('param1','post')
formData.append('param1','公众号:愤怒的it男')
//如果是application/json,body请求体内容为JSON字符串:
JSON.stringify({'param1':'fetch','param2':'post','param3':'公众号:愤怒的it男'})(2)response返回的3种数据格式:
//如果是json格式
fetch(url [,options]).then(rsp => {return rsp.json()}).then(data => {console.log(data)})
//如果是文本格式
fetch(url [,options]).then(rsp => {return rsp.text()}).then(data => {console.log(data)})
//如果是二进制流
fetch(url [,options]).then(rsp => {return rsp.blob()}).then(data => {console.log(data)})fetch的get请求示例代码:
<button>fetch的get请求</button>
<script>
const btn = document.querySelector("button");
btn.onclick = function() {
fetch('http://127.0.0.1:8000/test?param1=fetch¶m2=get¶m3=公众号:愤怒的it男', {
'method': 'GET',
'body': null,
'headers': {
"accept": "*/*",
"sec-fetch-dest": "empty",
"sec-fetch-mode": "cors",
"sec-fetch-site": "none",
'content-type': 'application/json, text/plain, */*'
}
}).then(res => {return res.json()}).then(data => {
console.log(data)
});
}
</script>
fetch的post请求示例代码:
<button>fetch的post请求</button>
<script>
const btn = document.querySelector("button");
btn.onclick = function() {
fetch('http://127.0.0.1:8000/test', {
'method': 'POST',
'body': JSON.stringify({'param1':'fetch','param2':'post','param3':'公众号:愤怒的it男'}),
'headers': {
"accept": "*/*",
"sec-fetch-dest": "empty",
"sec-fetch-mode": "cors",
"sec-fetch-site": "none",
'content-type': 'application/json; charset=UTF-8'
}
}).then(res => {return res.json()}).then(data => {
console.log(data)
});
}
</script>3、jQuery请求
jQuery的get请求示例代码:
<script src="https://apps.bdimg.com/libs/jquery/2.1.4/jquery.min.js"></script>
<button>jQuery的get请求</button>
<script>
const btn = document.querySelector("button");
btn.onclick = function() {
$.get("http://127.0.0.1:8000/test?param1=jQuery¶m2=get¶m3=公众号:愤怒的it男",function(data,status){
console.log(JSON.parse(data));
});
}
</script>jQuery的post请求示例代码:
<script src="https://apps.bdimg.com/libs/jquery/2.1.4/jquery.min.js"></script>
<button>jQuery的post请求</button>
<script>
const btn = document.querySelector("button");
btn.onclick = function() {
data = JSON.stringify({'param1':'fetch','param2':'post','param3':'公众号:愤怒的it男'});
$.post("http://127.0.0.1:8000/test", data, function(data,status){
console.log(JSON.parse(data));
});
}
</script>$.get等价于jQuery.get,$.post等价于jQuery.post。
4、axios请求
axios的get请求基础使用示例代码:
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/axios/dist/axios.min.js"></script>
<button>axios的get请求</button>
<script>
const btn = document.querySelector("button");
btn.onclick = function() {
axios.get("http://127.0.0.1:8000/test?param1=axios¶m2=get¶m3=公众号:愤怒的it男").then(response => {
console.log(response.data)
});
}
</script>axios的post请求基础使用示例代码:
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/axios/dist/axios.min.js"></script>
<button>axios的post请求</button>
<script>
const btn = document.querySelector("button");
btn.onclick = function() {
data={
param1:'axios',
param2:'post',
param3:'公众号:愤怒的it男'
}
axios.post('http://127.0.0.1:8000/test',data).then(response => {
console.log(response.data)
});
}
</script>axios支持多请求并发,可以添加全局或局部配置,也可以添加请求拦截器和响应拦截器。拦截器会在发生响应请求之前和收到响应数据之后第一时间被调用,其中请求拦截器是先发的请求先拦截,而响应拦截器则是先发的请求后拦截。如下代码涉及axios的多个高级用法:
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/axios/dist/axios.min.js"></script>
<button>axios请求(高级用法)</button>
<script>
const btn = document.querySelector("button");
btn.onclick = function() {
// 全局配置baseURL和timeout
axios.defaults.baseURL = 'http://127.0.0.1:8000';
axios.defaults.timeout = 3000;
// 添加请求拦截器
axios.interceptors.request.use(config =>{
console.log(config);
return config;
},err => {
console.log(err);
})
// 添加响应拦截器
axios.interceptors.response.use(res=>{
console.log(res);
return res;
},err=>{
console.log(err);
})
// 多个请求并发
axios.all([
axios({
method:"get", // 请求方式不写则默认为get请求
//单个axios配置baseURL和timeout
//baseURL:'http://127.0.0.1:8000',
//timeout:3000,
url:"/test",
params:{ // get请求中,url后面的参数可以分开单独放在params中
param1:'axios1',
param2:'get',
param3:'公众号:愤怒的it男'
}
}),
axios({
method:"post",
//单个axios配置baseURL和timeout
//baseURL:'http://127.0.0.1:8000',
//timeout:3000,
url:"/test",
data:{
param1:'axios2',
param2:'post',
param3:'公众号:愤怒的it男'
}
}),
]).then(response => {
console.log(response[0].data);
console.log(response[1].data);
});
}
</script>
输出结果如下:
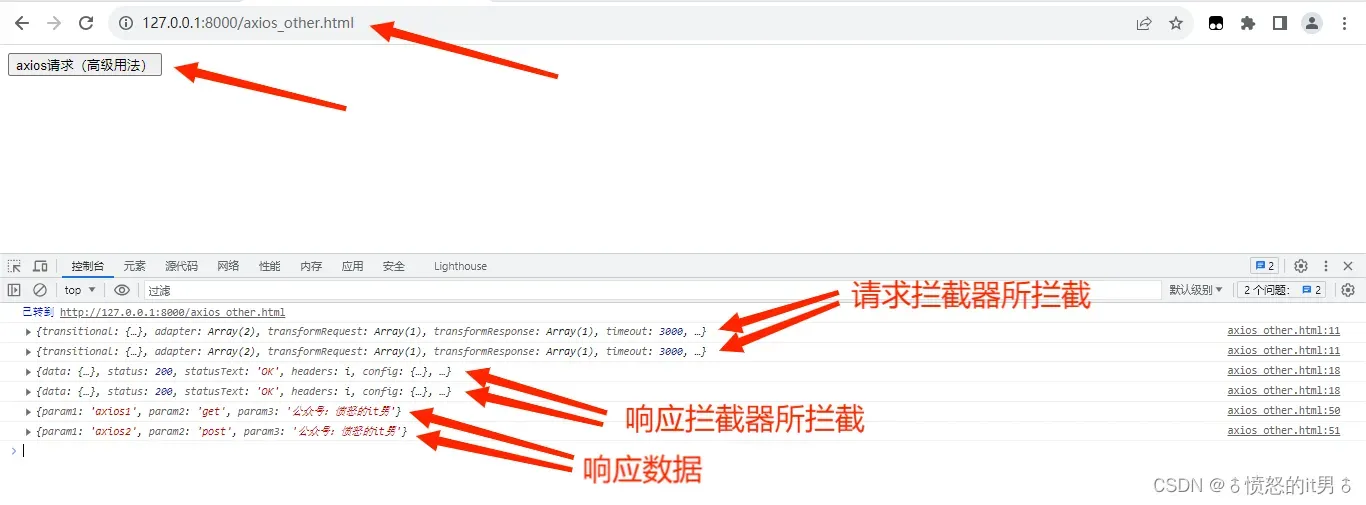
有时候请求不想使用全局的配置或者拦截器,则我们可以创建axios实例,在该axios实例中配置或者添加拦截器,则之后只在该实例内有效。具体示例代码如下:
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/axios/dist/axios.min.js"></script>
<button>axios请求(实例用法)</button>
<script>
const btn = document.querySelector("button");
btn.onclick = function() {
// 创建实例并为实例配置
const instance = axios.create({
baseURL:'http://127.0.0.1:8000',
timeout:3000,
});
// 为实例添加请求拦截器
instance.interceptors.request.use(config =>{
console.log(config);
return config;
},err => {
console.log(err);
});
// 为实例添加响应拦截器
instance.interceptors.response.use(res=>{
console.log(res);
return res;
},err=>{
console.log(err);
});
// 发起get请求
instance({
method:"get",
url:"/test",
params:{
param1:'axios1',
param2:'get',
param3:'公众号:愤怒的it男'
}
}).then(response => {
console.log(response.data);
});
// 发起post请求
instance({
method:"post",
url:"/test",
data:{
param1:'axios2',
param2:'post',
param3:'公众号:愤怒的it男'
}
}).then(response => {
console.log(response.data);
});
}
</script>
输出结果如下:
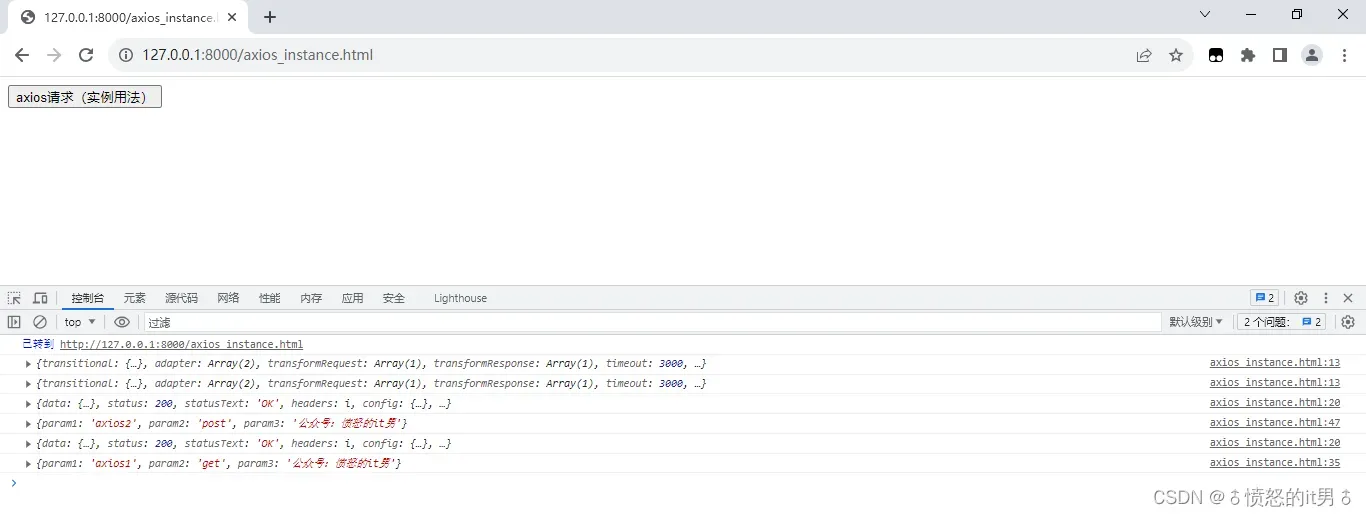
更多爬虫知识以及实例源码,可关注微信公众号【愤怒的it男】
文章出处登录后可见!
