前言
前期实现了导入MySQL元数据到Apache Atlas, 由于是初步版本,且功能参照Atlas Hive Hook,实现的不够完美
本期对功能进行改进,实现了导入多种关系型数据库元数据到Apache Atlas
数据库schema与catalog
按照SQL标准的解释,在SQL环境下Catalog和Schema都属于抽象概念,可以把它们理解为一个容器或者数据库对象命名空间中的一个层次,主要用来解决命名冲突问题。从概念上说,一个数据库系统包含多个Catalog,每个Catalog又包含多个Schema,而每个Schema又包含多个数据库对象(表、视图、字段等),反过来讲一个数据库对象必然属于一个Schema,而该Schema又必然属于一个Catalog,这样我们就可以得到该数据库对象的完全限定名称,从而解决命名冲突的问题了;例如数据库对象表的完全限定名称就可以表示为:Catalog名称.Schema名称.表名称。这里还有一点需要注意的是,SQL标准并不要求每个数据库对象的完全限定名称是唯一的。
从实现的角度来看,各种数据库系统对Catalog和Schema的支持和实现方式千差万别,针对具体问题需要参考具体的产品说明书,比较简单而常用的实现方式是使用数据库名作为Catalog名,使用用户名作为Schema名,具体可参见下表:
表1 常用数据库
| 供应商 | Catalog支持 | Schema支持 |
|---|---|---|
| Oracle | 不支持 | Oracle User ID |
| MySQL | 不支持 | 数据库名 |
| MS SQL Server | 数据库名 | 对象属主名,2005版开始有变 |
| DB2 | 指定数据库对象时,Catalog部分省略 | Catalog属主名 |
| Sybase | 数据库名 | 数据库属主名 |
| Informix | 不支持 | 不需要 |
| PointBase | 不支持 | 数据库名 |
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/ECNB/p/4611309.html
元数据模型层级抽象
不同的关系型数据库,其数据库模式有所区别,对应与下面的层级关系
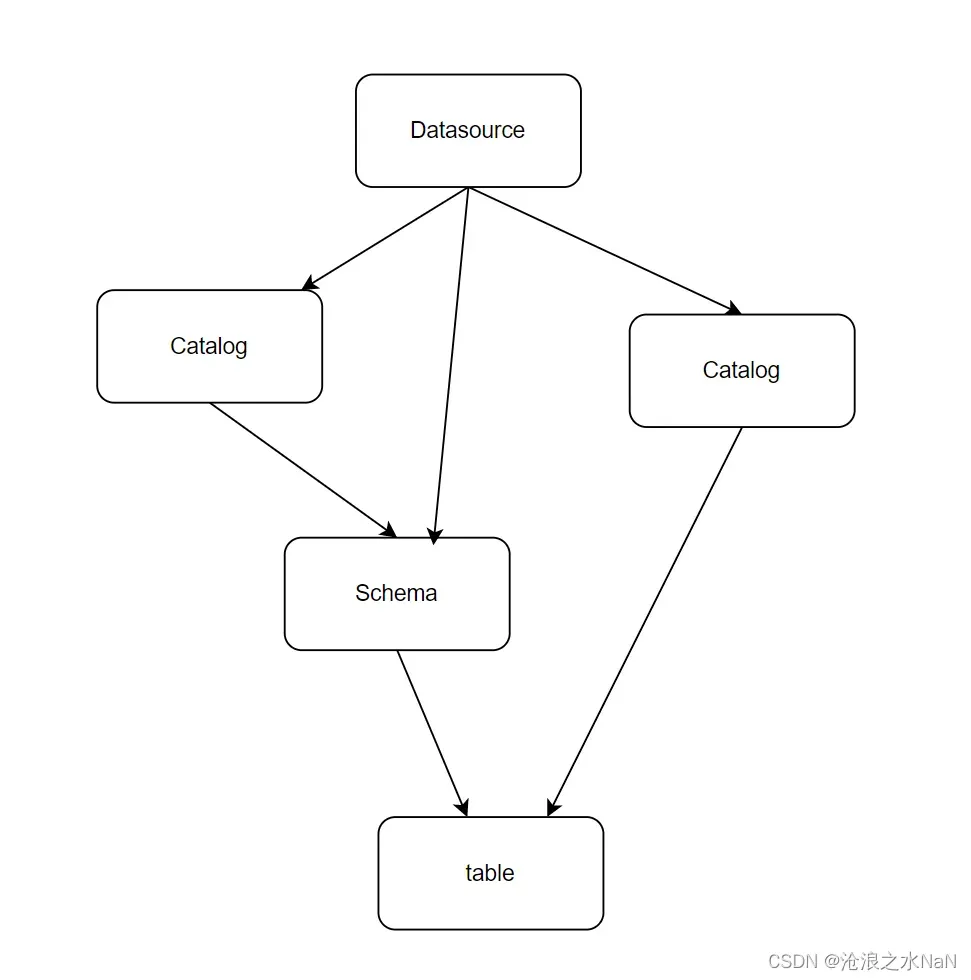
- Datasource -> Catalog -> Schema -> Table -> Column
- Datasource -> Catalog -> Table -> Column
- Datasource -> Schema -> Table -> Column
元数据转换设计

提供元数据
借鉴Apache DolphinScheduler中获取Connection的方式,不多赘述。
public Connection getConnection(DbType dbType, ConnectionParam connectionParam) throws ExecutionException {
BaseConnectionParam baseConnectionParam = (BaseConnectionParam) connectionParam;
String datasourceUniqueId = DataSourceUtils.getDatasourceUniqueId(baseConnectionParam, dbType);
logger.info("Get connection from datasource {}", datasourceUniqueId);
DataSourceClient dataSourceClient = uniqueId2dataSourceClientCache.get(datasourceUniqueId, () -> {
Map<String, DataSourceChannel> dataSourceChannelMap = dataSourcePluginManager.getDataSourceChannelMap();
DataSourceChannel dataSourceChannel = dataSourceChannelMap.get(dbType.getDescp());
if (null == dataSourceChannel) {
throw new RuntimeException(String.format("datasource plugin '%s' is not found", dbType.getDescp()));
}
return dataSourceChannel.createDataSourceClient(baseConnectionParam, dbType);
});
return dataSourceClient.getConnection();
}
转换元数据
- 元数据模型
创建数据库的元数据模型
private AtlasEntityDef createJdbcDatabaseDef() {
AtlasEntityDef typeDef = createClassTypeDef(DatabaseProperties.JDBC_TYPE_DATABASE,
Collections.singleton(DatabaseProperties.ENTITY_TYPE_DATASET),
createOptionalAttrDef(DatabaseProperties.ATTR_URL, "string"),
createOptionalAttrDef(DatabaseProperties.ATTR_DRIVER_NAME, "string"),
createOptionalAttrDef(DatabaseProperties.ATTR_PRODUCT_NAME, "string"),
createOptionalAttrDef(DatabaseProperties.ATTR_PRODUCT_VERSION, "string")
);
typeDef.setServiceType(DatabaseProperties.ENTITY_SERVICE_TYPE);
return typeDef;
}
创建数据库模式的元数据模型
private AtlasEntityDef createJdbcSchemaDef() {
AtlasEntityDef typeDef = AtlasTypeUtil.createClassTypeDef(
SchemaProperties.JDBC_TYPE_SCHEMA,
Collections.singleton(SchemaProperties.ENTITY_TYPE_DATASET)
);
typeDef.setServiceType(SchemaProperties.ENTITY_SERVICE_TYPE);
typeDef.setOptions(new HashMap<>() {{
put("schemaElementsAttribute", "tables");
}});
return typeDef;
}
创建数据库表的元数据模型
private AtlasEntityDef createJdbcTableDef() {
AtlasEntityDef typeDef = createClassTypeDef(
TableProperties.JDBC_TYPE_TABLE,
Collections.singleton(TableProperties.ENTITY_TYPE_DATASET),
createOptionalAttrDef(TableProperties.ATTR_TABLE_TYPE, "string")
);
typeDef.setServiceType(BaseProperties.ENTITY_SERVICE_TYPE);
typeDef.setOptions(new HashMap<>() {{
put("schemaElementsAttribute", "columns");
}});
return typeDef;
}
创建数据库列的元数据模型
private AtlasEntityDef createJdbcColumnDef() {
AtlasEntityDef typeDef = createClassTypeDef(
ColumnProperties.JDBC_TYPE_COLUMN,
Collections.singleton(ColumnProperties.ENTITY_TYPE_DATASET),
createOptionalAttrDef(ColumnProperties.ATTR_COLUMN_TYPE, "string"),
createOptionalAttrDef(ColumnProperties.ATTR_IS_PRIMARY_KEY, "string"),
createOptionalAttrDef(ColumnProperties.ATTR_COLUMN_IS_NULLABLE, "string"),
createOptionalAttrDef(ColumnProperties.ATTR_COLUMN_DEFAULT_VALUE, "string"),
createOptionalAttrDef(ColumnProperties.ATTR_COLUMN_AUTO_INCREMENT, "string")
);
typeDef.setServiceType(BaseProperties.ENTITY_SERVICE_TYPE);
HashMap<String, String> options = new HashMap<>() {{
put("schemaAttributes", "[\"name\", \"isPrimaryKey\", \"columnType\", \"isNullable\" , \"isAutoIncrement\", \"description\"]");
}};
typeDef.setOptions(options);
return typeDef;
}
创建实体之间的关系模型
private List<AtlasRelationshipDef> createAtlasRelationshipDef() {
String version = "1.0";
// 数据库和模式的关系
AtlasRelationshipDef databaseSchemasDef = createRelationshipTypeDef(
BaseProperties.RELATIONSHIP_DATABASE_SCHEMAS,
BaseProperties.RELATIONSHIP_DATABASE_SCHEMAS,
version, COMPOSITION, AtlasRelationshipDef.PropagateTags.NONE,
createRelationshipEndDef(BaseProperties.JDBC_TYPE_DATABASE, "schemas", SET, true),
createRelationshipEndDef(BaseProperties.JDBC_TYPE_SCHEMA, "database", SINGLE, false)
);
databaseSchemasDef.setServiceType(BaseProperties.ENTITY_SERVICE_TYPE);
AtlasRelationshipDef databaseTablesDef = createRelationshipTypeDef(
BaseProperties.RELATIONSHIP_DATABASE_TABLES,
BaseProperties.RELATIONSHIP_DATABASE_TABLES,
version, AGGREGATION, AtlasRelationshipDef.PropagateTags.NONE,
createRelationshipEndDef(BaseProperties.JDBC_TYPE_DATABASE, "tables", SET, true),
createRelationshipEndDef(BaseProperties.JDBC_TYPE_TABLE, "database", SINGLE, false)
);
databaseTablesDef.setServiceType(BaseProperties.ENTITY_SERVICE_TYPE);
// 模式和数据表的关系
// 注意 schema 已经被使用, 需要更换否则会冲突, 例如改为 Jschema(jdbc_schema)
AtlasRelationshipDef schemaTablesDef = createRelationshipTypeDef(
BaseProperties.RELATIONSHIP_SCHEMA_TABLES,
BaseProperties.RELATIONSHIP_SCHEMA_TABLES,
version, AGGREGATION, AtlasRelationshipDef.PropagateTags.NONE,
createRelationshipEndDef(BaseProperties.JDBC_TYPE_SCHEMA, "tables", SET, true),
createRelationshipEndDef(BaseProperties.JDBC_TYPE_TABLE, "Jschema", SINGLE, false)
);
schemaTablesDef.setServiceType(BaseProperties.ENTITY_SERVICE_TYPE);
// 表和数据列的关系
AtlasRelationshipDef tableColumnsDef = createRelationshipTypeDef(
BaseProperties.RELATIONSHIP_TABLE_COLUMNS,
BaseProperties.RELATIONSHIP_TABLE_COLUMNS,
version, COMPOSITION, AtlasRelationshipDef.PropagateTags.NONE,
createRelationshipEndDef(BaseProperties.JDBC_TYPE_TABLE, "columns", SET, true),
createRelationshipEndDef(BaseProperties.JDBC_TYPE_COLUMN, "table", SINGLE, false)
);
tableColumnsDef.setServiceType(BaseProperties.ENTITY_SERVICE_TYPE);
return Arrays.asList(databaseSchemasDef, databaseTablesDef, schemaTablesDef, tableColumnsDef);
}
-
提取元数据
不再赘述
-
转换元数据
使用工厂模式,提供不同类型的元数据转换方式
public interface JdbcTransferFactory {
JdbcTransfer getTransfer(DatabaseMetaData metaData, AtlasClientV2 client);
boolean supportType(String type);
String getName();
}
List ignorePatterns 用来过滤不想导入的数据库元数据,例如mysql的information_schema
public interface JdbcTransfer {
void transfer();
JdbcTransfer setIgnorePatterns(List<Pattern> ignorePatterns);
}
举例:JdbcMysqlTransfer 和 MysqlTransferFactory
@AutoService(JdbcTransferFactory.class)
public class MysqlTransferFactory implements JdbcTransferFactory {
public static final String MYSQL = "mysql";
@Override
public JdbcTransfer getTransfer(DatabaseMetaData metaData, AtlasClientV2 client) {
return new JdbcMysqlTransfer(metaData, client);
}
@Override
public boolean supportType(String type) {
return MYSQL.equalsIgnoreCase(type);
}
@Override
public String getName() {
return MYSQL;
}
}
public class JdbcMysqlTransfer implements JdbcTransfer {
private final Jdbc jdbc;
private final AtlasService atlasService;
private List<Pattern> ignorePatterns;
public JdbcMysqlTransfer(DatabaseMetaData metaData, AtlasClientV2 client) {
this.jdbc = new Jdbc(new JdbcMetadata(metaData));
this.atlasService = new AtlasService(client);
this.ignorePatterns = Collections.emptyList();
}
@Override
public JdbcTransfer setIgnorePatterns(List<Pattern> ignorePatterns) {
this.ignorePatterns = ignorePatterns;
return this;
}
private boolean tableIsNotIgnored(String tableName) {
return ignorePatterns.stream().noneMatch(regex -> regex.matcher(tableName).matches());
}
@Override
public void transfer() {
// 1.数据库实体转换
DatabaseTransfer databaseTransfer = new DatabaseTransfer(atlasService);
AtlasEntity databaseEntity = databaseTransfer.apply(jdbc);
// 2.表实体转换
String catalog = (String) databaseEntity.getAttribute(BaseProperties.ATTR_NAME);
List<AtlasEntity> tableEntities = jdbc.getTables(catalog, catalog).parallelStream()
.filter(jdbcTable -> tableIsNotIgnored(jdbcTable.getTableName()))
.map(new TableTransfer(atlasService, databaseEntity))
.toList();
// 3.列转换
for (AtlasEntity tableEntity : tableEntities) {
String tableName = (String) tableEntity.getAttribute(BaseProperties.ATTR_NAME);
List<JdbcPrimaryKey> primaryKeys = jdbc.getPrimaryKeys(catalog, tableName);
jdbc.getColumns(catalog, catalog, tableName).parallelStream()
.forEach(new ColumnTransfer(atlasService, tableEntity, primaryKeys));
}
}
}
- 元数据存入Atlas
public class DatabaseTransfer implements Function<Jdbc, AtlasEntity> {
private final AtlasService atlasService;
public DatabaseTransfer(AtlasService atlasService) {
this.atlasService = atlasService;
}
@Override
public AtlasEntity apply(Jdbc jdbc) {
String userName = jdbc.getUserName();
String driverName = jdbc.getDriverName();
String productName = jdbc.getDatabaseProductName();
String productVersion = jdbc.getDatabaseProductVersion();
String url = jdbc.getUrl();
String urlWithNoParams = url.contains("?") ? url.substring(0, url.indexOf("?")) : url;
String catalogName = urlWithNoParams.substring(urlWithNoParams.lastIndexOf("/") + 1);
// 特殊处理 Oracle
if (productName.equalsIgnoreCase("oracle")){
catalogName = userName.toUpperCase();
urlWithNoParams = urlWithNoParams + "/" + catalogName;
}
DatabaseProperties properties = new DatabaseProperties();
properties.setQualifiedName(urlWithNoParams);
properties.setDisplayName(catalogName);
properties.setOwner(userName);
properties.setUrl(url);
properties.setDriverName(driverName);
properties.setProductName(productName);
properties.setProductVersion(productVersion);
// 1.创建Atlas Entity
AtlasEntity atlasEntity = new AtlasEntity(DatabaseProperties.JDBC_TYPE_DATABASE, properties.getAttributes());
// 2.判断是否存在实体, 存在则填充GUID
Map<String, String> searchParam = Collections.singletonMap(DatabaseProperties.ATTR_QUALIFIED_NAME, urlWithNoParams);
Optional<AtlasEntityHeader> entityHeader = atlasService.checkAtlasEntityExists(DatabaseProperties.JDBC_TYPE_DATABASE, searchParam);
entityHeader.ifPresent(header -> atlasEntity.setGuid(header.getGuid()));
// 3,存储或者更新到Atlas中
if (entityHeader.isPresent()){
atlasService.createAtlasEntity(new AtlasEntity.AtlasEntityWithExtInfo(atlasEntity));
}else {
AtlasEntityHeader header = atlasService.createAtlasEntity(new AtlasEntity.AtlasEntityWithExtInfo(atlasEntity));
atlasEntity.setGuid(header.getGuid());
}
return atlasEntity;
}
}
效果展示
- 元数据类型定义


- 测试导入元数据
由于mysql没有采用schema,因此jdbc_schema为空
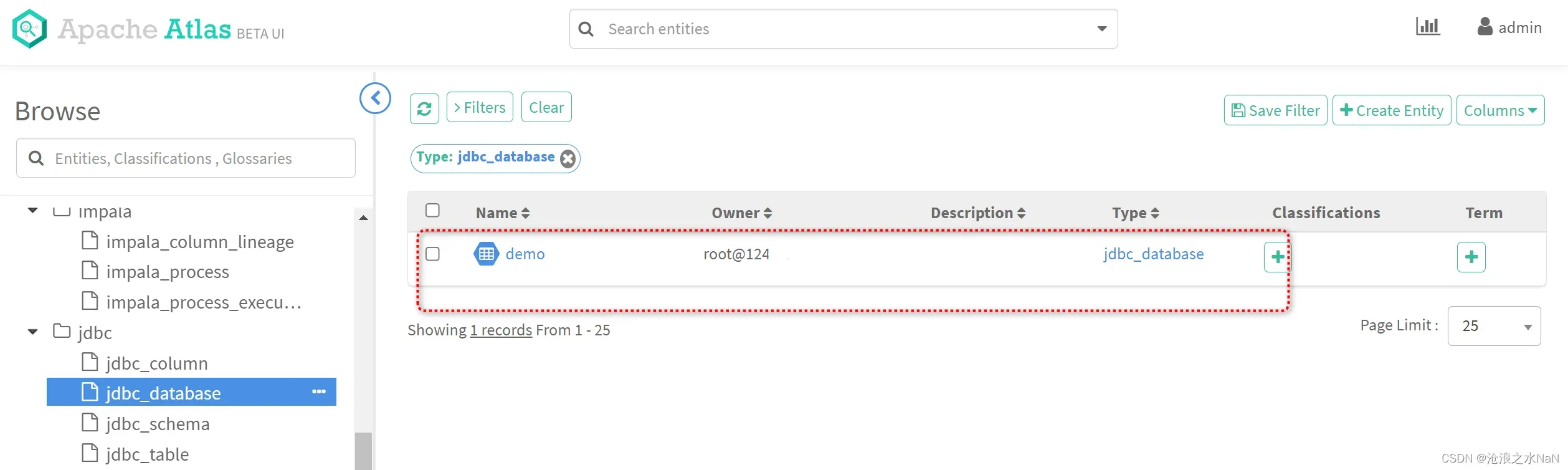
如图所示,可以清晰的了解mysql数据库中demo数据库的数据表内容
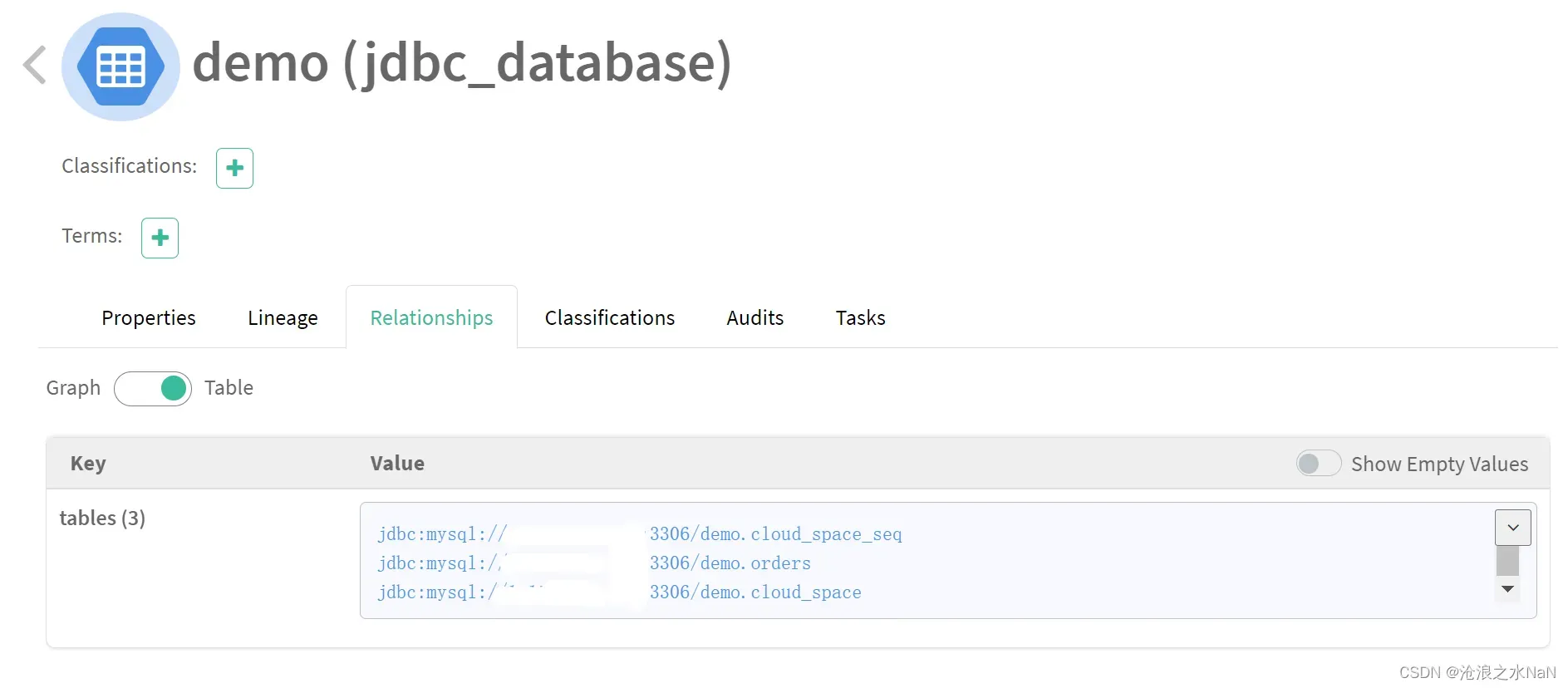
数据表元数据,qualifiedName使用数据库连接url.表名

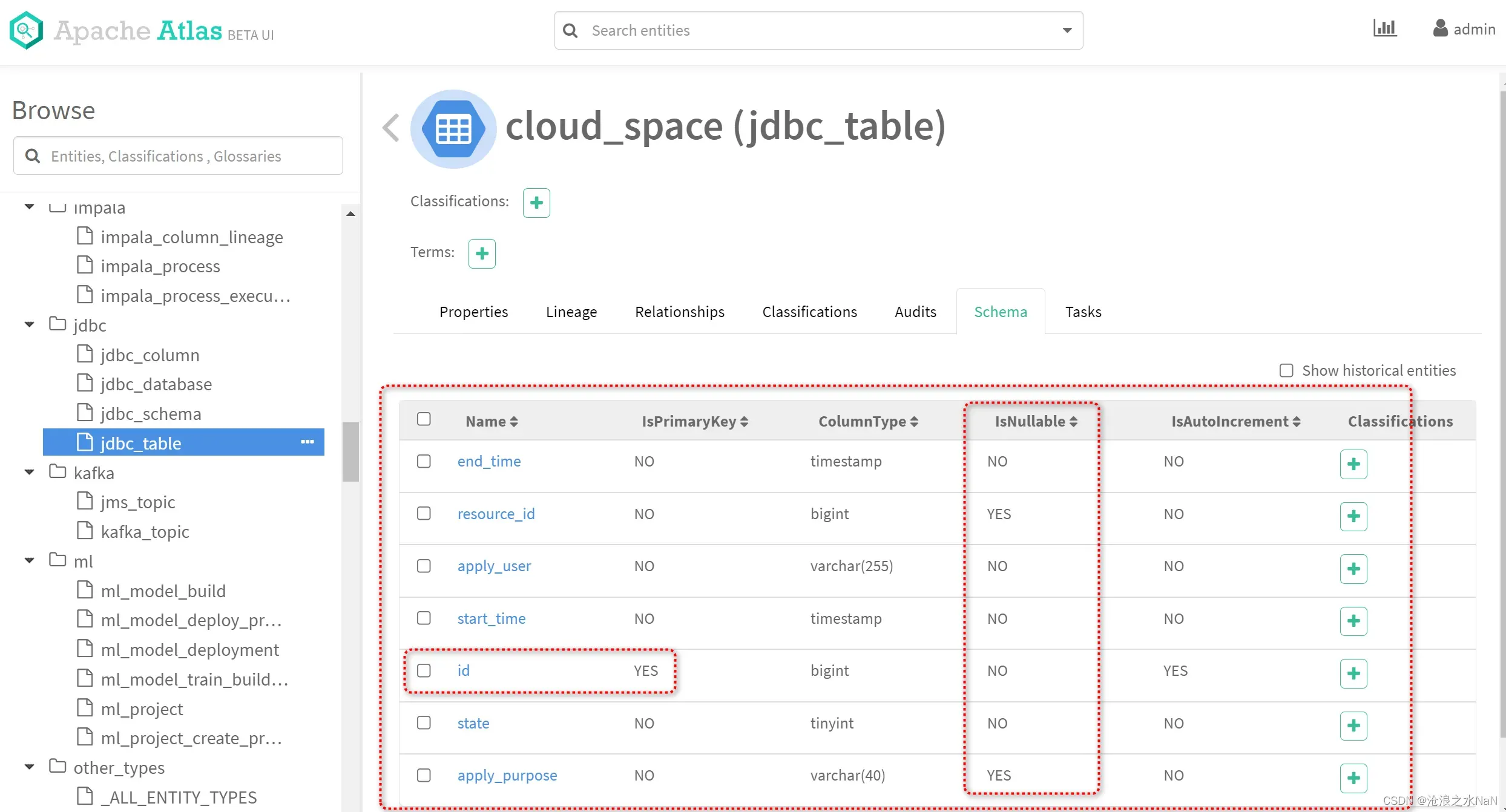
如同所示,数据表内各个列的元数据;可以清晰的了解该数据表的各个字段信息
文章出处登录后可见!
