1、LED指示灯的控制
训练题目:

相关原理图:
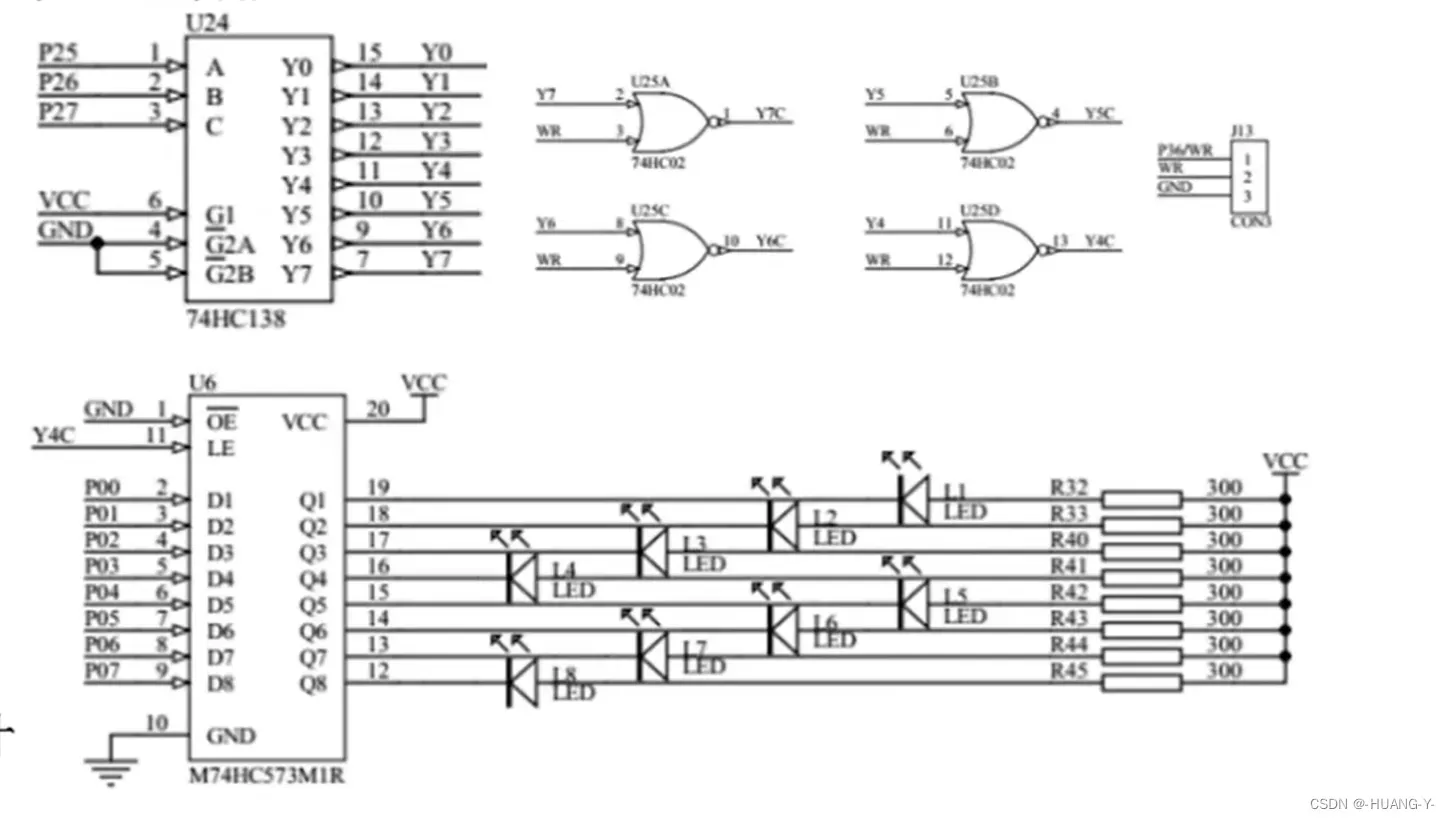
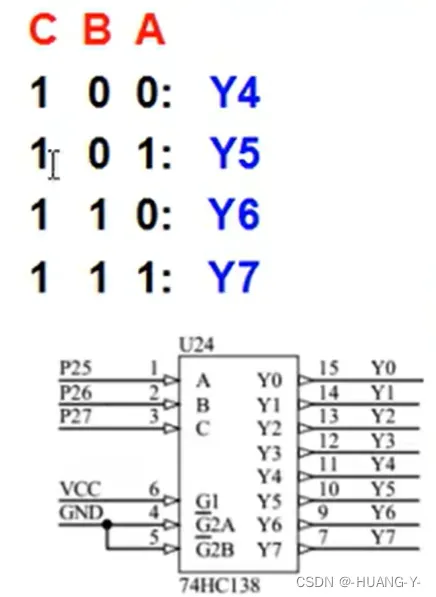
138译码器:
C,B,A所成二进制数转化为十进制后对应与Yn中n的值。
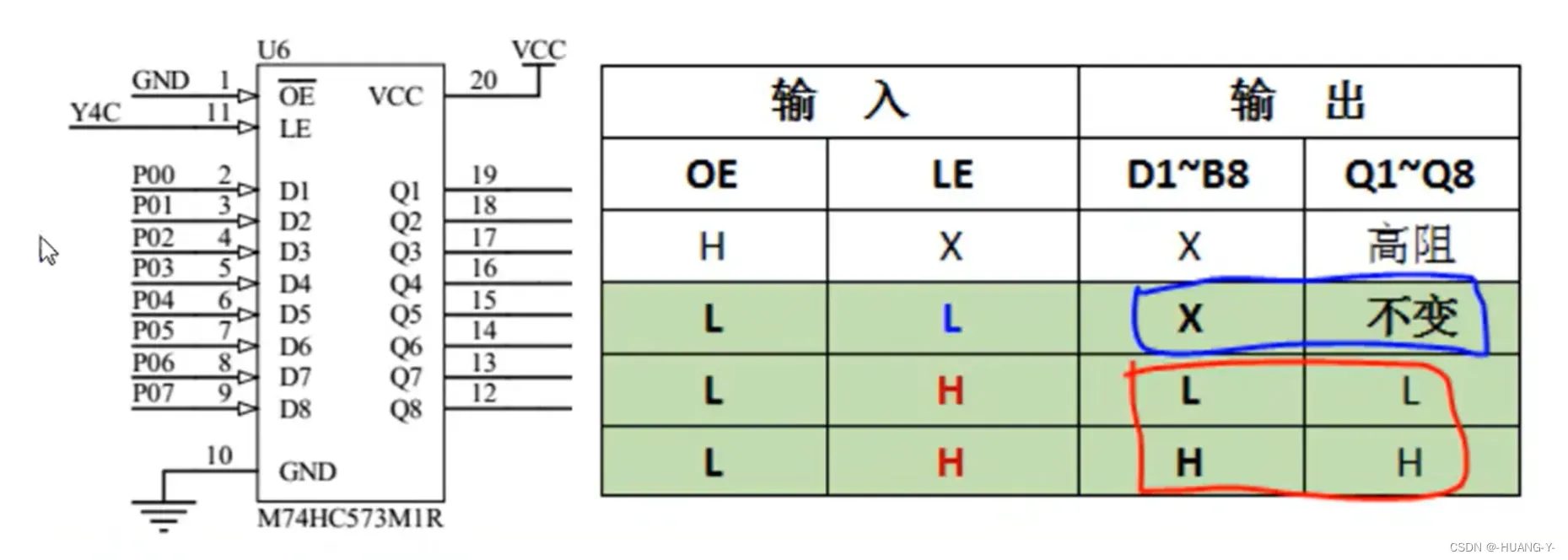
573锁存器:
思路:

关键代码:
//LED逐个点亮,通过位运算实现
for(i = 1; i <= 8; i++)
{
P0 = 0xff << i; //逐个熄灭:P0 = ~(0xff << i);
Delay(60000);
Delay(60000);
}
整体代码实现:
#include "reg52.h"
sbit HC138_A = P2^5;
sbit HC138_B = P2^6;
sbit HC138_C = P2^7;
void Delay(unsigned int t)
{
while(t--);
while(t--);
}
void LEDRunning()
{
unsigned char i;
HC138_C = 1;
HC138_B = 0;
HC138_A = 0;
for(i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
P0 = 0x00;
Delay(60000);
Delay(60000);
P0 = 0xff;
Delay(60000);
Delay(60000);
}
for(i = 1; i <= 8; i++)
{
P0 = 0xff << i;
Delay(60000);
Delay(60000);
}
for(i = 1; i <= 8; i++)
{
P0 = ~(0xff << i);
Delay(60000);
Delay(60000);
}
}
void main()
{
while(1)
{
LEDRunning();
}
}
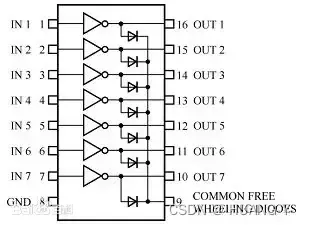
2、蜂鸣器与继电器的控制
训练题目及原理图:
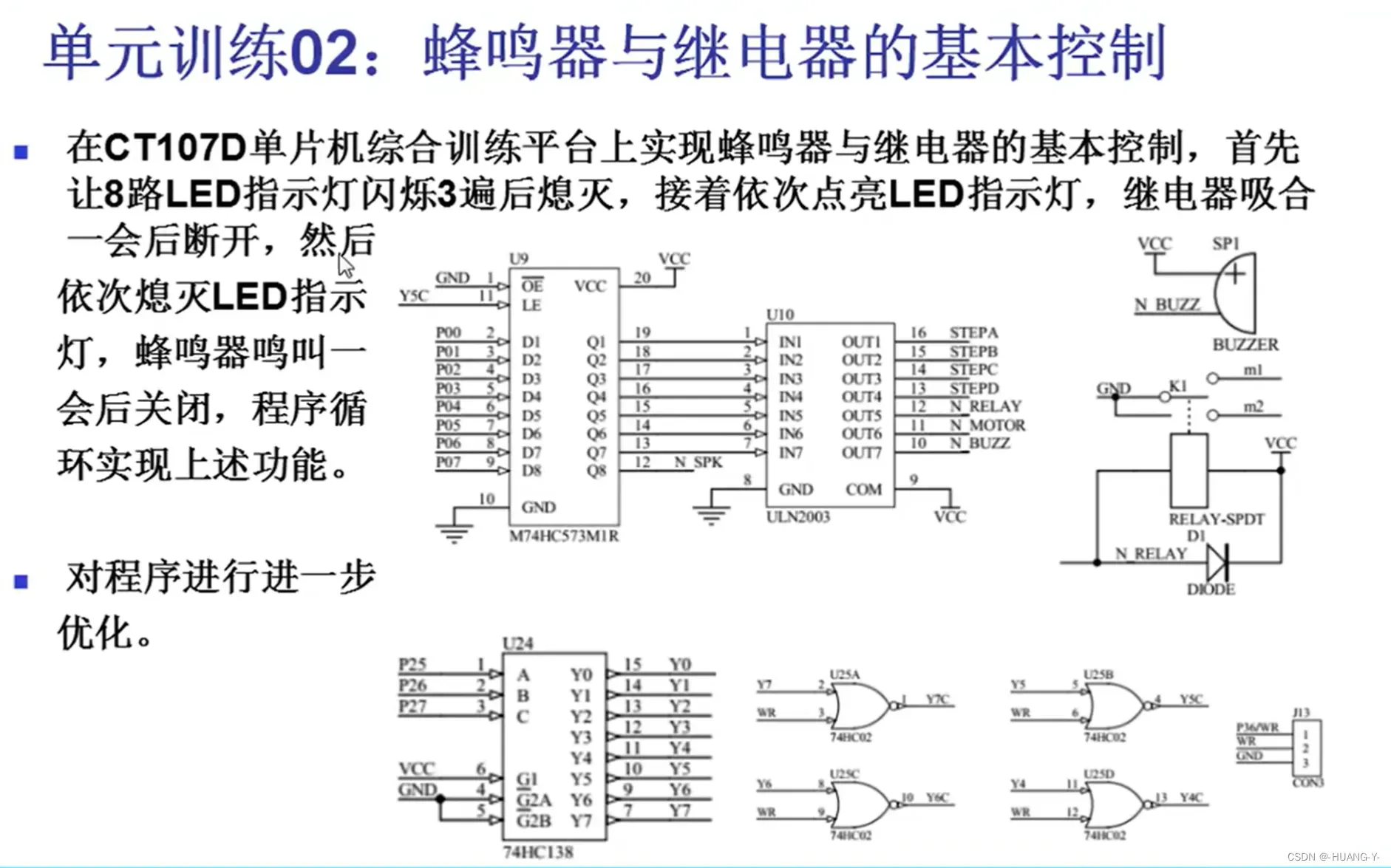
UNL2003:
关键:非门。
思路:
与LED类似,注意要通过非门,N_BUZZ和N_RELAY低电平时器件工作。
关键代码:
//138译码器初始化代码。
//LED、蜂鸣器和继电器、数码管使用时均需要
void InitHC138(unsigned char n)
{
switch(n)
{
case 4:
P2 = (P2 & 0X1f) | 0x80;
break; //LED
case 5:
P2 = (P2 & 0X1f) | 0xa0;
break; //蜂鸣器、继电器
case 6:
P2 = (P2 & 0X1f) | 0xc0;
break; //数码管位选
case 7:
P2 = (P2 & 0X1f) | 0xe0;
break; //数码管段选
}
}
整体代码实现:
#include "reg52.h"
void Delay(unsigned int t)
{
while(t--);
while(t--);
}
void InitHC138(unsigned char n)
{
switch(n)
{
case 4:
P2 = (P2 & 0X1f) | 0x80;
break;
case 5:
P2 = (P2 & 0X1f) | 0xa0;
break;
case 6:
P2 = (P2 & 0X1f) | 0xc0;
break;
case 7:
P2 = (P2 & 0X1f) | 0xe0;
break;
}
}
void OutPutP0(unsigned char channel, unsigned char dat)
{
InitHC138(channel);
P0 = dat;
}
void LEDRunning()
{
unsigned char i;
for(i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
OutPutP0(4,0x00);
Delay(60000);
Delay(60000);
OutPutP0(4,0xff);
Delay(60000);
Delay(60000);
}
for(i = 1; i <= 8; i++)
{
OutPutP0(4,(0xff << i));
Delay(60000);
}
OutPutP0(5,0x10);
Delay(60000);
Delay(60000);
OutPutP0(5,0x00);
InitHC138(4);
for(i = 1; i <= 8; i++)
{
OutPutP0(4,~(0xff << i));
Delay(60000);
}
OutPutP0(5,0x40);
Delay(60000);
Delay(60000);
OutPutP0(5,0x00);
}
void InitSystem()
{
OutPutP0(5,0x00);
}
void main()
{
InitSystem();
while(1)
{
LEDRunning();
}
}3、共阳数码管的静态显示
训练题目: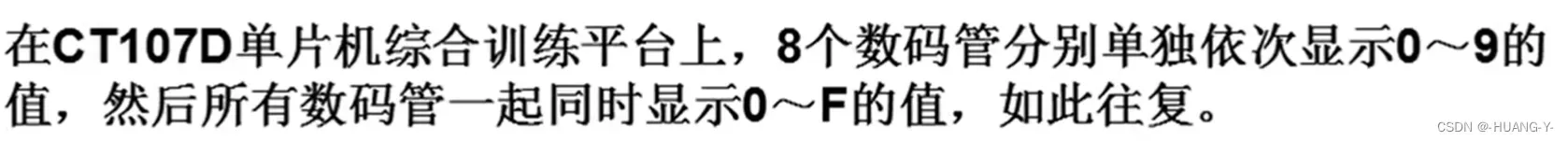
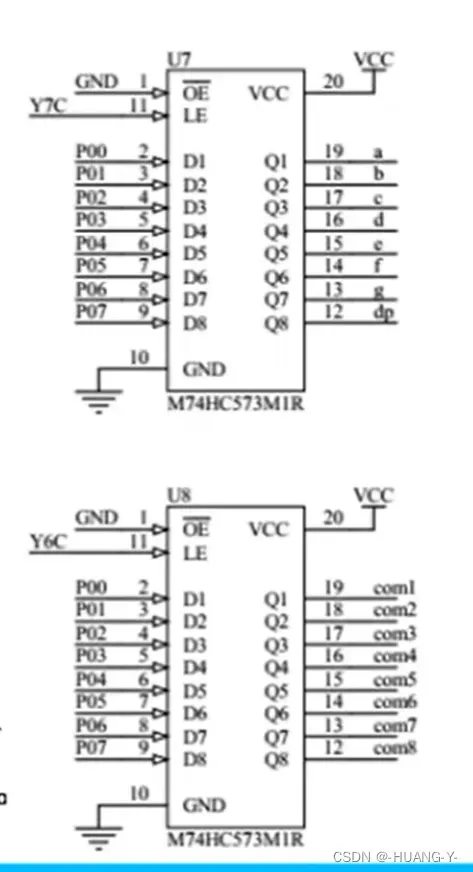
相关原理图:
两块锁存器分别控制数码管的段选和位选。
共阳P0低电平点亮,共阴高电平点亮。
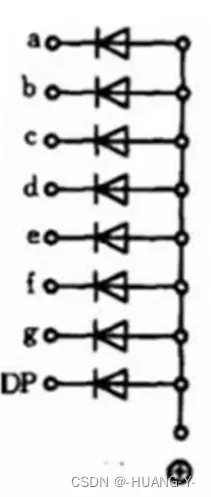
段选十六进制数:首先为八位二进制数,顺序由高到低为:hgfedcba。
再转为十六进制:四位一组,高到低,为:8/4/2/1。

位选:因为是共阳,所以选哪位哪位应为高电平。
进制转换补充:

关键代码:
//单个数码管显示
void ShowSMG_Bit(unsigned char dat, unsigned pos)
{
InitHC138(6); //数码管的位置
P0 = 0x01 << pos;
InitHC138(7); //数码管的内容
P0 = dat;
}整体代码实现:
#include "reg52.h"
unsigned char code SMG_duanma[18]=
{0xc0,0xf9,0xa4,0xb0,0x99,0x92,0x82,0xf8,
0x80,0x90,0x88,0x80,0xc6,0xc0,0x86,0x8e,
0xbf,0x7f};
void Delay(unsigned int t)
{
while(t--);
while(t--);
}
void InitHC138(unsigned char n)
{
switch(n)
{
case 4:
P2 = (P2 & 0x1f) | 0x80;
break;
case 5:
P2 = (P2 & 0x1f) | 0xa0;
break;
case 6:
P2 = (P2 & 0x1f) | 0xc0;
break;
case 7:
P2 = (P2 & 0x1f) | 0xe0;
break;
}
}
void ShowSMG_Bit(unsigned char dat, unsigned pos)
{
InitHC138(6); //数码管的位置
P0 = 0x01 << pos;
InitHC138(7); //数码管的内容
P0 = dat;
}
void SMG_Static()
{
unsigned char i,j;
for(i = 0; i < 8; i++)
{
for(j = 0; j < 10; j++)
{
ShowSMG_Bit(SMG_duanma[j],i);
Delay(60000);
}
}
for(j = 0; j < 16; j++)
{
InitHC138(6); //数码管的位置
P0 = 0xff;
InitHC138(7); //数码管的内容
P0 = SMG_duanma[j];
Delay(60000);
Delay(60000);
}
}
void main()
{
while(1)
{
SMG_Static();
}
}4、共阳数码管的动态显示
训练题目:

原理:
视觉暂留效应,每位显示只延时很短时间。
关键代码:
//注意用全局变量来计数
void Display_Dynamic()
{
DisplaySMG_Bit(SMG_duanma[2],0);
DelaySMG(500);
DisplaySMG_Bit(SMG_duanma[0],1);
DelaySMG(500);
DisplaySMG_Bit(SMG_duanma[1],2);
DelaySMG(500);
DisplaySMG_Bit(SMG_duanma[8],3);
DelaySMG(500);
DisplaySMG_Bit(SMG_duanma[16],4);
DelaySMG(500);
DisplaySMG_Bit(SMG_duanma[16],5);
DelaySMG(500);
DisplaySMG_Bit(SMG_duanma[yu/10],6);
DelaySMG(500);
DisplaySMG_Bit(SMG_duanma[yu%10],7);
DelaySMG(500);
}
//因为单纯延时数码管会熄灭,所以里面嵌套了动态显示函数,以达到中断的效果
void Delay(unsigned char t)
{
while(t--)
{
Display_Dynamic();
}
}
整体代码实现:
#include "reg52.h"
unsigned char yu = 1;
unsigned char code SMG_duanma[18]=
{0xc0,0xf9,0xa4,0xb0,0x99,0x92,0x82,0xf8,
0x80,0x90,0x88,0x80,0xc6,0xc0,0x86,0x8e,
0xbf,0x7f};
void SelectHC573(unsigned char channel)
{
switch(channel)
{
case 4:
P2 = (P2 & 0x1f) | 0x80;
break;
case 5:
P2 = (P2 & 0x1f) | 0xa0;
break;
case 6:
P2 = (P2 & 0x1f) | 0xc0;
break;
case 7:
P2 = (P2 & 0x1f) | 0xe0;
break;
}
}
void DisplaySMG_Bit(unsigned char value, unsigned char pos)
{
P0 = 0xff;
SelectHC573(6);
P0 = 0x01 << pos;
SelectHC573(7);
P0 = value;
}
void DelaySMG(unsigned int t)
{
while(t--);
}
void Display_Dynamic()
{
DisplaySMG_Bit(SMG_duanma[2],0);
DelaySMG(500);
DisplaySMG_Bit(SMG_duanma[0],1);
DelaySMG(500);
DisplaySMG_Bit(SMG_duanma[1],2);
DelaySMG(500);
DisplaySMG_Bit(SMG_duanma[8],3);
DelaySMG(500);
DisplaySMG_Bit(SMG_duanma[16],4);
DelaySMG(500);
DisplaySMG_Bit(SMG_duanma[16],5);
DelaySMG(500);
DisplaySMG_Bit(SMG_duanma[yu/10],6);
DelaySMG(500);
DisplaySMG_Bit(SMG_duanma[yu%10],7);
DelaySMG(500);
}
void Delay(unsigned char t)
{
while(t--)
{
Display_Dynamic();
}
}
void main()
{
while(1)
{
Display_Dynamic();
yu++;
if(yu > 12)
{
yu = 1;
}
Delay(200);
}
}5、独立按键:
基本训练题目:

扩展训练题目:
原理:
跳帽接23端,若按键按下则可接收到低电平。
基本训练关键代码:
//按键扫描,以S7为例
void ScanKeys_Alone()
{
if(S7 == 0)
{
DelayK(100);
if(S7 == 0)//延时消抖
{
L1 = 0;
while(S7 == 0);//按下常亮,松开熄灭,闪烁效果
L1 = 1;
}
}基本训练整体代码实现:
#include "reg52.h"
sbit S7 = P3^0;
sbit S6 = P3^1;
sbit S5 = P3^2;
sbit S4 = P3^3;
sbit L1 = P0^0;
sbit L2 = P0^1;
sbit L3 = P0^2;
sbit L4 = P0^3;
sbit L5 = P0^4;
sbit L6 = P0^5;
void SelectHC573(unsigned char channel)
{
switch(channel)
{
case 4:
P2 = (P2 & 0x1f) | 0x80;
break;
case 5:
P2 = (P2 & 0x1f) | 0xa0;
break;
case 6:
P2 = (P2 & 0x1f) | 0xc0;
break;
case 7:
P2 = (P2 & 0x1f) | 0xe0;
break;
}
}
void DelayK(unsigned char t)
{
while(t--);
}
void ScanKeys_Alone()
{
if(S7 == 0)
{
DelayK(100);
if(S7 == 0)
{
L1 = 0;
while(S7 == 0);
L1 = 1;
}
}
if(S6 == 0)
{
DelayK(100);
if(S6 == 0)
{
L2 = 0;
while(S6 == 0);
L2 = 1;
}
}
if(S5 == 0)
{
DelayK(100);
if(S5 == 0)
{
L3 = 0;
while(S5 == 0);
L3 = 1;
}
}
if(S4 == 0)
{
DelayK(100);
if(S4 == 0)
{
L4 = 0;
while(S4 == 0);
L4 = 1;
}
}
}
void main()
{
SelectHC573(4);
while(1)
{
ScanKeys_Alone();
}
}扩展训练整体代码实现:
#include "reg52.h"
sbit S7 = P3^0;
sbit S6 = P3^1;
sbit S5 = P3^2;
sbit S4 = P3^3;
sbit L1 = P0^0;
sbit L2 = P0^1;
sbit L3 = P0^2;
sbit L4 = P0^3;
sbit L5 = P0^4;
sbit L6 = P0^5;
void SelectHC573(unsigned char channel)
{
switch(channel)
{
case 4:
P2 = (P2 & 0x1f) | 0x80;
break;
case 5:
P2 = (P2 & 0x1f) | 0xa0;
break;
case 6:
P2 = (P2 & 0x1f) | 0xc0;
break;
case 7:
P2 = (P2 & 0x1f) | 0xe0;
break;
}
}
void DelayK(unsigned char t)
{
while(t--);
}
unsigned char stat_k = 0;//全局状态变量实现按键控制分支按键,且不互相干扰
void ScanKeys_Alone()
{
if(S7 == 0)
{
DelayK(100);
if(S7 == 0)
{
if(stat_k == 0)
{
L1 = 0;
stat_k = 1;
}
else if(stat_k == 1)
{
L1 = 1;
stat_k = 0;
}
while(S7 == 0);//避免一次按下读多次
}
}
if(S6 == 0)
{
DelayK(100);
if(S6 == 0)
{
if(stat_k == 0)
{
L2 = 0;
stat_k = 2;
}
else if(stat_k == 2)
{
L2 = 1;
stat_k = 0;
}
while(S6 == 0);
}
}
if(S5 == 0)
{
DelayK(100);
if(S5 == 0)
{
if(stat_k == 1)
{
L3 = 0;
while(S5 == 0);
L3 = 1;
}
else if(stat_k == 2)
{
L5 = 0;
while(S5 == 0);
L5 = 1;
}
}
}
if(S4 == 0)
{
DelayK(100);
if(S4 == 0)
{
if(stat_k == 1)
{
L4 = 0;
while(S4 == 0);
L4 = 1;
}
else if(stat_k == 2)
{
L6 = 0;
while(S4 == 0);
L6 = 1;
}
}
}
}
void main()
{
SelectHC573(4);
while(1)
{
ScanKeys_Alone();
}
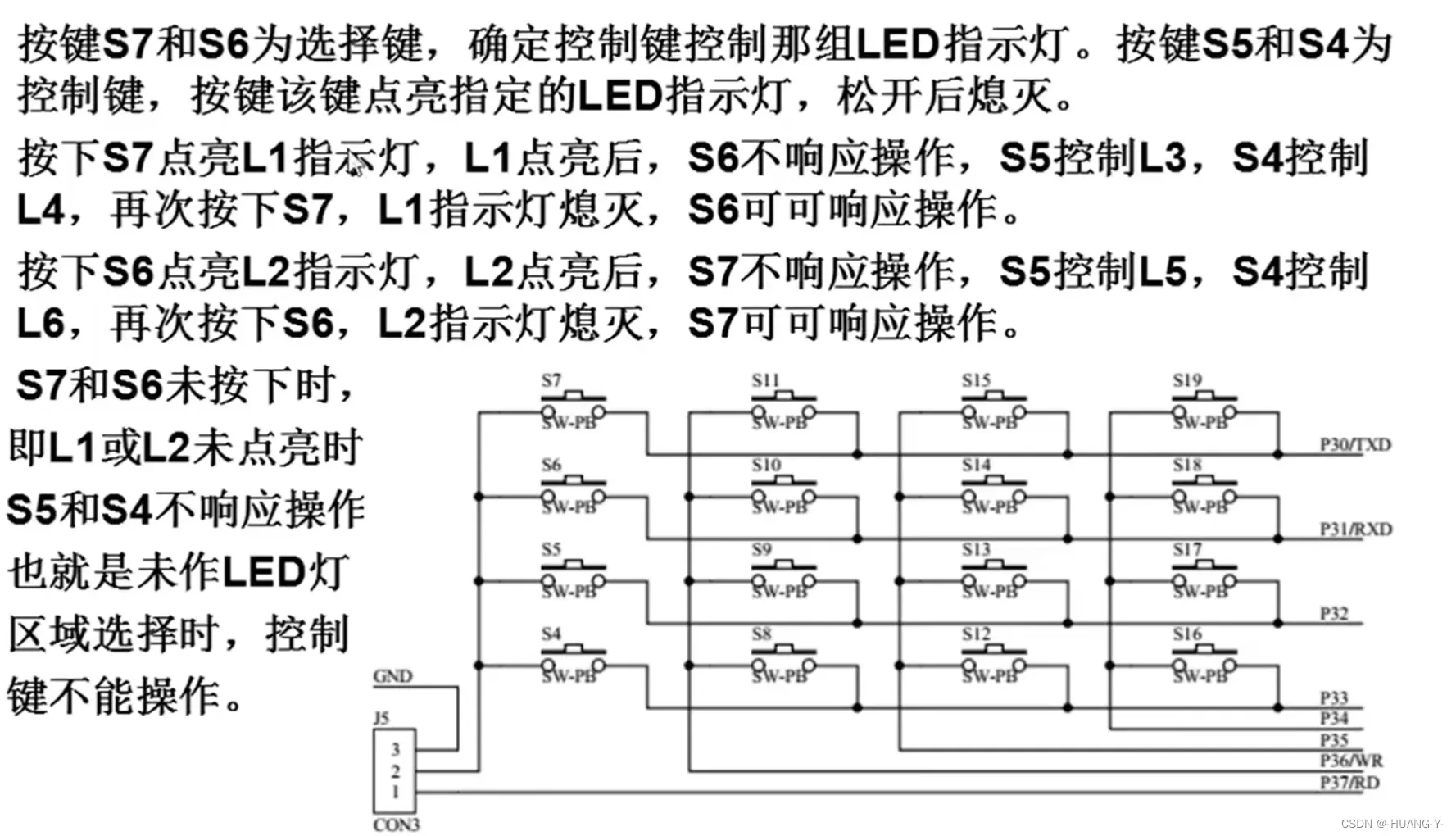
}6、矩阵按键:
训练题目:

原理:
P36、P37改为P42、P44。跳帽接到12端。通过逐行输入低电平信号,从检查哪列收到低电平信号,确定按键按下位置。
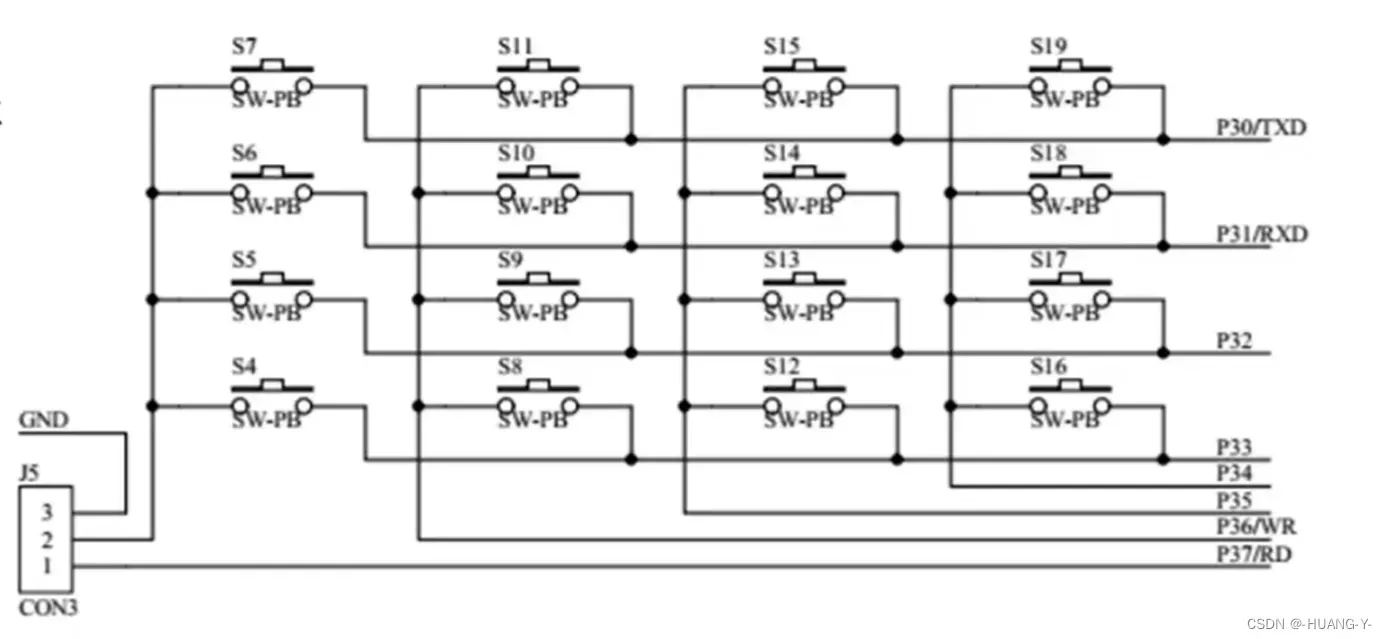
独立按键内部结构:
未按下时高电平,按下后低电平。
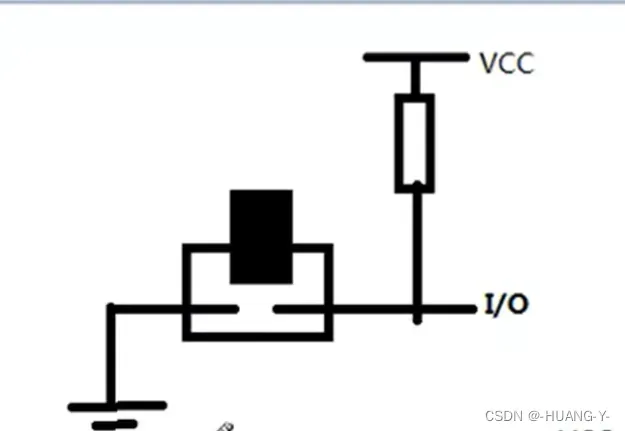
矩阵按键内部结构:
图中,左边为行IO口,右边为列IO口。当行IO口输出低电平时,按键按下,右边可检测到低电平。
整体代码实现:
#include "reg52.h"
sfr P4 = 0xC0;
sbit R1 = P3^0;
sbit R2 = P3^1;
sbit R3 = P3^2;
sbit R4 = P3^3;
sbit C4 = P3^4;
sbit C3 = P3^5;
sbit C2 = P4^2;
sbit C1 = P4^4;
unsigned char code SMG_duanma[18]=
{0xc0,0xf9,0xa4,0xb0,0x99,0x92,0x82,0xf8,
0x80,0x90,0x88,0x80,0xc6,0xc0,0x86,0x8e,
0xbf,0x7f};
void SelectHC573(unsigned char channel)
{
switch(channel)
{
case 4:
P2 = (P2 & 0x1f) | 0x80;
break;
case 5:
P2 = (P2 & 0x1f) | 0xa0;
break;
case 6:
P2 = (P2 & 0x1f) | 0xc0;
break;
case 7:
P2 = (P2 & 0x1f) | 0xe0;
break;
}
}
void DisplayKeyNum(unsigned char value)
{
P0 = 0xff;
SelectHC573(6);
P0 = 0x01;
SelectHC573(7);
P0 = value;
}
unsigned char key_num;
void ScanKeysMulti()
{
R1 = 0;
R2 = R3 = R4 = 1;
C1 = C2 = C3 = C4 =1;
if(C1 == 0)
{
while(C1 == 0);//避免按下一次扫描多次
key_num = 0;
DisplayKeyNum(SMG_duanma[key_num]);
}
else if(C2 == 0)
{
while(C2 == 0);
key_num = 1;
DisplayKeyNum(SMG_duanma[key_num]);
}
else if(C3 == 0)
{
while(C3 == 0);
key_num = 2;
DisplayKeyNum(SMG_duanma[key_num]);
}
else if(C4 == 0)
{
while(C4 == 0);
key_num = 3;
DisplayKeyNum(SMG_duanma[key_num]);
}
R2 = 0;
R1 = R3 = R4 = 1;
C1 = C2 = C3 = C4 =1;
if(C1 == 0)
{
while(C1 == 0);
key_num = 4;
DisplayKeyNum(SMG_duanma[key_num]);
}
else if(C2 == 0)
{
while(C2 == 0);
key_num = 5;
DisplayKeyNum(SMG_duanma[key_num]);
}
else if(C3 == 0)
{
while(C3 == 0);
key_num = 6;
DisplayKeyNum(SMG_duanma[key_num]);
}
else if(C4 == 0)
{
while(C4 == 0);
key_num = 7;
DisplayKeyNum(SMG_duanma[key_num]);
}
R3 = 0;
R2 = R1 = R4 = 1;
C1 = C2 = C3 = C4 =1;
if(C1 == 0)
{
while(C1 == 0);
key_num = 8;
DisplayKeyNum(SMG_duanma[key_num]);
}
else if(C2 == 0)
{
while(C2 == 0);
key_num = 9;
DisplayKeyNum(SMG_duanma[key_num]);
}
else if(C3 == 0)
{
while(C3 == 0);
key_num = 10;
DisplayKeyNum(SMG_duanma[key_num]);
}
else if(C4 == 0)
{
while(C4 == 0);
key_num = 11;
DisplayKeyNum(SMG_duanma[key_num]);
}
R4 = 0;
R2 = R3 = R1 = 1;
C1 = C2 = C3 = C4 =1;
if(C1 == 0)
{
while(C1 == 0);
key_num = 12;
DisplayKeyNum(SMG_duanma[key_num]);
}
else if(C2 == 0)
{
while(C2 == 0);
key_num = 13;
DisplayKeyNum(SMG_duanma[key_num]);
}
else if(C3 == 0)
{
while(C3 == 0);
key_num = 14;
DisplayKeyNum(SMG_duanma[key_num]);
}
else if(C4 == 0)
{
while(C4 == 0);
key_num = 15;
DisplayKeyNum(SMG_duanma[key_num]);
}
}
void main()
{
while(1)
{
ScanKeysMulti();
}
}7、外部中断的基本操作
训练题目:
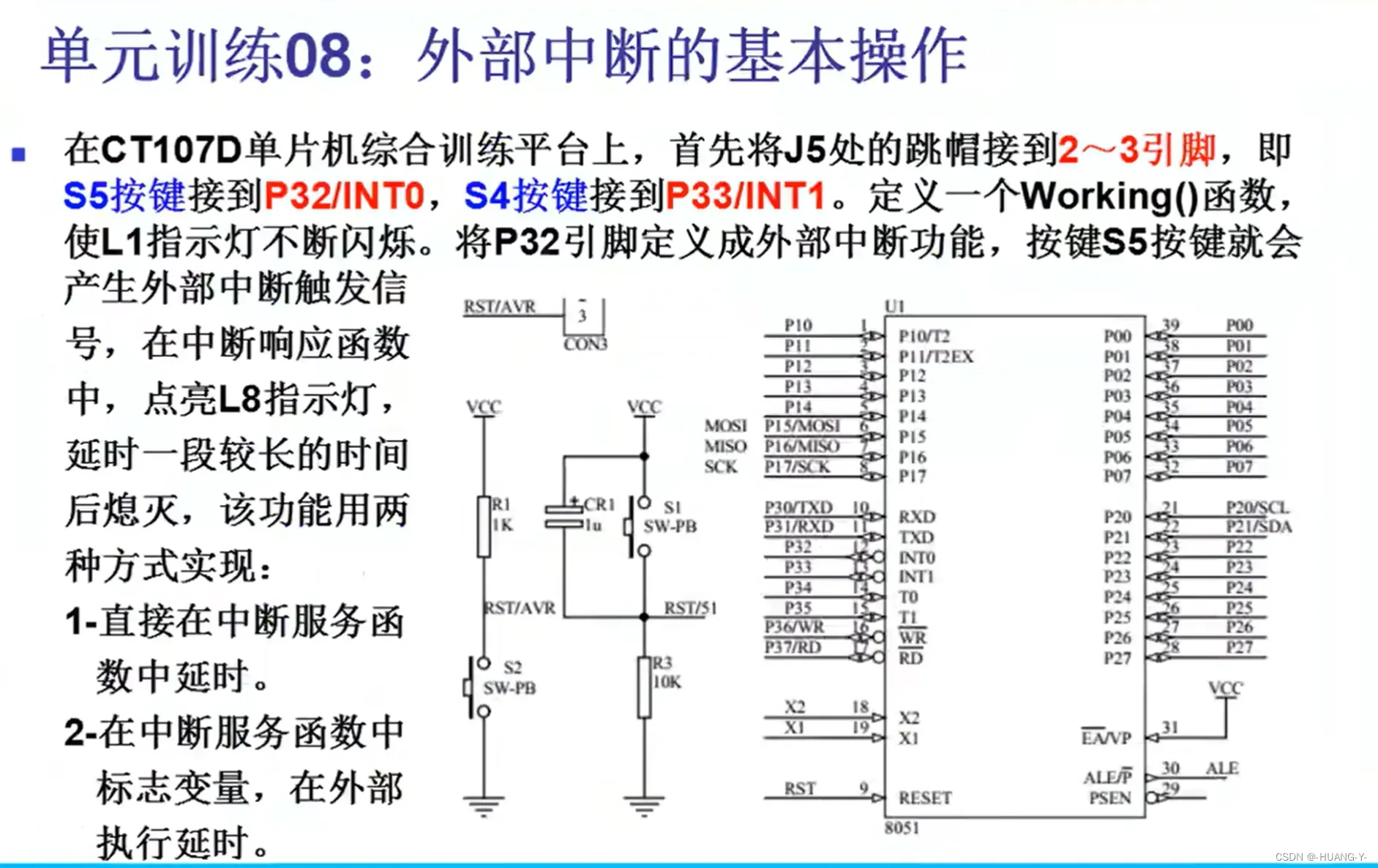
原理:
51有五个中断源,分为三类:外部中断、定时/计数器中断、串口中断。自然优先级如下图所示。

中断系统结构如下图。在这里我们只考虑外部中断。(以INT0为例)
EA:类似总开关。置1打开。
IT0:置1为下降沿触发,置0为低电平触发。
EX0:置1为外部中断0打开。
IE0:外部中断标志位
每个寄存器都可以位寻址,即只控制一位变化即可。
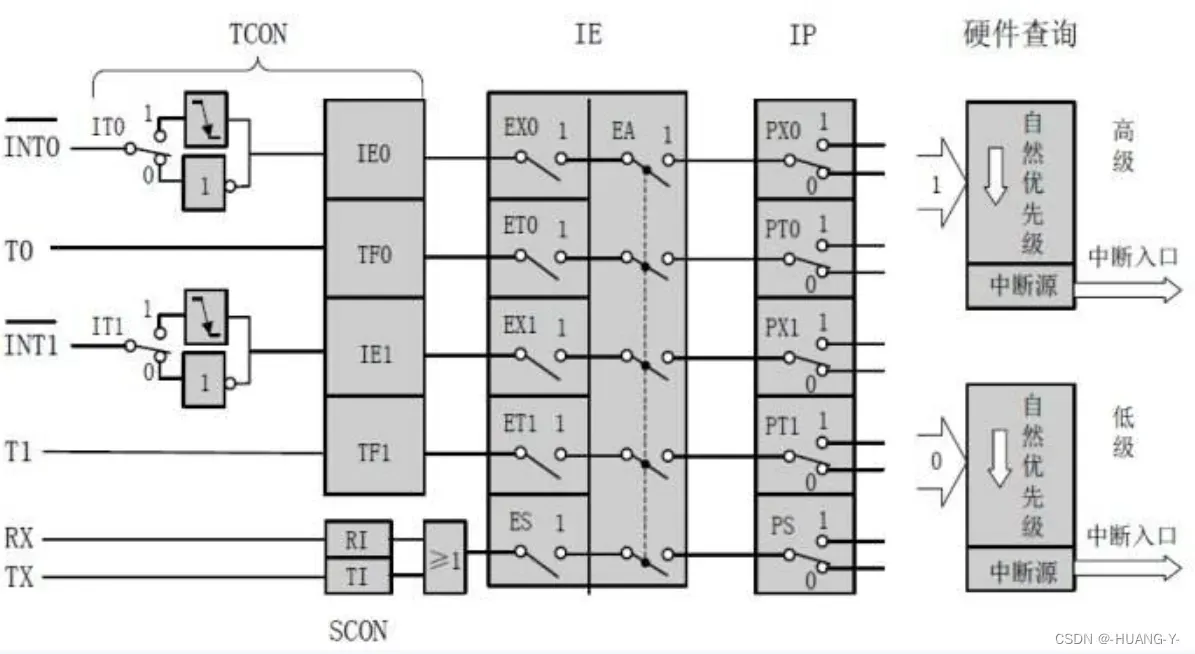
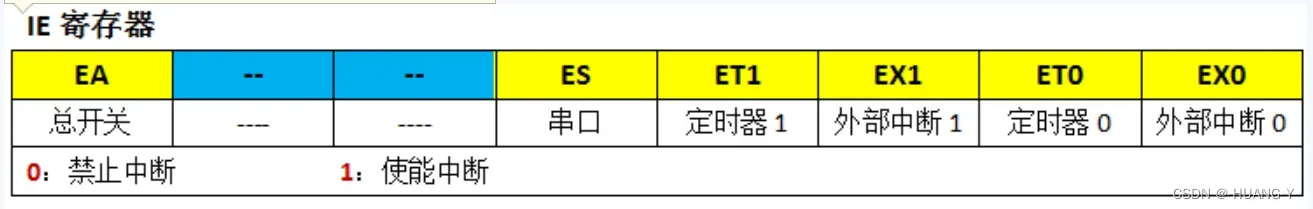
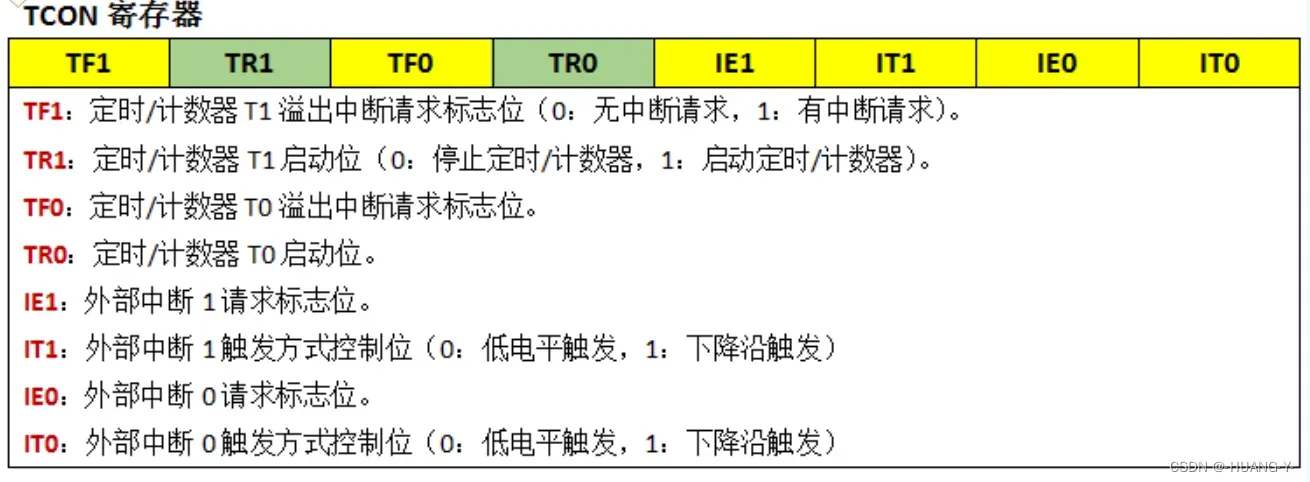
中断代码分为两部分:中断初始化函数,中断服务函数(注意中断序号)。

中断函数里尽量少写功能
整体代码实现:
#include "reg52.h"
sbit L1 = P0^0;
sbit L8 = P0^7;
void Delay(unsigned int t)
{
while(t--);
while(t--);
while(t--);
}
void SelectHC573()
{
P2 = (P2 & 0x1f) | 0x80;
}
void Working()
{
SelectHC573();
L1 = 0;
Delay(60000);
L1 = 1;
Delay(60000);
}
//================================
void Init_INT0()//外部中断初始化
{
IT0 = 1;
EX0 = 1;
EA = 1;
}
unsigned char stat_int = 0;
void ServiceINT0() interrupt 0
{
stat_int = 1;//通过状态变量控制中断中的功能
}
void LEDINT()
{
if(stat_int == 1)
{
L8 = 0;
Delay(60000);
Delay(60000);
Delay(60000);
Delay(60000);
Delay(60000);
Delay(60000);
L8 = 1;
}
stat_int = 0;
}
//================================
void main()//这种方式中断只会在L1熄灭后进行
{
Init_INT0();
while(1)
{
Working();
LEDINT();
}
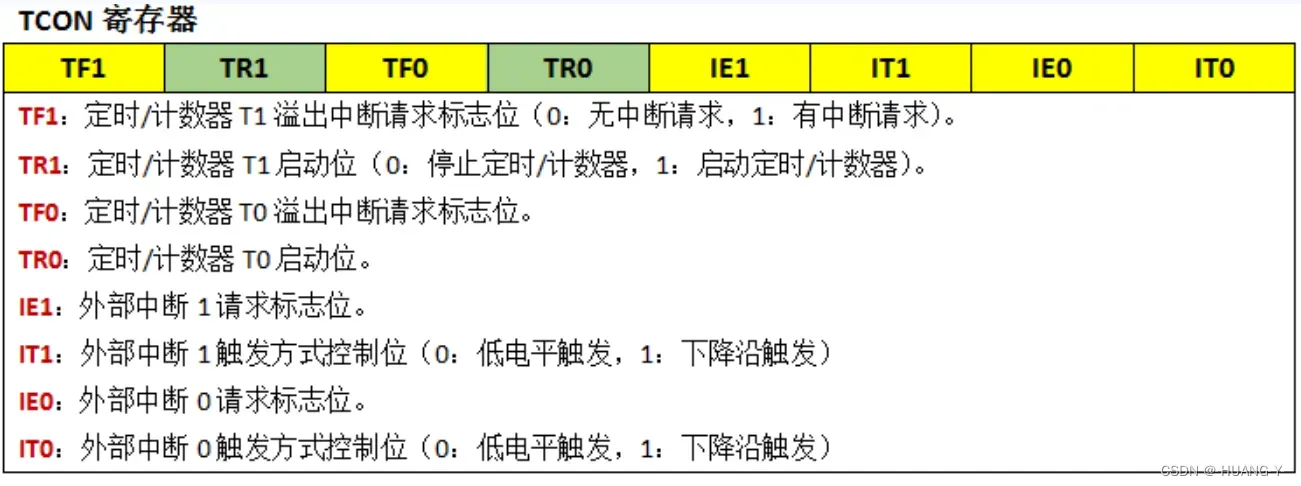
}8、定时器中断
训练题目:

原理:
定时/计数器的最基本工作原理是进行计数。作为定时器时,计数信号的来源选择周期性的内部时钟脉冲;用作计数器时,计数信号的来源选择非周期性的外部输入信号。
51单片机有两个定时/计数器T0和T1,为16位加法计数器,由低8位TLx和高8位THx两个寄存器组成,最大计数值为65535个计数脉冲。
该加1计数器的计数脉冲来源有2个:
<1> 系统时钟振荡器输出的12分频。
<2> T0或T1引脚输入的外部脉冲信号。
每接收到一个计数脉冲,计数器就会加1,当计数值累计至全为1时,再输入一个计数脉冲,计数器便会溢出回零,并且计数器的溢出是TCON寄存器的TF0或TF1位置1,同时向内核提出中断请求。
假设单片机的外部晶振为12MHz,那么,经过12分频后输入计数器的计数脉冲为1MHz,即每个脉冲的周期为1us。因此定时器T0的16位工作模式最大的定时时间为65535us,65.5ms。
1.计数初值寄存器THx和TLx的配置,确定初值的代码(以10ms为例):

2.TMOD寄存器的定时器功能配置,必须整个字节操作:

3.TCON中断标志寄存器(以定时器0为例):
ET0 = 1;
EA = 1;
TR0 = 1;//定时器特有,注意
整体代码实现:
#include "reg52.h"
sbit L1 = P0^0;
sbit L8 = P0^7;
void SelectHC573()
{
P2 = (P2 & 0x1f) | 0x80;
}
//=================================
void InitTimer0()
{
TMOD = 0x01;
TH0 = (65535 - 50000) / 256;
TL0 = (65535 - 50000) % 256;
ET0 = 1;
EA = 1;
TR0 = 1;
}
unsigned char count = 0;
void ServiceTimer0() interrupt 1
{
TH0 = (65535 - 50000) / 256;
TL0 = (65535 - 50000) % 256;//每次溢出清零,所以中断函数内部要重新赋值
count++;
if(count % 10 == 0)//用倍数的性质,减少了一个全局变量
{
L1 = ~L1;
}
if(count == 100)
{
L8 = ~L8;
count = 0;
}
}
//================================
void main()
{
SelectHC573();
InitTimer0();
while(1)
{
}
}9、定时器扩展应用
训练内容:

整体代码实现:
#include "reg52.h"
sbit S4 = P3^3;
sbit S5 = P3^2;
unsigned char t_m = 0;
unsigned char t_s = 0;
unsigned char t_005s = 0;
unsigned char code SMG_NoDot[18] =
{0xc0,0xf9,0xa4,0xb0,0x99,0x92,0x82,0xf8,
0x80,0x90,0x88,0x80,0xc6,0xc0,0x86,0x8e,
0xbf,0x7f};
void SelectHC573(unsigned char channel)
{
switch(channel)
{
case 4:
P2 = (P2 & 0x1f) | 0x80;
break;
case 5:
P2 = (P2 & 0x1f) | 0xa0;
break;
case 6:
P2 = (P2 & 0x1f) | 0xc0;
break;
case 7:
P2 = (P2 & 0x1f) | 0xe0;
break;
}
}
void DisplaySMG_Bit(unsigned char value, unsigned char pos)
{
P0 = 0xff;
SelectHC573(6);
P0 = 0x01 << pos;
SelectHC573(7);
P0 = value;
}
void DelaySMG(unsigned int t)
{
while(t--);
}
void DisplayTime()
{
DisplaySMG_Bit(SMG_NoDot[t_005s%10],7);//从0开始数
DelaySMG(500);
DisplaySMG_Bit(SMG_NoDot[t_005s/10],6);
DelaySMG(500);
DisplaySMG_Bit(SMG_NoDot[16],5);
DelaySMG(500);
DisplaySMG_Bit(SMG_NoDot[t_s%10],4);
DelaySMG(500);
DisplaySMG_Bit(SMG_NoDot[t_s/10],3);
DelaySMG(500);
DisplaySMG_Bit(SMG_NoDot[16],2);
DelaySMG(500);
DisplaySMG_Bit(SMG_NoDot[t_m%10],1);
DelaySMG(500);
DisplaySMG_Bit(SMG_NoDot[t_m/10],0);
DelaySMG(500);
}
void InitTimer0()
{
TMOD = 0x01;
TH0 = (65535 - 50000) / 256;
TL0 = (65535 - 50000) % 256;
ET0 = 1;
EA = 1;
TR0 = 1;
}
void ServiceTimer0() interrupt 1
{
TH0 = (65535 - 50000) / 256;
TL0 = (65535 - 50000) % 256;
t_005s++;
if(t_005s == 20)
{
t_s++;
t_005s = 0;
if(t_s == 60)
{
t_m++;
t_s = 0;
}
if(t_m == 99)
{
t_m = 0;
}
}
}
void DelayK(unsigned char t)
{
while(t--);
}
void ScanKeys()
{
if(S4 == 0)
{
DelayK(100);
if(S4 == 0)//消抖
{
TR0 = ~TR0;
while(S4 == 0)//防止一个语句经历多次循环
{
DisplayTime();//注意要加显示语句,否则什么都不做会熄灭
}
}
}
if(S5 == 0)
{
DelayK(100);
if(S5 == 0)
{
t_005s = 0;
t_s = 0;
t_m = 0;
while(S5 == 0)
{
DisplayTime();
}
}
}
}
void main()
{
InitTimer0();
while(1)
{
DisplayTime();
ScanKeys();
}
}
10、PWM
训练题目:

原理:
占空比:高电平在一个周期的比例。
PWM常用于电机、舵机、灯光亮暗等。注意时高电平还是低电平导通。
1ms = 1000 us
整体代码实现:
#include "reg52.h"
sbit L1 = P0^0;
sbit S7 = P3^0;
void SelectHC573()
{
P2 = (P2 & 0x1f) | 0x80;
}
//============定时相关的函数================
unsigned char count = 0;
unsigned char pwm_duty = 0;
void InitTimer0()
{
TMOD = 0x01;
TH0 = (65535 - 100) / 256;
TL0 = (65535 - 100) % 256;
ET0 = 1;
EA = 1;
}
void ServiceTimer0() interrupt 1
{
TH0 = (65535 - 100) / 256;//10ms分为100份,来控制占空比
TL0 = (65535 - 100) % 256;
count++;
if(count == pwm_duty)
{
L1 = 1;
}
else if(count == 100)
{
L1 = 0;
count = 0;
}
}
//============按键相关的函数================
void Delay(unsigned int t)
{
while(t--);
}
unsigned char stat = 0;//用状态变量来控制不同分支
void ScanKeys()
{
if(S7 == 0)
{
Delay(100);
if(S7 == 0)
{
switch(stat)
{
case 0:
L1 = 0;
TR0 = 1;//按键按下定时器才启动
pwm_duty = 10;
stat = 1;
break;
case 1:
pwm_duty = 50;
stat = 2;
break;
case 2:
pwm_duty = 90;
stat = 3;
break;
case 3:
L1 = 1;//灯熄灭
TR0 = 0;//定时器关闭
stat = 0;
break;
}
while(S7 == 0);//防止多次循环检测
}
}
}
void main()
{
SelectHC573();
L1 = 1;
InitTimer0();
while(1)
{
ScanKeys();
}
}
11、串口通信基础
训练题目:
串口通信基本原理:
分类:

SPI,IIC,UART均属串行通信。串口通信常指UART。
串行通信分类:
单工(只能接收)、半双工(接收、发送,只有一个信道)、全双工(接收、发送、两个信道)。
串行通信方式:
同步(一个时钟,数据块传输)、异步(多个时钟,波特率一致,数据帧传输)。
波特率:串口每秒传输的位数。
代码实现的前提准备:
波特率取决于定时器1的溢出率,即每溢出一次,串口就发送一次数据。
而定时器1通常我们采用工作模式2(8位自动重装),当计数到最大值溢出时,TH1的值会自动重装到TL1。
SMOD:0时(默认值)波特率正常,1时波特率翻倍。

∴TH1 = 0xfd;TL1 = 0xfd;
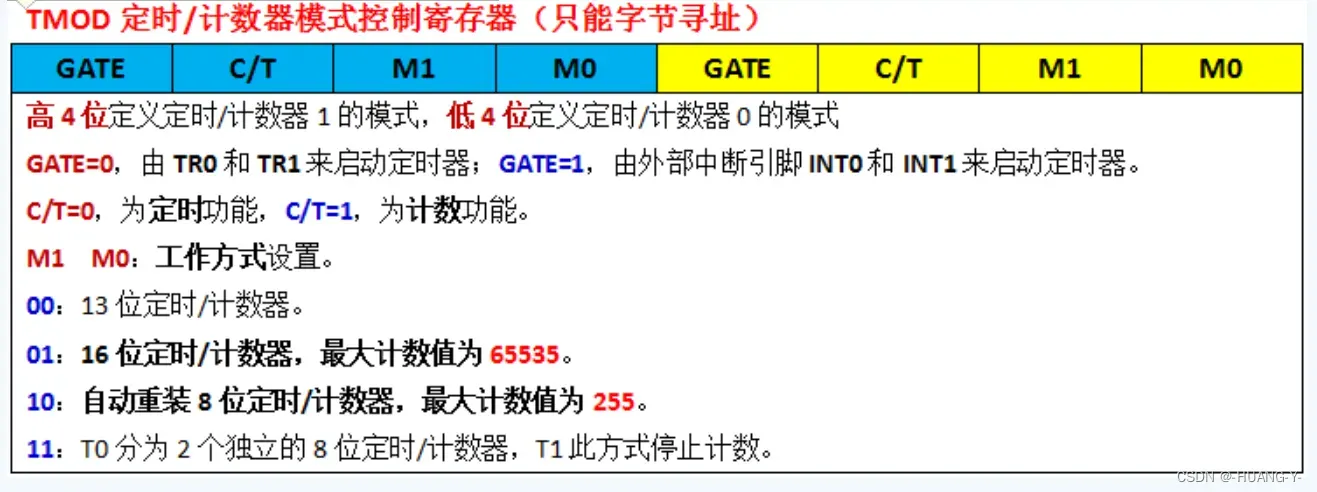
此处使用的是定时器1(自动重装),所以控制高四位,应为0010 0000,即TMOD = 0x20;
SCON寄存器:
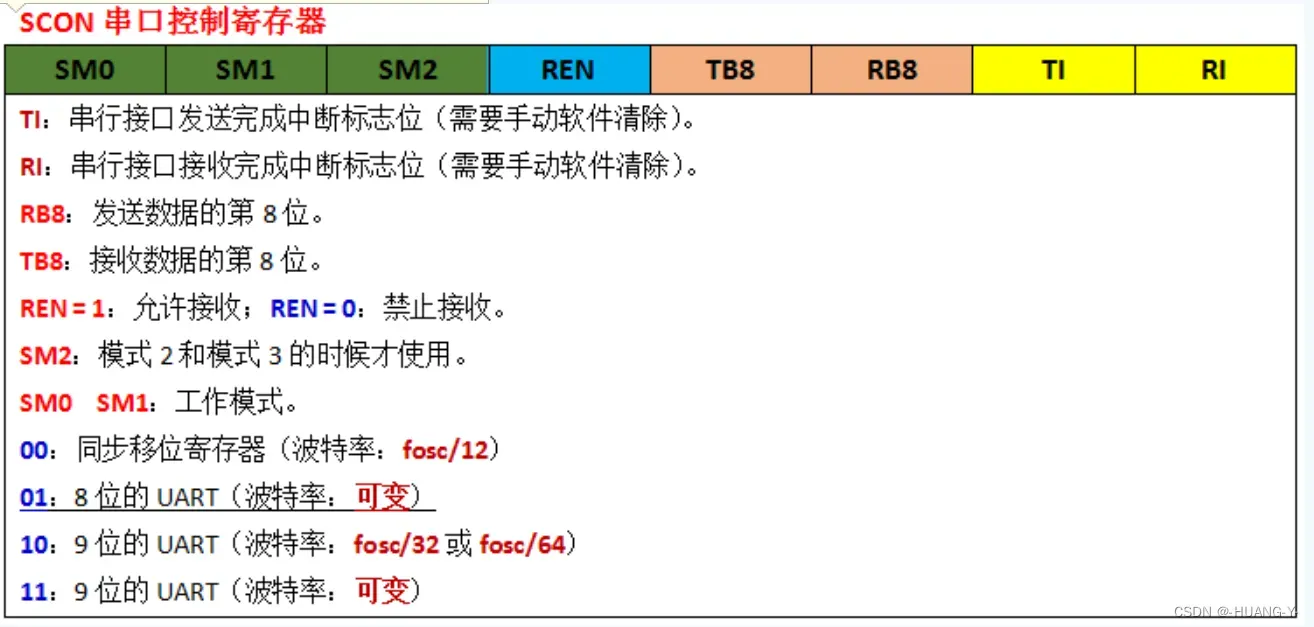
SM0,SM1:01(八位波特率UART,常用);TB8,RB8功能不常用,置零即可。
所以,SCON = 0x50;
sfr AUXR = 0x8e;
AUXR = 0x00;(蓝桥杯板子要用)
ES = 1;(串口开关)
EA = 1;(总开关)
串口初始化函数:
sfr AUXR = 0x8e;
void InitUart()
{
TMOD = 0x20;
TH1 = 0xfd;
TL1 = 0xfd;
TR1 = 1;
SCON = 0x50;
AUXR = 0x00;
ES = 1;
EA = 1;
}RI(接收完成中断标志),TI(发送完成中断标志)。都需手动清零。
SBUF寄存器:
SBUF = 数据/变量;(发送)
变量 = SBUF ;(接收)
中断函数用interrupt 4
整体代码实现:
#include "reg52.h"
sfr AUXR = 0x8e;
unsigned char urdat;
void SendByte(unsigned char dat);
void InitUart()
{
TMOD = 0x20;
TH1 = 0xfd;
TL1 = 0xfd;
TR1 = 1;
SCON = 0x50;
AUXR = 0x00;
ES = 1;
EA = 1;
}
void ServiceUart() interrupt 4
{
if(RI == 1)
{
RI = 0;
urdat = SBUF;
SendByte(urdat + 1);
}
}
void SendByte(unsigned char dat)
{
SBUF = dat;
while(TI == 0);
TI = 0;
}
void main()
{
InitUart();
SendByte(0x5a);
SendByte(0xa5);
while(1);
}12、串口通信进阶
训练题目:

整体代码:
#include "reg52.h"
sfr AUXR = 0x8e;
void SelectHC573(unsigned char channel)
{
switch(channel)
{
case 4:
P2 = (P2 & 0x1f) | 0x80;
break;
case 5:
P2 = (P2 & 0x1f) | 0xa0;
break;
case 6:
P2 = (P2 & 0x1f) | 0xc0;
break;
case 7:
P2 = (P2 & 0x1f) | 0xe0;
break;
case 0:
P2 = (P2 & 0x1f) | 0x00;//保持锁存器的值不变
break;
}
}
void InitSystem()
{
SelectHC573(5);
P0 = 0x00;
SelectHC573(4);
P0 = 0xff;
}
//=======================================
void InitUart()
{
TMOD = 0x20;
TH1 = 0xfd;
TL1 = 0xfd;
TR1 = 1;
SCON = 0x50;
AUXR = 0x00;
ES = 1;
EA = 1;
}
unsigned char command = 0x00;
void ServiceUart() interrupt 4
{
if(RI == 1)
{
command = SBUF;
RI = 0;
}
}
void SendByte(unsigned char dat)
{
SBUF = dat;
while(TI == 0);
TI = 0;
}
void SendString(unsigned char *str)//字符串的发送
{
while(*str != '\0')
{
SendByte(*str++);
}
}
//=======================================
void Working()
{
if(command != 0x00)
{
switch(command & 0xf0)
{
case 0xa0:
P0 = (P0 | 0x0f) & (~command | 0xf0);//前者保证高四位不变,低四位熄灭;后者控制低四位
command = 0x00;
break;
case 0xb0:
P0 = (P0 | 0xf0) & ((~command << 4)| 0x0f);//类似
command = 0x00;
break;
case 0xc0:
SendString("The System is Running...\r\n");
command = 0x00;
break;
}
}
}
void main()
{
InitSystem();
InitUart();
SendString("Welcome to XMF system!\r\n");
while(1)
{
Working();
}
}
13、存储器映射(可跳)
训练题目:

注:由于占用了P3.6,所以存储器映射与矩阵键盘不能复用。
整体代码实现:
#include "reg52.h"
#include "absacc.h"//
void Delay(unsigned int t)
{
while(t--);
while(t--);
}
void LEDRuning()
{
XBYTE[0x8000] = 0xf0;//
Delay(60000);
Delay(60000);
XBYTE[0x8000] = 0x0f; //
Delay(60000);
Delay(60000);
XBYTE[0x8000] = 0xff;//
Delay(60000);
Delay(60000);
}
void SMGRunning()
{
unsigned char i;
for(i = 0; i < 8; i++)
{
XBYTE[0xc000] = 0x01 << i;//
XBYTE[0xe000] = 0x00; //
Delay(60000);
Delay(60000);
}
XBYTE[0xe000] = 0xff;//
Delay(60000);
Delay(60000);
}
void main()
{
while(1)
{
LEDRuning();
SMGRunning();
}
}14、 综合设计
训练题目:
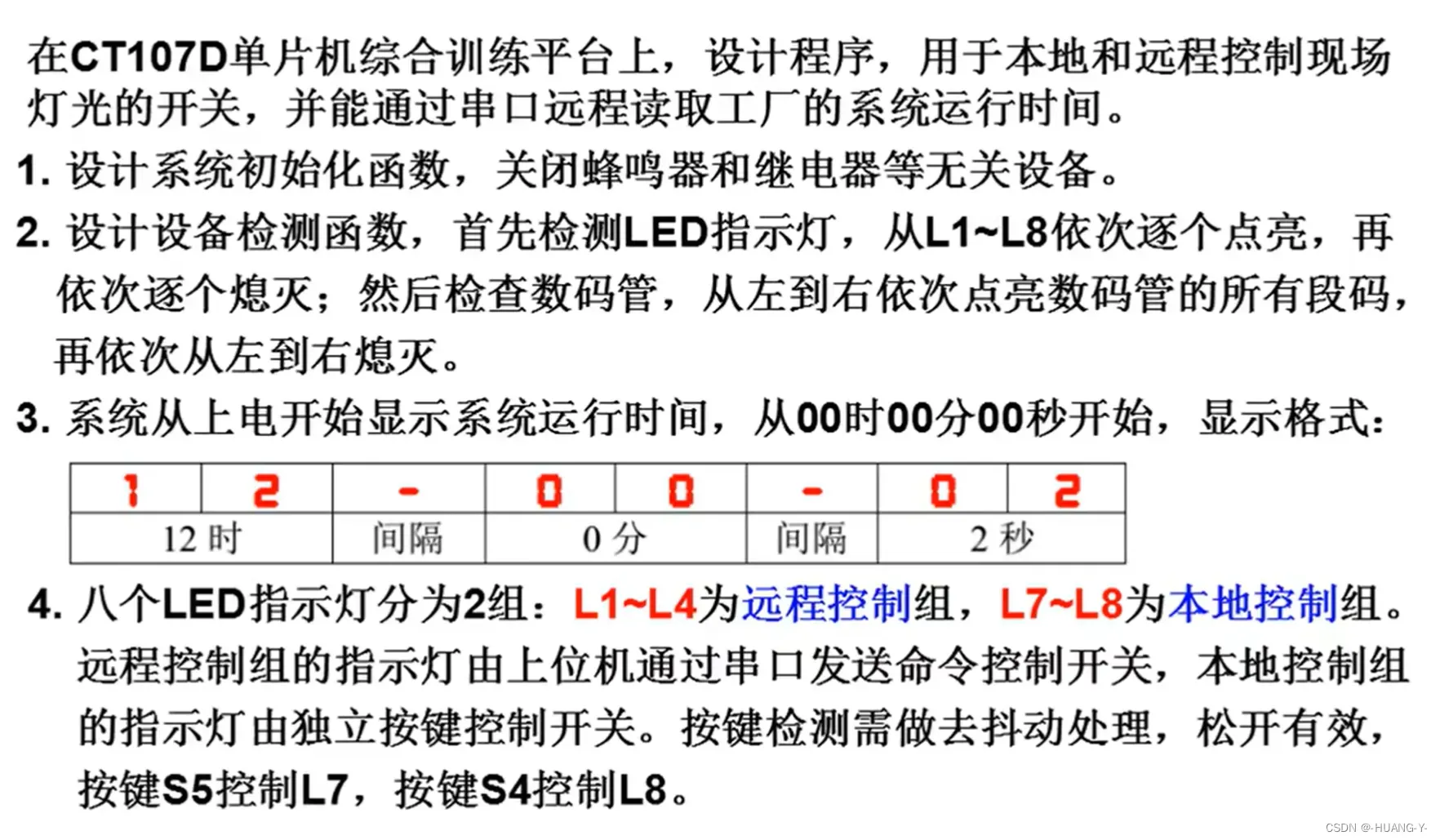
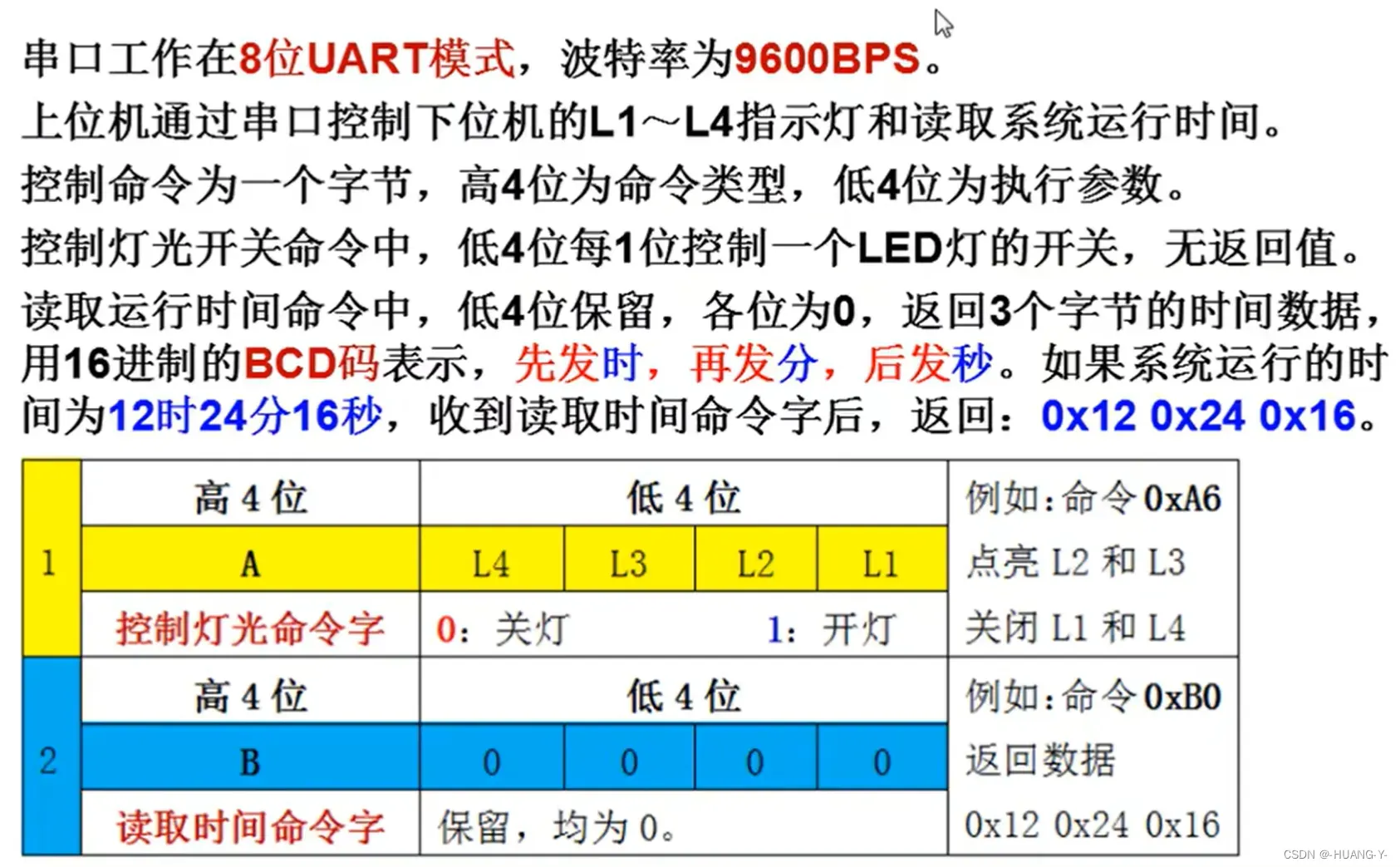
设计思路:
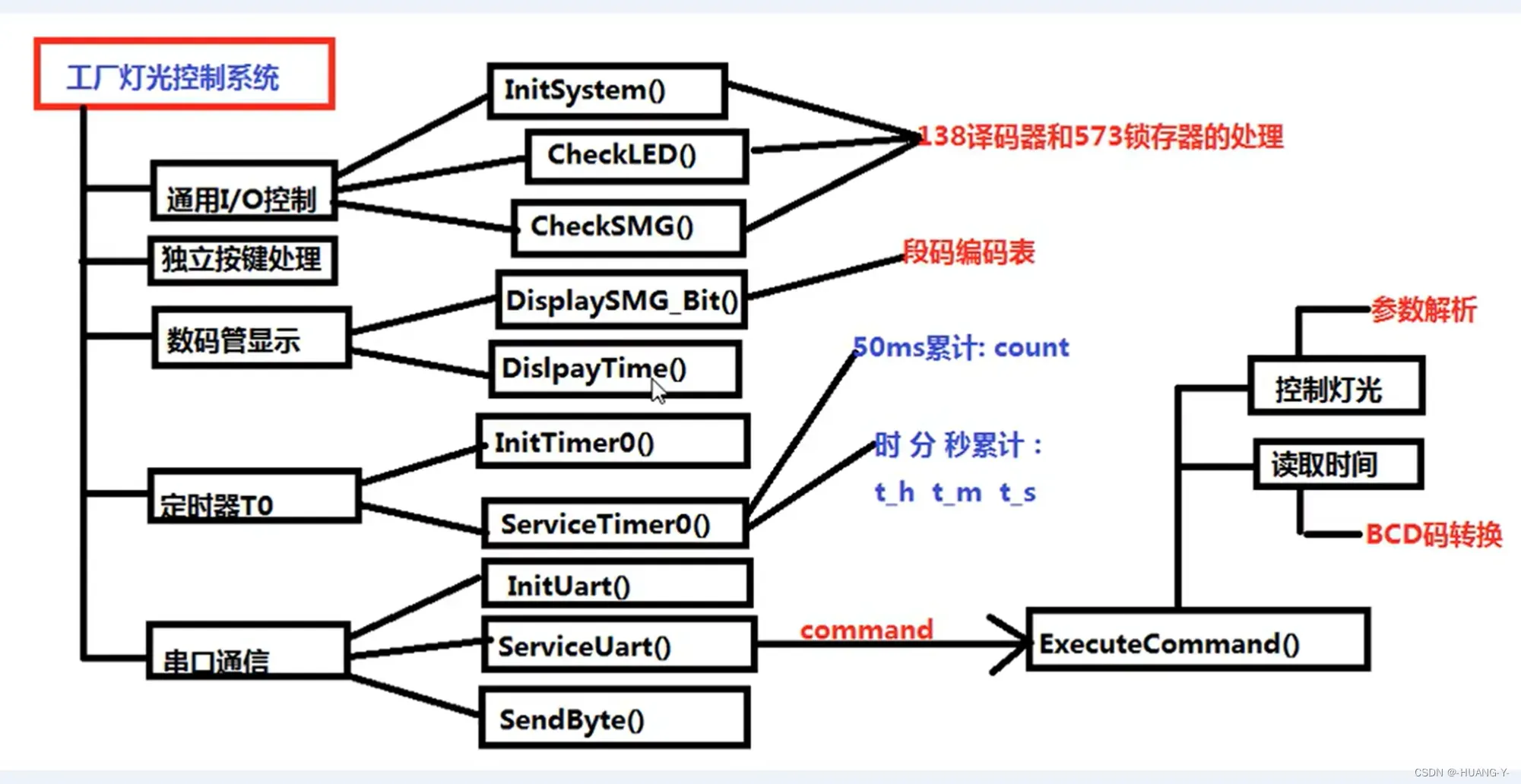
整体代码实现:

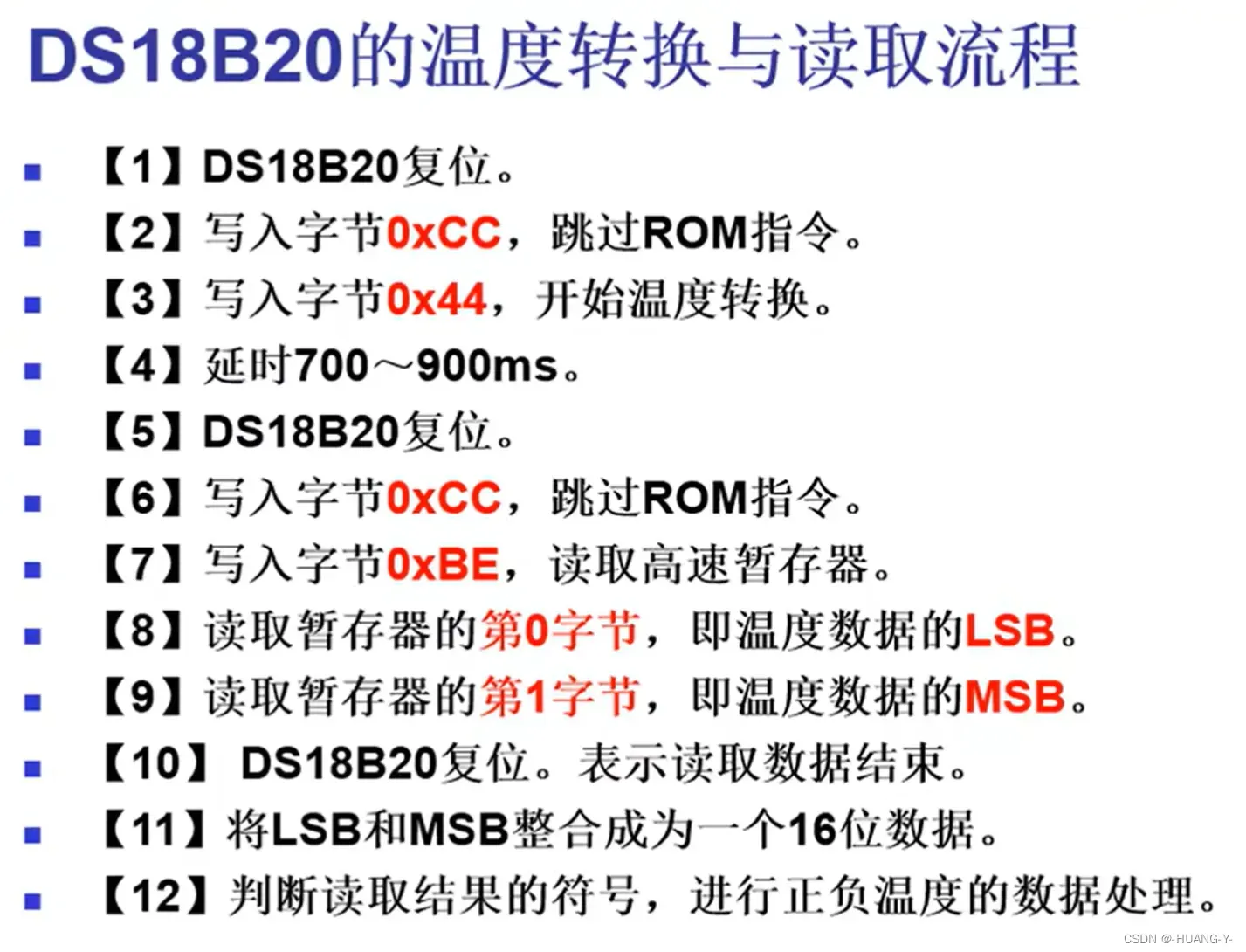
15、单总线温度传感器DS18B20
训练题目:

原理:
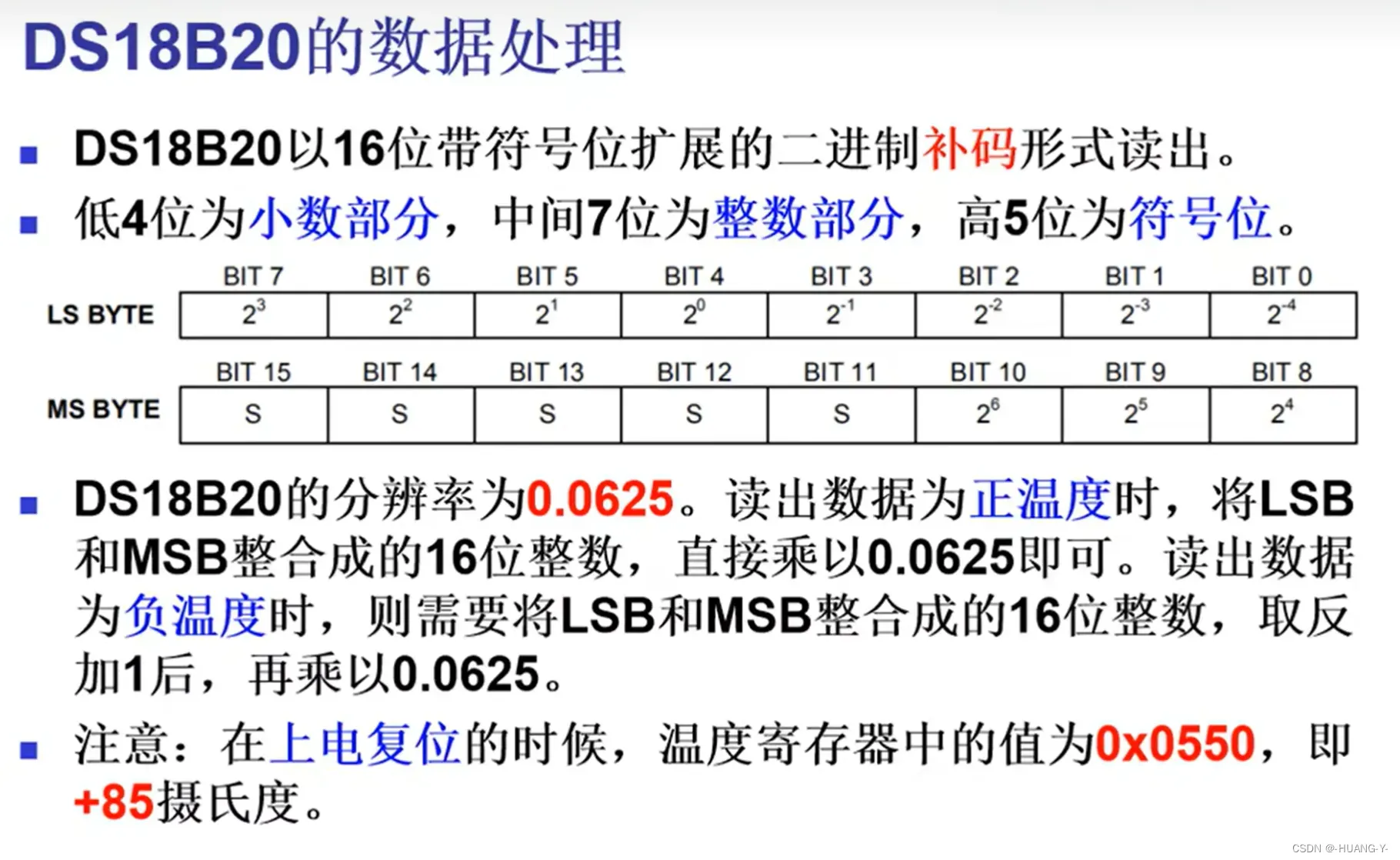
整体代码实现 :
带小数的温度显示:




蓝桥杯一般只保留整数部分。
注意:
1、onewire.h中需要声明初始化、读、写函数。
2、onewire.c中所有延时函数都需要乘10(近似即可),因为驱动代码时钟周期是12T,而单片机是1T的。
3、因为是MM模式,所以记得引脚上的帽子移动。
4、拷贝onwire.c和onewire.h到工程文件中。
16、头文件与模块设计
原理:
头文件.h:
#indef 头文件名//即if not define
#define 头文件名
函数声明 常量(如数组code)
#endif头文件.c:正常写函数。
记得把头文件.c加入进来。
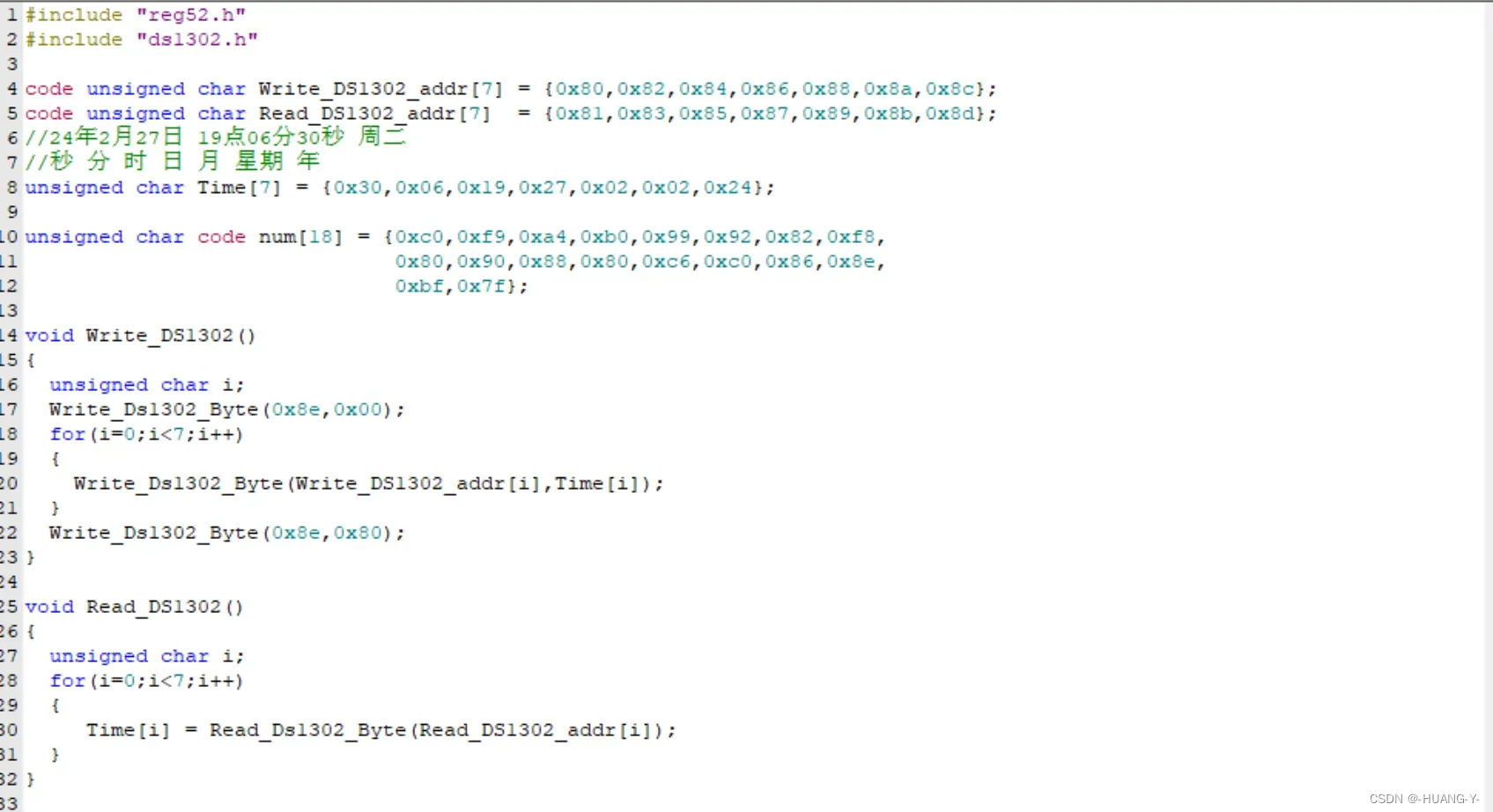
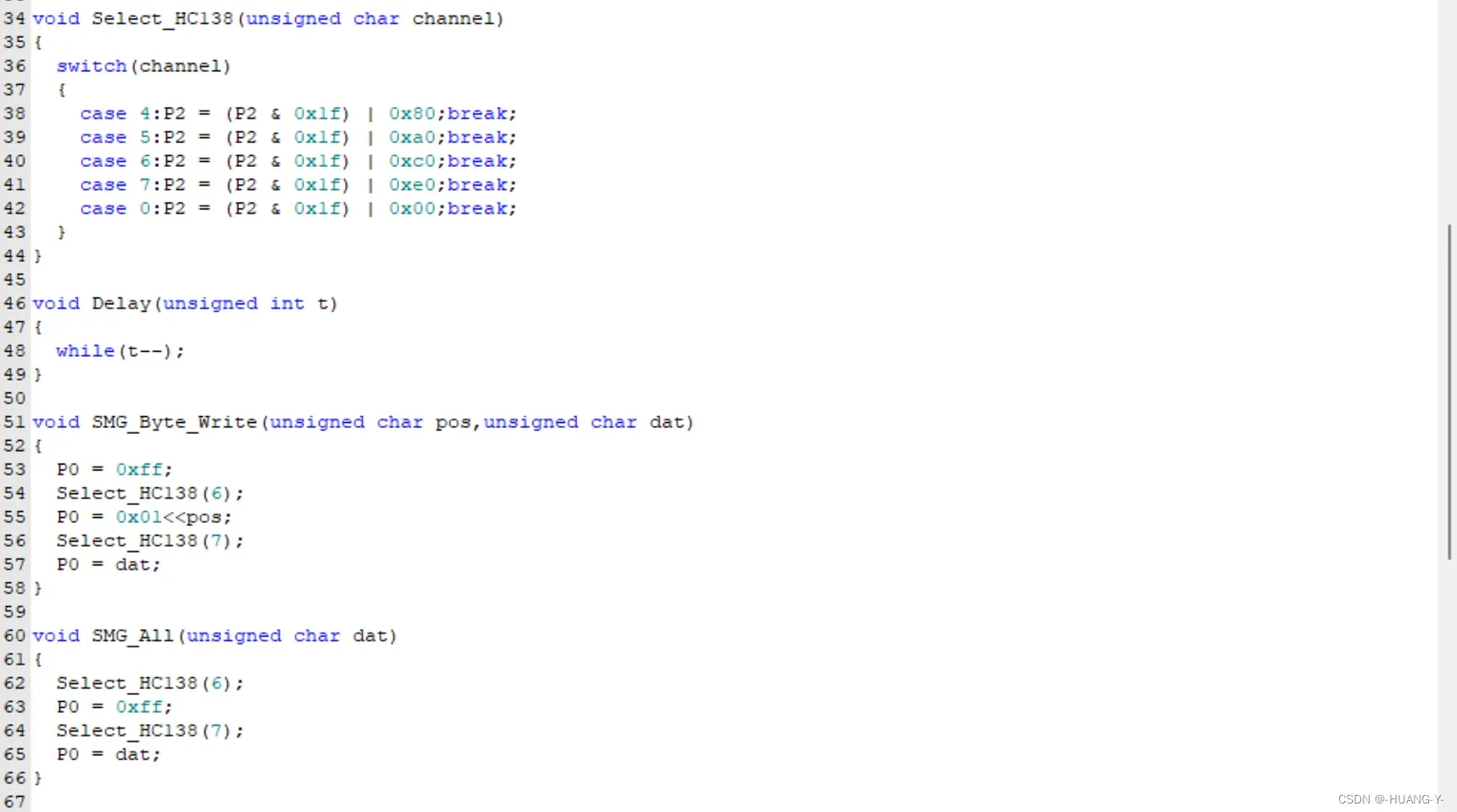
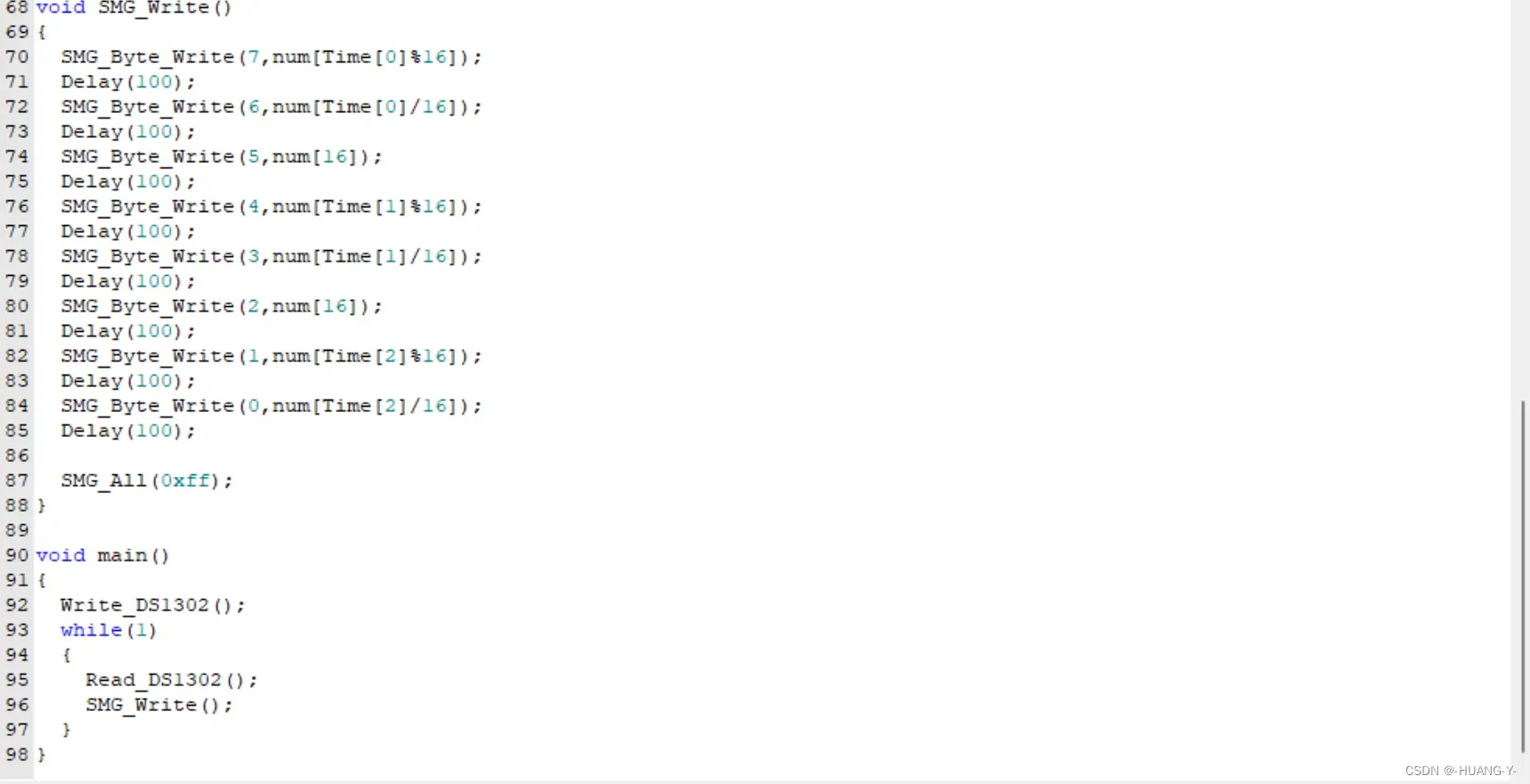
17、DS1302时钟
原理:
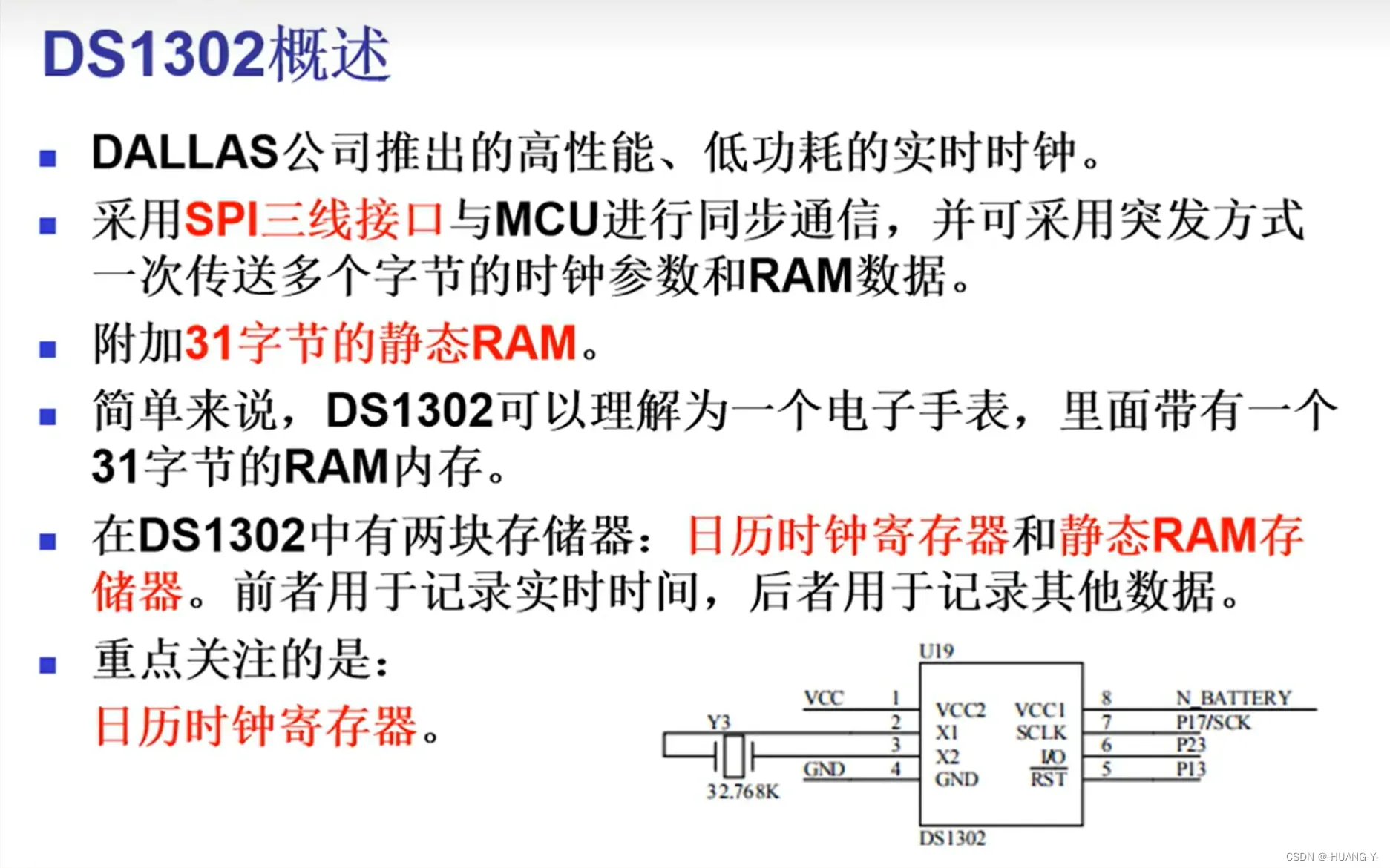
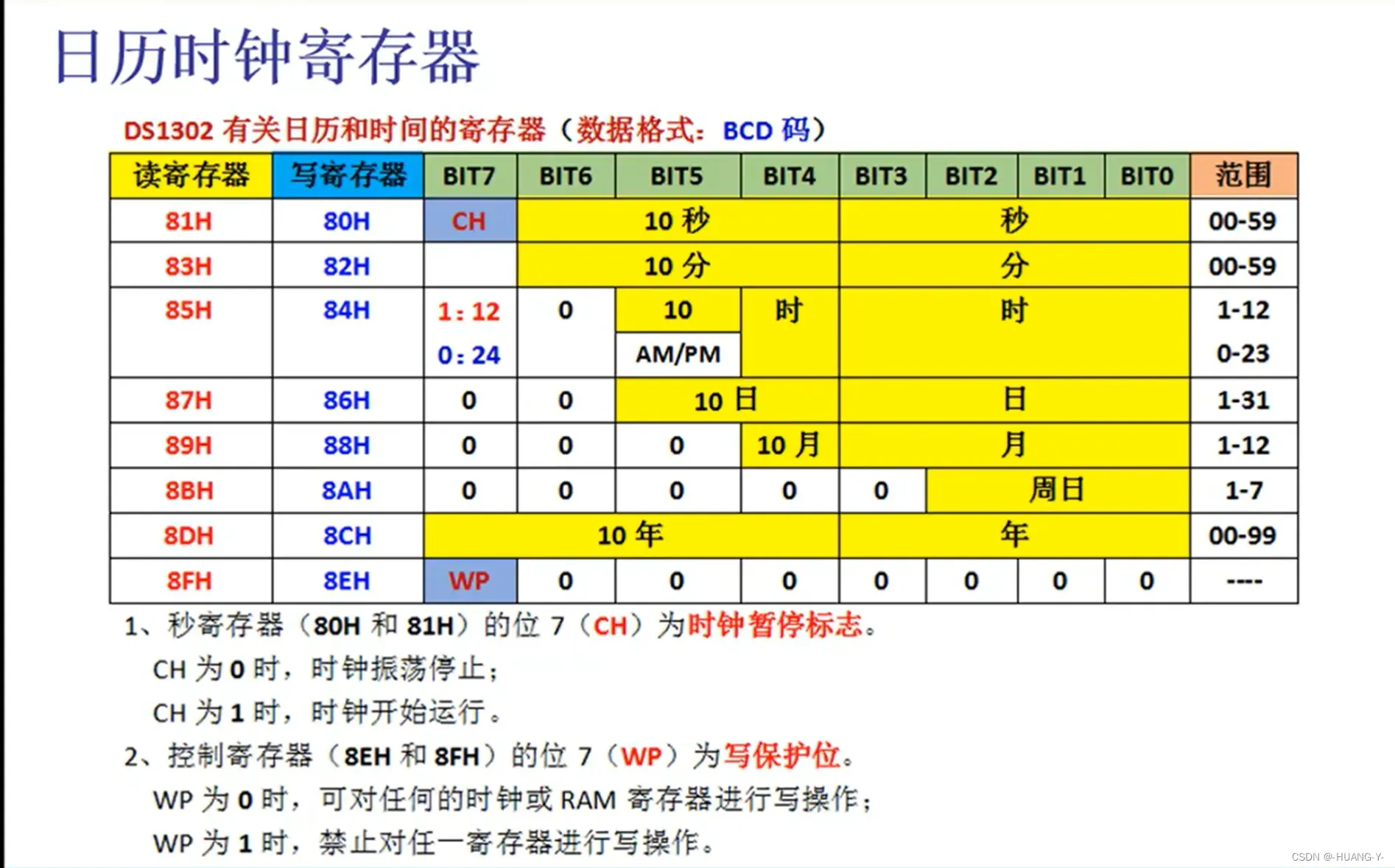
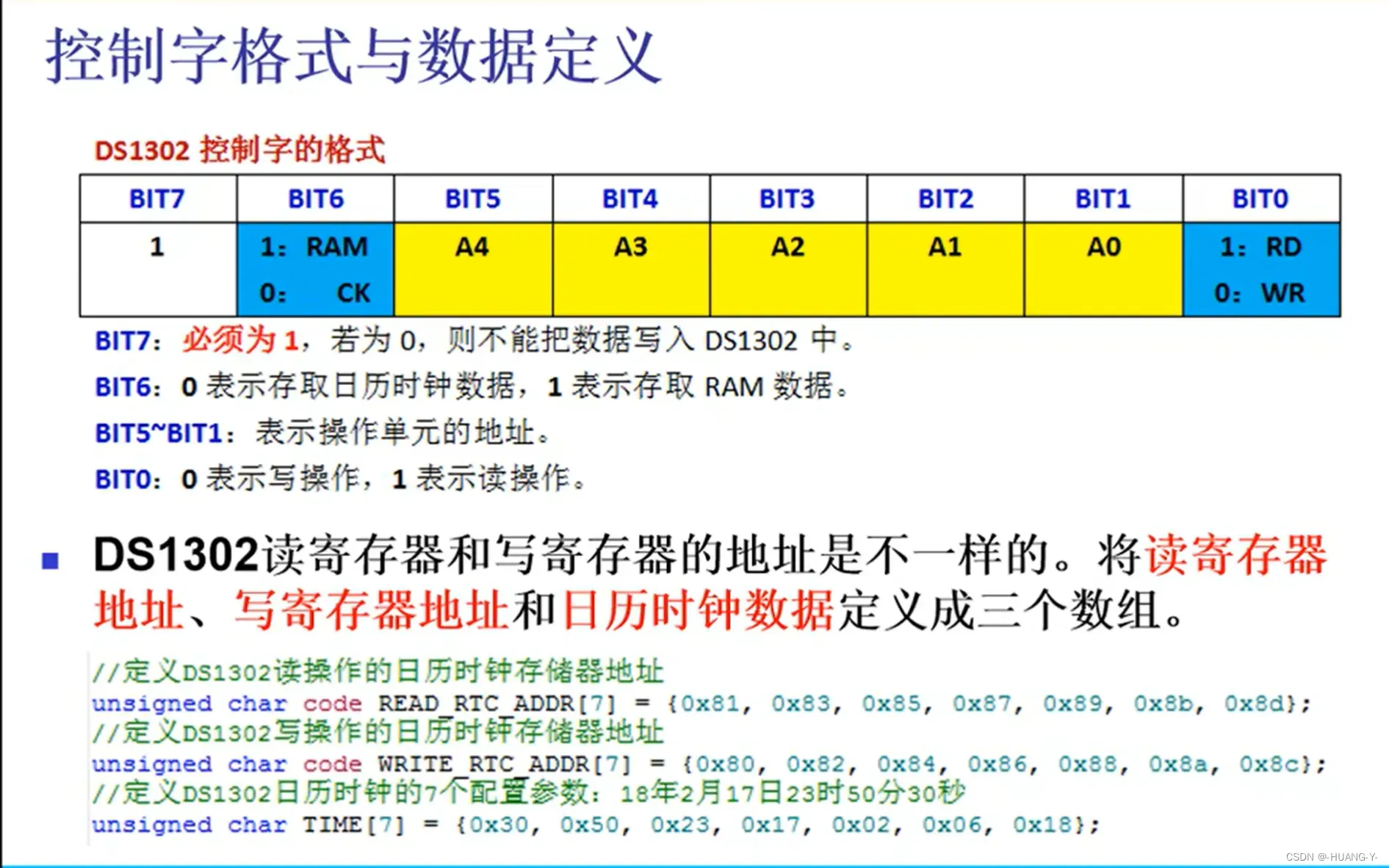
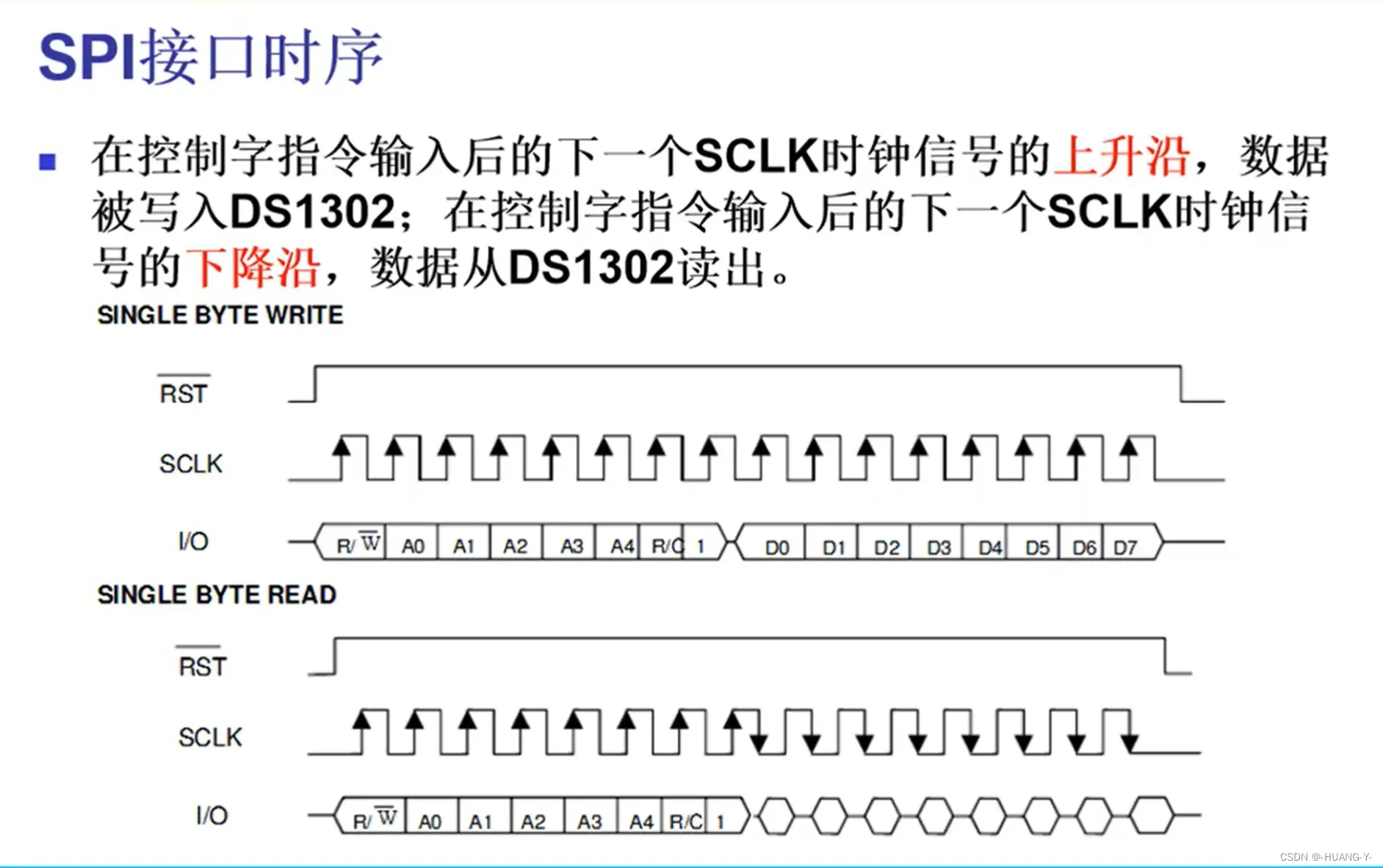
SPI和IIC时序有自己的时钟线,与单片机时钟无关,所以不用修改延时函数。
整体代码实现:

18、555定时器
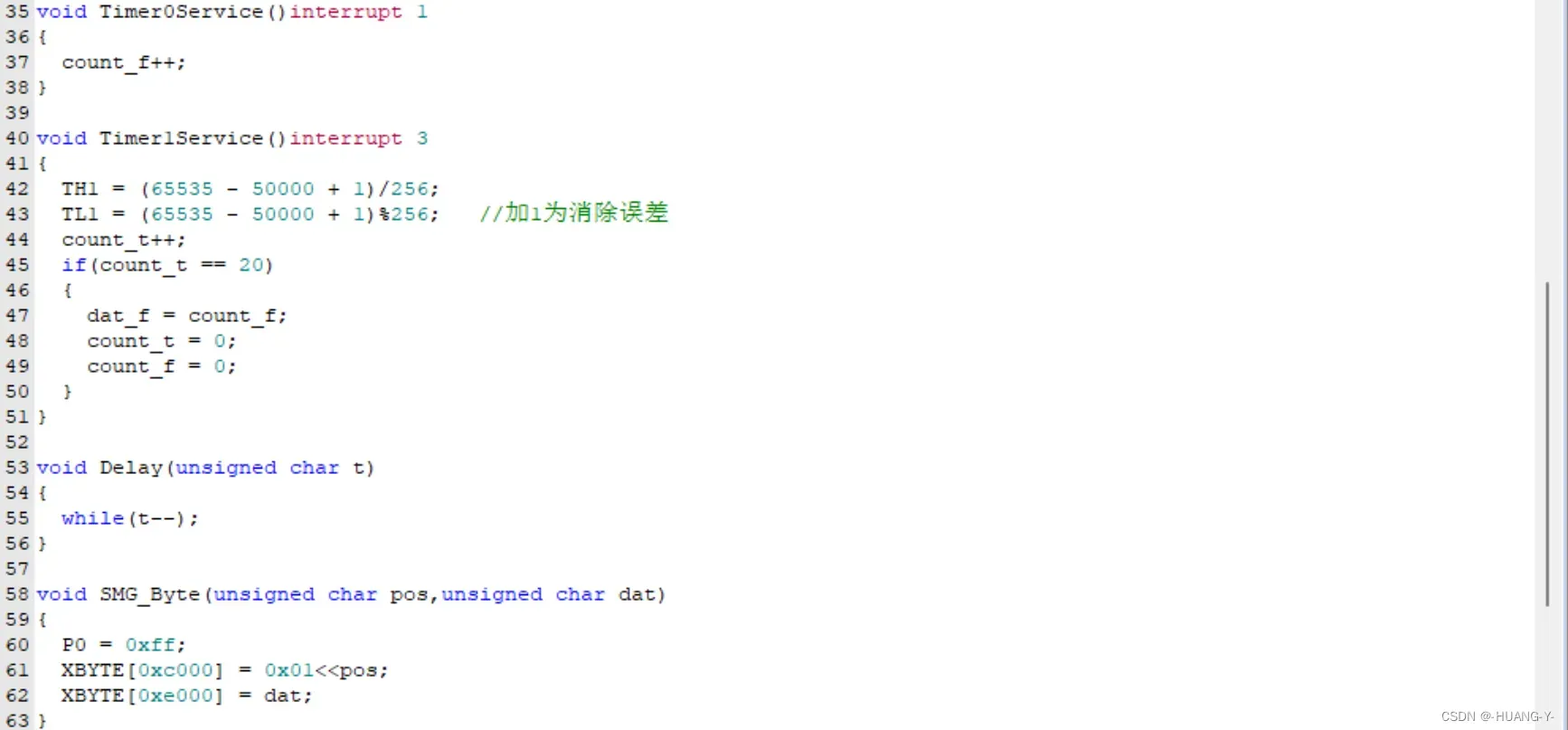
训练题目:

注意:555没有特殊的硬件操作,官方给的头文件中需注意引脚对应是否正确。
整体代码实现:



19、第零讲 倒计时系统
题目:

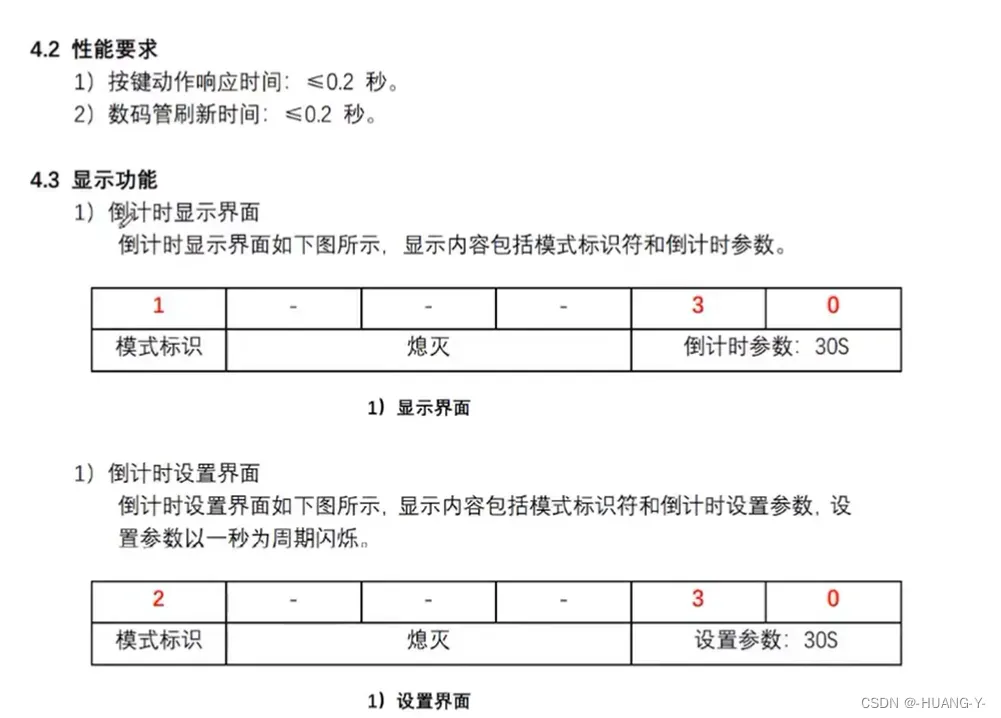


关键思路讲解:
1、因为有两个界面,分别是显示和设置界面,所以我们定义一个界面切换的全局变量。且此变量能确保SegBuf[6]数组里的值互不干扰。
unsigned char Seg_Mode = 0;//0为显示,1为设置2、此题中复位功能应最后写,因为复位后的值可能为15,30,60三种值,而这三种值与S4有关。
3、显示和设置都有时间的参与,为区分两个界面,一个用变量,一个用数组。最后通过按键按下界面切换的时候将两者关联。
4、注意倒计时减到零后溢出的情况。
整体代码实现:
#include "reg52.h"
unsigned char Seg_Dula[] = {0xc0,0xf9,0xa4,0xb0,0x99,0x92,0x82,0xf8,0x80,0x90,0xff};
unsigned char Seg_Wela[] = {0x01,0x02,0x04,0x08,0x10,0x20,0x40,0x80};
//ÊýÂë¹Ü»ù±¾º¯Êý
void Seg_Disp(unsigned char wela,dula)
{
P0=0xff;
P2=P2&0x1f|0xe0;
P2&=0x1f;
P0=Seg_Wela[wela];
P2=P2&0x1f|0xc0;
P2&=0x1f;
P0=Seg_Dula[dula];
P2=P2&0x1f|0xe0;
P2&=0x1f;
}
unsigned char Key_Read(void)
{
unsigned char Key_temp;
unsigned char Key_Value;
P3 |= 0x0f;
Key_temp = P3&0x0f;
switch(Key_temp)
{
case 0x0e : Key_Value = 7; break; //S7
case 0x0d : Key_Value = 6; break; //S6
case 0x0b : Key_Value = 5; break; //S5
case 0x07 : Key_Value = 4; break; //S4
default: Key_Value = 0;
}
return Key_Value;
}
unsigned char Key_Val,Key_Down,Key_Old;
unsigned char Key_Slow_Down;
unsigned char Seg_Buf[8] = {10,10,10,10,10,10,10,10};
unsigned char Seg_Pos;
unsigned int Seg_Slow_Down;
bit openflag = 0;
bit Seg_Mode = 0;
unsigned int ms_1000 = 0;
unsigned char count = 30;
unsigned char Seg_count[] = {15,30,60};
unsigned char count_index = 1;
bit Shin_flag = 0;
unsigned int ms_500 = 0;
void Key_Proc()
{
if(Key_Slow_Down) return;
Key_Slow_Down = 1;
Key_Val = Key_Read();
Key_Down = Key_Val & (Key_Old ^ Key_Val);
Key_Old = Key_Val;
switch(Key_Down)
{
case 4:
if(Seg_Mode == 0)
{
openflag = 1;
count = Seg_count[count_index];
}
break;
case 5:
if(Seg_Mode == 0)
{
count = Seg_count[count_index];
}
break;
case 6:
Seg_Mode = ~Seg_Mode;
if(Seg_Mode == 0)
{
count = Seg_count[count_index];
}
break;
case 7:
if(Seg_Mode == 1)
{
if(++count_index == 3)
{
count_index = 0;
}
}
break;
}
}
void Seg_Proc()
{
if(Seg_Slow_Down) return;
Seg_Slow_Down = 1;
if(Seg_Mode==0)
{
Seg_Buf[0] = 1;
Seg_Buf[6] = count/10;
Seg_Buf[7] = count%10;
}
else if(Seg_Mode==1)
{
Seg_Buf[0] = 2;
if(Shin_flag == 0)
{
Seg_Buf[6] = Seg_count[count_index]/10;
Seg_Buf[7] = Seg_count[count_index]%10;
}
else
{
Seg_Buf[6] = 10;
Seg_Buf[7] = 10;
}
}
}
void Led_Proc()
{
if(count == 0)
{
P0 = 0x00;
P2 = (P2 & 0x1f) | 0x80;
}
else
{
P0 = 0xff;
P2 = (P2 & 0x1f) | 0x80;
}
}
void Timer0Init(void)
{
TMOD = 0x01;
TL0 = (65535 - 1000)%256;
TH0 = (65535 - 1000)/256;
TR0 = 1;
ET0 = 1;
EA = 1;
}
void Timer0Server() interrupt 1
{
TL0 = (65535 - 1000)%256;
TH0 = (65535 - 1000)/256;
if(++Key_Slow_Down == 10) Key_Slow_Down = 0;
if(++Seg_Slow_Down == 500) Seg_Slow_Down = 0;
if(++Seg_Pos == 8) Seg_Pos = 0;
Seg_Disp(Seg_Pos,Seg_Buf[Seg_Pos]);
if(openflag == 1)
{
if(++ms_1000 == 1000)
{
ms_1000 = 0;
if(--count == 255)
{
count = 0;
}
}
}
if(++ms_500 == 500)
{
ms_500 = 0;
Shin_flag = ~Shin_flag;
}
}
void main()
{
Timer0Init();
while (1)
{
Key_Proc();
Seg_Proc();
Led_Proc();
}
}20、第零讲 时钟系统
题目:
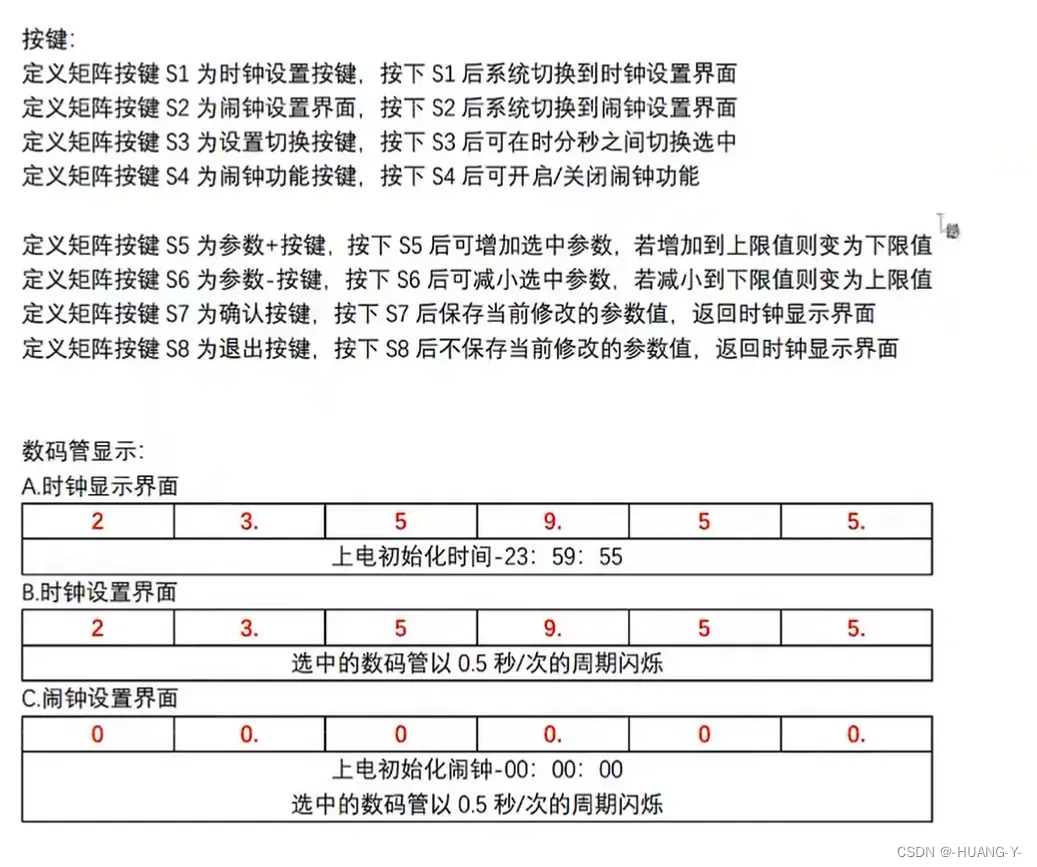
关键思路讲解:
1、显示界面和设置界面要用两个数组存储时间显示。
2、切换按键闪烁:
else if(Seg_Mode == 1)
{
Seg_Buf[0] = SegSet[0]/10;//先正常显示,保持未选中位常亮
Seg_Buf[1] = SegSet[0]%10;
Seg_Buf[3] = SegSet[1]/10;
Seg_Buf[4] = SegSet[1]%10;
Seg_Buf[6] = SegSet[2]/10;
Seg_Buf[7] = SegSet[2]%10;
switch(SegSetindex)//覆盖数据闪烁
{
case 0:
Seg_Buf[0] = ShinFlag?SegSet[0]/10:10;
Seg_Buf[1] = ShinFlag?SegSet[0]%10:10;
break;
case 1:
Seg_Buf[3] = ShinFlag?SegSet[1]/10:10;
Seg_Buf[4] = ShinFlag?SegSet[1]%10:10;
break;
case 2:
Seg_Buf[6] = ShinFlag?SegSet[2]/10:10;
Seg_Buf[7] = ShinFlag?SegSet[2]%10:10;
break;
}
}3、最大值溢出
if(Seg_Mode == 1)
{
++SegSet[SegSetindex];
if(SegSet[SegSetindex] == (SegSetindex==0?24:60))
{
SegSet[SegSetindex] = 0;
}
}4、最小值溢出 注意是255
if(Seg_Mode == 1)
{
--SegSet[SegSetindex];
if(SegSet[SegSetindex] == 255)
{
SegSet[SegSetindex] = ((SegSetindex == 0)?23:59);
}
}5、为保证闹钟开启时一直响,用标志变量控制。
6、四个LED闪烁,异或
if(ShowNum[0]<12)
{
Led ^= 0xf0;
}
else
{
Led ^= 0x0f;
}整体代码实现:
#include "reg52.h"
sfr P4 = 0xC0;
sbit A0 = P3^4;
sbit A1 = P3^5;
sbit A2 = P4^2;
sbit A3 = P4^4;
sbit BUZZ = P0^6;
/*===================???======================*/
unsigned char Seg_Dula[] = {0xc0,0xf9,0xa4,0xb0,0x99,0x92,0x82,0xf8,0x80,0x90,0xff};//?? 0~9+??
unsigned char Seg_Wela[] = {0x01,0x02,0x04,0x08,0x10,0x20,0x40,0x80};//??
unsigned char Seg_Mode = 0;//0-ÏÔʾ 1-ʱÖÓÉèÖã¬2-ÄÖÖÓÉèÖÃ
unsigned char ShowNum[] = {23,59,55};
unsigned char PointShow[8] = {0,1,0,0,1,0,0,1};
unsigned char SegSet[3];
unsigned char SegSetindex = 0;
unsigned char AlarmSetindex = 0;
unsigned int ms_500 = 0;
bit ShinFlag = 0;
unsigned int ms_1000 = 0;
unsigned char AlarmSet[] = {0,0,0};
bit AlarmFlag = 0;
unsigned char Led;
void Seg_Disp(unsigned char wela,dula,point)//
{
P0=0xff;//??
P2=P2&0x1f|0xe0;
P2&=0x1f;
P0=Seg_Wela[wela];//??
P2=P2&0x1f|0xc0;
P2&=0x1f;
if(point)
{
P0=Seg_Dula[dula] & 0x7f;
}
else
{
P0=Seg_Dula[dula];
}
P2=P2&0x1f|0xe0;
P2&=0x1f;
}
/*===================??======================*/
unsigned char Key4_Read(void) //????????
{
unsigned char Key_temp;
unsigned char Key_Value;
P3 |= 0x0f;
Key_temp = P3&0x0f;
switch(Key_temp)
{
case 0x0e : Key_Value = 7; break; //S7
case 0x0d : Key_Value = 6; break; //S6
case 0x0b : Key_Value = 5; break; //S5
case 0x07 : Key_Value = 4; break; //S4
default: Key_Value = 0;
}
return Key_Value;
}
unsigned char Key16_Read(void)
{
unsigned int Key_temp;
unsigned char Key_Value;
A3=0;
A2=1;
A1=1;
A0=1;
P3|=0X0F;
Key_temp = P3;
A3=1;
A2=0;
A1=1;
A0=1;
P3|=0X0F;
Key_temp = (Key_temp<<4) | (P3&0X0F);
A3=1;
A2=1;
A1=0;
A0=1;
P3|=0X0F;
Key_temp = (Key_temp<<4) | (P3&0X0F);
A3=1;
A2=1;
A1=1;
A0=0;
P3|=0X0F;
Key_temp = (Key_temp<<4) | (P3&0X0F);
switch(~Key_temp)
{
case 0X8000: Key_Value = 4; break; //S4
case 0X4000: Key_Value = 5; break; //S5
case 0X2000: Key_Value = 6; break; //S6
case 0X1000: Key_Value = 7; break; //S7
case 0X0800: Key_Value = 8; break; //S8
case 0X0400: Key_Value = 9; break; //S9
case 0X0200: Key_Value = 10; break; //S10
case 0X0100: Key_Value = 11; break; //S11
case 0X0080: Key_Value = 12; break; //S12
case 0X0040: Key_Value = 13; break; //S13
case 0X0020: Key_Value = 14; break; //S14
case 0X0010: Key_Value = 15; break; //S15
case 0X0008: Key_Value = 16; break; //S16
case 0X0004: Key_Value = 17; break; //S17
case 0X0002: Key_Value = 18; break; //S18
case 0X0001: Key_Value = 19; break; //S19
default: Key_Value = 0;
}
return Key_Value;
}
/*===================????======================*/
unsigned char Key_Val,Key_Down,Key_Old;//??????
unsigned char Key_Slow_Down;//????????
unsigned char Seg_Buf[8] = {10,10,10,10,10,10,10,10};//???????
unsigned char Seg_Pos;//?????????
unsigned int Seg_Slow_Down;//?????????
/*===================????======================*/
void Key_Proc()//??????
{
if(Key_Slow_Down) return;
Key_Slow_Down = 1;
Key_Val = Key16_Read();
Key_Down = Key_Val & (Key_Old ^ Key_Val);
Key_Old = Key_Val;
if(Key_Down != 0)
{
AlarmFlag = 0;
}
switch(Key_Down)
{
case 4://½øÈëʱÖÓÉèÖÃ
SegSetindex = 0;
Seg_Mode = 1;
SegSet[0] = ShowNum[0];
SegSet[1] = ShowNum[1];
SegSet[2] = ShowNum[2];
break;
case 5:
Seg_Mode = 2;
AlarmSetindex = 0;//ÄÖÖÓÉèÖÃ
break;
case 6://Çл»ÉÁ˸
if(Seg_Mode == 1)
{
if(++SegSetindex == 3)
{
SegSetindex = 0;
}
}
if(Seg_Mode == 2)
{
if(++AlarmSetindex == 3)
{
AlarmSetindex = 0;
}
}
break;
case 7:
break;
case 8://°´¼ü¼Ó
if(Seg_Mode == 1)
{
++SegSet[SegSetindex];
if(SegSet[SegSetindex] == (SegSetindex==0?24:60))
{
SegSet[SegSetindex] = 0;
}
}
if(Seg_Mode == 2)
{
++AlarmSet[AlarmSetindex];
if(AlarmSet[AlarmSetindex] == (AlarmSetindex==0?24:60))
{
AlarmSet[AlarmSetindex] = 0;
}
}
break;
case 9://°´¼ü¼õ
if(Seg_Mode == 1)
{
--SegSet[SegSetindex];
if(SegSet[SegSetindex] == 255)
{
SegSet[SegSetindex] = ((SegSetindex == 0)?23:59);
}
}
if(Seg_Mode == 2)
{
--AlarmSet[AlarmSetindex];
if(AlarmSet[AlarmSetindex] == 255)
{
AlarmSet[AlarmSetindex] = ((AlarmSetindex == 0)?23:59);
}
}
break;
case 10:
if(Seg_Mode == 1)
{
ShowNum[0] = SegSet[0];
ShowNum[1] = SegSet[1];
ShowNum[2] = SegSet[2];
Seg_Mode = 0;
}
break;
case 11:
Seg_Mode = 0;
break;
}
}
void Seg_Proc()//???????
{
if(Seg_Slow_Down) return;
Seg_Slow_Down = 1;//???????
if(Seg_Mode == 0)
{
Seg_Buf[0] = ShowNum[0]/10;
Seg_Buf[1] = ShowNum[0]%10;
Seg_Buf[3] = ShowNum[1]/10;
Seg_Buf[4] = ShowNum[1]%10;
Seg_Buf[6] = ShowNum[2]/10;
Seg_Buf[7] = ShowNum[2]%10;
}
else if(Seg_Mode == 1)
{
Seg_Buf[0] = SegSet[0]/10;//ÏÈÕý³£ÏÔʾ
Seg_Buf[1] = SegSet[0]%10;
Seg_Buf[3] = SegSet[1]/10;
Seg_Buf[4] = SegSet[1]%10;
Seg_Buf[6] = SegSet[2]/10;
Seg_Buf[7] = SegSet[2]%10;
switch(SegSetindex)//Ñ¡ÖеÄÊýÂë¹ÜÉÁ˸
{
case 0:
Seg_Buf[0] = ShinFlag?SegSet[0]/10:10;
Seg_Buf[1] = ShinFlag?SegSet[0]%10:10;
break;
case 1:
Seg_Buf[3] = ShinFlag?SegSet[1]/10:10;
Seg_Buf[4] = ShinFlag?SegSet[1]%10:10;
break;
case 2:
Seg_Buf[6] = ShinFlag?SegSet[2]/10:10;
Seg_Buf[7] = ShinFlag?SegSet[2]%10:10;
break;
}
}
else
{
Seg_Buf[0] = AlarmSet[0]/10;
Seg_Buf[1] = AlarmSet[0]%10;
Seg_Buf[3] = AlarmSet[1]/10;
Seg_Buf[4] = AlarmSet[1]%10;
Seg_Buf[6] = AlarmSet[2]/10;
Seg_Buf[7] = AlarmSet[2]%10;
switch(AlarmSetindex)//Ñ¡ÖеÄÊýÂë¹ÜÉÁ˸
{
case 0:
Seg_Buf[0] = ShinFlag?AlarmSet[0]/10:10;
Seg_Buf[1] = ShinFlag?AlarmSet[0]%10:10;
break;
case 1:
Seg_Buf[3] = ShinFlag?AlarmSet[1]/10:10;
Seg_Buf[4] = ShinFlag?AlarmSet[1]%10:10;
break;
case 2:
Seg_Buf[6] = ShinFlag?AlarmSet[2]/10:10;
Seg_Buf[7] = ShinFlag?AlarmSet[2]%10:10;
}
}
}
void Led_Proc()//LED
{
if(Seg_Mode == 0)
{
if((AlarmSet[0] == ShowNum[0])&&(AlarmSet[1] == ShowNum[1])&&(AlarmSet[2] == ShowNum[2]))
{
AlarmFlag = 1;
}
if(AlarmFlag == 1)
{
P2 = (P2 &0x1f) | 0xa0;
BUZZ = 1;
P2 = P2 &0x1f;
P2 = (P2 &0x1f) | 0x80;
P0 = Led;
P2 = P2 &0x1f;
}
else if(AlarmFlag == 0)
{
P2 = (P2 &0x1f) | 0xa0;
BUZZ = 0;
P2 = P2 &0x1f;
P2 = (P2 &0x1f) | 0x80;
P0 = 0xff;
P2 = P2 &0x1f;
}
}
}
/*===================???0????======================*/
void Timer0Init(void) //1ms???????
{
TMOD = 0x01;
TL0 = (65535 - 1000)%256;
TH0 = (65535 - 1000)/256;
TR0 = 1;
ET0 = 1;
EA = 1;
}
void Timer0Server() interrupt 1//???0??????
{
TL0 = (65535 - 1000)%256;
TH0 = (65535 - 1000)/256;
if(++Key_Slow_Down == 10) Key_Slow_Down = 0;//10ms????
if(++Seg_Slow_Down == 500) Seg_Slow_Down = 0;//500ms?????
if(++Seg_Pos == 8) Seg_Pos = 0;
Seg_Disp(Seg_Pos,Seg_Buf[Seg_Pos],PointShow[Seg_Pos]);
if(Seg_Mode == 1)
{
if(++ms_500 == 500)
{
ms_500 = 0;
ShinFlag = ~ShinFlag;
}
}
if(Seg_Mode == 2)
{
if(++ms_500 == 500)
{
ms_500 = 0;
ShinFlag = ~ShinFlag;
if(ShowNum[0]<12)
{
Led ^= 0xf0;
}
else
{
Led ^= 0x0f;
}
}
}
if(Seg_Mode == 0)
{
if(++ms_1000 == 1000)
{
ms_1000 = 0;
++ShowNum[2];
if(ShowNum[2] == 60)
{
ShowNum[2] = 0;
++ShowNum[1];
if(ShowNum[1] == 60)
{
ShowNum[1] = 0;
++ShowNum[0];
if(ShowNum[0] == 24)
{
ShowNum[0] = 0;
}
}
}
}
}
}
/*===================???======================*/
void main()
{
Timer0Init();
while (1)
{
Key_Proc();
Seg_Proc();
Led_Proc();
}
}21、第一讲 决赛试题和过渡模拟
决赛试题题目:
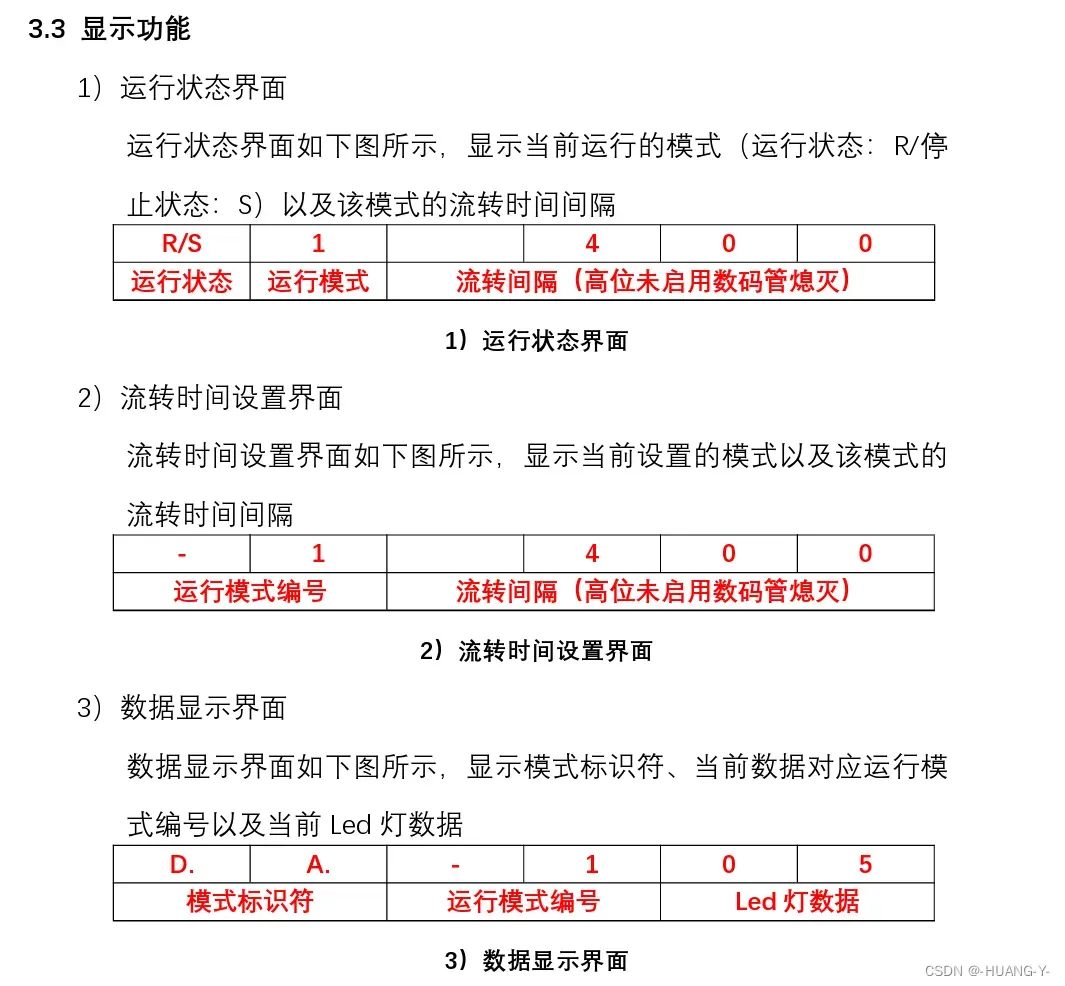


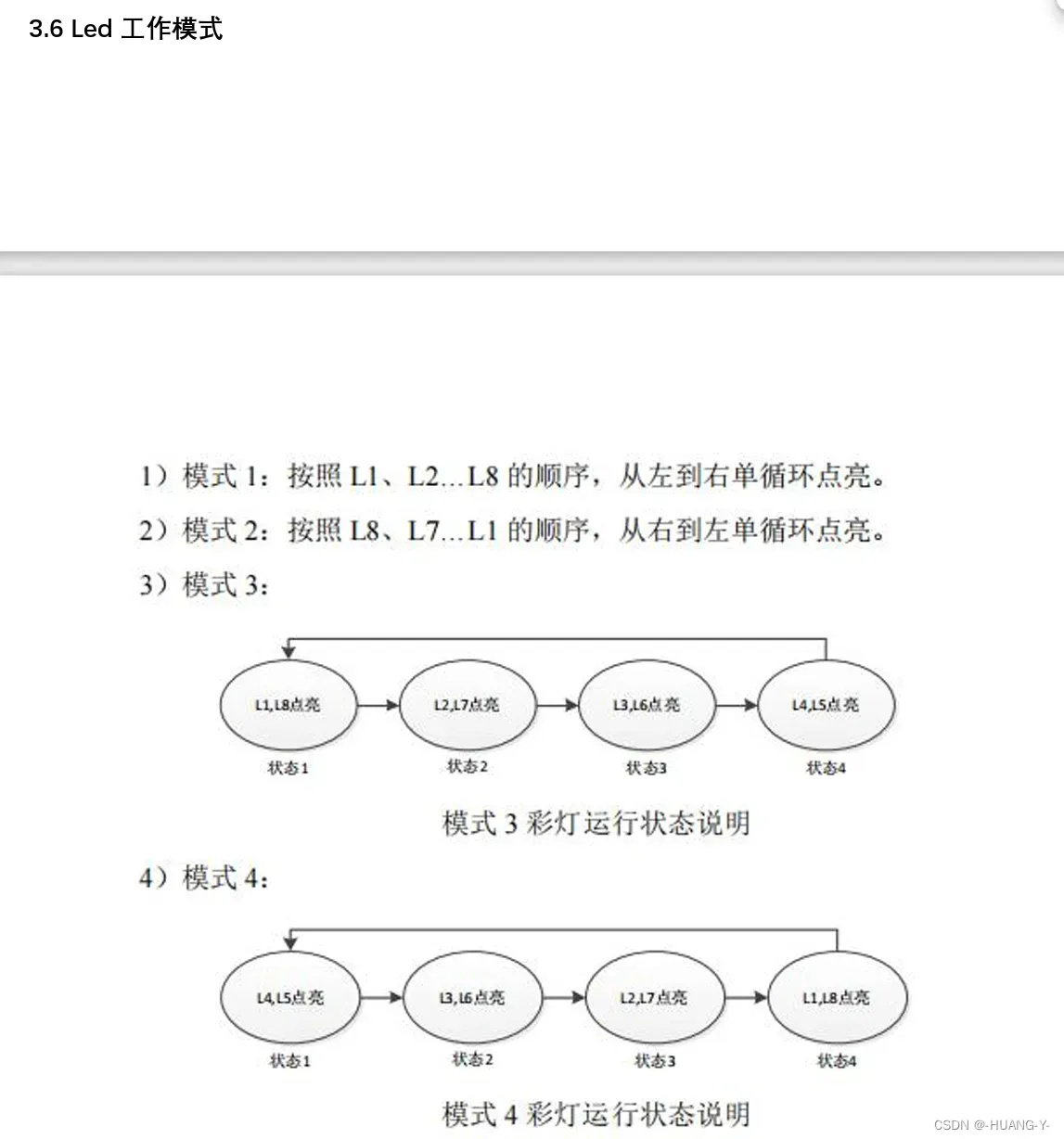
关键思路讲解:
1、控制LED的流转不要直接对P0口操作,应该P0 = LED,对变量LED进行过渡操作。
2、LED流转函数
#include "intrins.h"
Led = _crol_(Led,1);//L1-L8
Led = _cror_(Led,1);//L8-L1
3、避免模式四到模式一的变换出错
版权声明:本文为博主作者:-堂吉诃德-原创文章,版权归属原作者,如果侵权,请联系我们删除!
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/m0_73527150/article/details/135886346