
一.Hadoop快速入门(真题在文章尾)
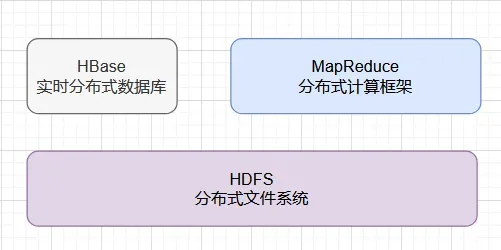
Hadoop的核心就是HDFS和MapReduce
HDFS为海量数据提供了存储
而MapReduce为海量数据提供了计算框架
一.HDFS
整个HDFS有三个重要角色:NameNode(名称节点)、DataNode(数据节点)和Client(客户机)
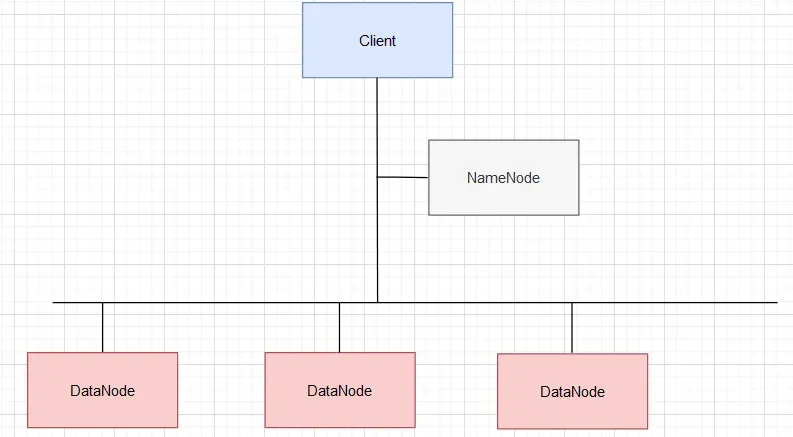
- NameNode:是Master节点(主节点)
- DataNode: 是Slave节点(从节点),是文件存储的基本单元,周期性将所有存在的block信息发送给NameNode
- Client: 与NameNode交互,读取与写入数据
- Block: Block(块)是HDFS中的基本读写单元;HDFS中的文件都是被分割为block进行储存的;这些块被复制到多个DataNode中。
二.MapReduce
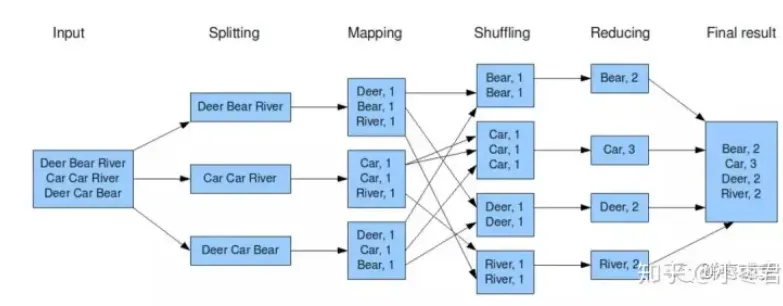
MapReduce其实是一种编程模型。这个模型的核心步骤主要分两部分:Map(映射)和Reduce(归约)。
当你向MapReduce框架提交一个计算作业时,它会首先把计算作业拆分成若干个Map任务,然后分配到不同的节点上去执行,每一个Map任务处理输入数据中的一部分,当Map任务完成后,它会生成一些中间文件,这些中间文件将会作为Reduce任务的输入数据。Reduce任务的主要目标就是把前面若干个Map的输出汇总到一起并输出。
哦,差点忘了,在MapReduce里,为了完成上面这些过程,需要两个角色:JobTracker和TaskTracker。
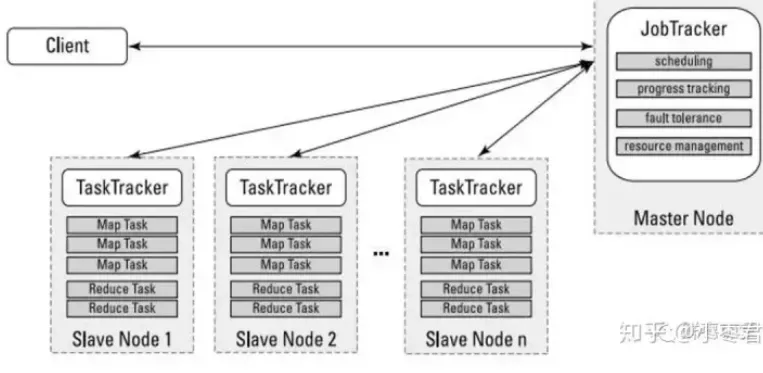
JobTracker用于调度和管理其它的TaskTracker。JobTracker可以运行于集群中任一台计算机上。TaskTracker 负责执行任务,必须运行于 DataNode 上。
二.mapreduce案例及其比赛准备
HDFS命令:
- 查看目录下的文件 hdfs dfs -ls /score
- 将文件上传hdfs上 hdfs dfs -put /score/student.txt(目录) /bean(hdfs中的目录)
- 在hdfs上创建文件夹 hdfs dfs -mkdir /test
- 查看hdfs上文件内容 hdfs dfs -cat /score/test.txt
pom.xml配置
- hadoop-common -v 2.7.6
- hadoop-client -v 2.7.6
- hadoop-hdfs -v 2.7.6
在xshell中上传并执行
hadoop jar hadoop_hdfs_api-1.0.jar com.dataAhut.phonetraffic.PhoneTrafficSort /score/score.txt /output12
整体java的JDK是8,maven都是8,打包package,注意引入的包都是最新版的MapReduce
double avgScore = sum / count;
String formattedAverage = String.format("%.1f", avgScore);
double avgScore2 = Double.parseDouble(formattedAverage);
// 获取文件数据的路径
FileSplit fs = (FileSplit) context.getInputSplit();
String path = fs.getPath().toString();
if(path.contains("student")){
// 150000 小明 18 男 文科六班
String student = value.toString();
String id = student.split(",")[0];
String k = "#" + student;
context.write(new Text(id),new Text(k));
// key150000, value#150000 小明 18 男 文科六班
}else {
// 1500000 100001 98
String score = value.toString();
String id = score.split(",")[0];
String k = "@" + score;
context.write(new Text(id),new Text(k));
// key1500000 value@1500000 100001 98
}
// 先定义学生为空
String student = null;
// 存放成绩表
ArrayList<String> scores = new ArrayList<>();
for (Text value : values) {
String line = value.toString();
// 判断学生信息
if (line.startsWith("#")){
// key150000, value#150000 小明 18 男 文科六班
// 如果是学生表则正常一行读取后放入学生信息中
student = line.substring(1);
}else {
// 成绩表
scores.add(line.substring(1));
}
}
// 将学生信息保存到info中,记住是每一行保存一次
String info = student;
for (String score : scores) {
String s = score.split(",")[2];
// 150000 小明 18 男 文科六班 98 5
info = info + "," + s;
}
context.write(new Text(info),NullWritable.get());
Mapper端
Mapper端
<LongWritable, Text,X,Y >
String lines = value.toString();
String[] data = lines.split(","); // 表格中用的都是“,”,数据间隔的话用“\t”
String name = data[1];
// 输出到reducer端
Context.write(new Text(id),new IntWritable(score));
Reducer端
<X,Y,Text,NullWritable>
// 遍历values
for(IntWritable value : values){
int score = value.get(); // get()方法是IntWritable中的方法
}
FlowBean实现WritableComparable接口
public class FlowBean implements WritableComparable<FlowBean> {
// 属性私有化
private String phone; // 手机号码
// 提供无参构造方法
public FlowBean() {
}
// 对外提供set、get方法
、、、、、
// 重写toString方法(这个方法直接映射到hadoop生成的文件格式)
@Override
public String toString() {
return "电话号码: " + phone + "\t" + upflow + "\t" + downflow + "\t" + sumflow;
}
// 按要求进行排序
@Override
public int compareTo(FlowBean other) {
// 注意一定是get方法,不能用属性
// 按照总流量进行升序排列
return this.getSumflow() - other.getSumflow();
// 按照总流量进行降序排列
return other.getSumflow() - this.getSumflow();
}
@Override
public int compareTo(PairWritable other) {
// 先比较first(字符串的比较)
int result = this.first.compareTo(other.first); // abc bbb
if (result == 0) {
return this.second - other.second;
}
return result;
}
// 序列化
@Override
public void write(DataOutput dataOutput) throws IOException {
dataOutput.writeUTF(phone);
dataOutput.writeInt(upflow);
}
// 反序列化
@Override
public void readFields(DataInput dataInput) throws IOException {
this.phone = dataInput.readUTF();
this.upflow = dataInput.readInt();
}
}
main
Configuration configuration = new Configuration();
Job job = new Job(configuration);
job.setJobName("flowBean");
job.setJarByClass(PhoneTrafficSort.class);
// mapper
job.setMapperClass(FlowBeanMapper.class);
job.setMapOutputKeyClass(FlowBean.class);
job.setMapOutputValueClass(NullWritable.class);
// reducer
job.setReducerClass(FlowBeanReducer.class);
job.setOutputKeyClass(FlowBean.class);
job.setOutputValueClass(NullWritable.class);
FileInputFormat.addInputPath(job,new Path(args[0]));
FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job,new Path(args[1]));
boolean b = job.waitForCompletion(true);
System.exit(b ? 0 : 1);
for (String word:words){
context.write(new Text(word),new LongWritable(1));
}
long sum = 0;
for (LongWritable value : values) {
// 拿到map集合Text, LongWritable的value:LongWritable
sum = sum + value.get();
}
// 获取key值,Text
String word = key.toString();
context.write(new Text(word),new LongWritable(sum));
分区
public class MyPartitoner extends Partitioner<FlowBean, NullWritable> {
@Override
public int getPartition(FlowBean flowBean, NullWritable nullWritable, int i) {
if (flowBean.getCourse().equals("algorithm")) {
return 0;
} else if (flowBean.getCourse().equals("english")) {
return 1;
} else if (flowBean.getCourse().equals("computer")) {
return 2;
} else
return 3;
}
}
// 设置分区
job.setPartitionerClass(MyPartitoner.class);
// 设置分区数量
job.setNumReduceTasks(4);
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
#导入库
plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif']=['SimHei'] #用来正常显示中文标签
plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus']=False #用来正常显示负号
df = df.groupby(by=['学校'])['学生人数'].sum()
data = pd.read_csv(r'E:\table.csv')
# 创建散点图
plt.scatter(days, sales, color='red', marker='o', alpha=0.7) # 设置散点的颜色、标记样式和透明度
# 创建扇形图
plt.figure(figsize=(6, 6)) # 设置图表大小
plt.pie(sales, labels=days, autopct='%1.1f%%', startangle=90, colors=['red', 'blue', 'green', 'yellow']) # 饼图的颜色和其他参数
# 创建柱状图
plt.bar(days, sales, color='red', alpha=0.7) # 设置柱子的颜色为红色,alpha为透明度
# 创建折线图
plt.plot(days, sales, color='red')
# 设置图表标题和轴标签
plt.title('销量随天数变化折线图')
plt.xlabel('天数')
plt.ylabel('销量')
# 显示图表
plt.show()
MapReduce四类题型
- 正常三类(Mapper、Reducer、Driver)简单
- 序列化(Mapper、Reducer、Driver、FlowBean implement Wirtable)
// 注意Writable接口,没有排序的功能
public class FlowBean implements Writable {
private long upFlow;
private long downFlow;
private long sumFlow;
public FlowBean() {
}
// setter getter方法
、、、、
@Override
public void write(DataOutput dataOutput) throws IOException {
dataOutput.writeLong(upFlow);
dataOutput.writeLong(downFlow);
dataOutput.writeLong(sumFlow);
}
@Override
public void readFields(DataInput dataInput) throws IOException {
this.upFlow = dataInput.readLong();
this.downFlow = dataInput.readLong();
this.sumFlow = dataInput.readLong();
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return upFlow + "\t" + downFlow + "\t" + sumFlow;
}
}
- 全局排序(Mapper、Reducer、Driver、Bean实现)
- 二次排序(Mapper、Reducer、Driver、Bean实现)
@Override
public int compareTo(OrderBean other) {
// 首先比较id,升序
if(this.id > other.id){
return 1;
} else if (this.id < other.id) {
return -1;
} else {
// price降序
return this.price > other.price ? -1 : 1;
}
}
int upflow = 0;
int downflow = 0;
int sumflow = 0;
for (NullWritable value : values) {
upflow += key.getUpflow();
downflow += key.getDownflow();
}
sumflow = upflow + downflow;
flowBean.setPhone(key.getPhone());
flowBean.setUpflow(upflow);
flowBean.setDownflow(downflow);
flowBean.setSumflow(sumflow);
context.write(flowBean,NullWritable.get());
private TreeMap<Integer, String> top3Temperatures = new TreeMap<>();
protected void reduce(Text key, Iterable<Text> values, Context context)
throws IOException, InterruptedException {
top3Temperatures.clear();
for (Text value : values) {
int temperature = Integer.parseInt(value.toString());
// 保持当前每年的温度前三
top3Temperatures.put(temperature, "");
// 移除不符合的数据
if (top3Temperatures.size() > 3) {
top3Temperatures.pollFirstEntry();
}
}
// 进行拼串
StringBuilder output = new StringBuilder("(" + key.toString() + ") ");
output.append("[");
boolean first = true;
for (Integer temperature : top3Temperatures.descendingKeySet()) {
if (!first) {
output.append(", ");
}
output.append(temperature);
first = false;
}
output.append("]");
context.write(new Text(output.toString()), new Text(""));
}
三.往年真题及其代码文件
2017年至2023年《大数据与人工智能比赛》往年真题+MapReduce代码文件如下
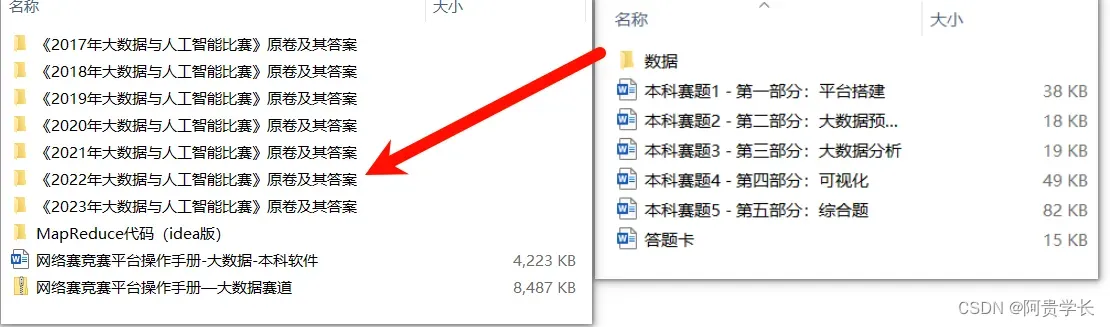
由于文件过大,链接如下:
2017年至2023年《大数据与人工智能比赛》往年真题+MapReduce代码文件
讲解视频:
大数据与人工智能比赛
版权声明:本文为博主作者:阿贵学长原创文章,版权归属原作者,如果侵权,请联系我们删除!
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_61644243/article/details/136096853
