目录
-
-
- 一、基本用法:
- 二、具体到题目中如何应用
-
-
- 1、数的范围
- 2、递增三元组
- 3、数组元素的目标和
-
-
一、基本用法:
lower_bound() 用于二分查找区间内第一个 大于等于某值(>= x) 的迭代器位置
upper_bound() 用于二分查找区间内第一个 大于某值(> x) 的迭代器位置
函数前两个参数分别是已被排序的序列的起始迭代器位置和结束迭代器位置,
将要被查询的范围为[ first, last ),是一个左闭右开区间的范围。
第三个参数则是需要搜寻的元素的值。最后返回查询成功的迭代器的地址。
搜索的序列当中若无合法答案返回 last 迭代器地址
注意点:
返回的是地址,不是那个要查找的数的下标。所以就注定了在这个函数的后边就要减去这个数组的首地址,即这个数组的数组名。只有这样才代表那个要查找的数字的下标
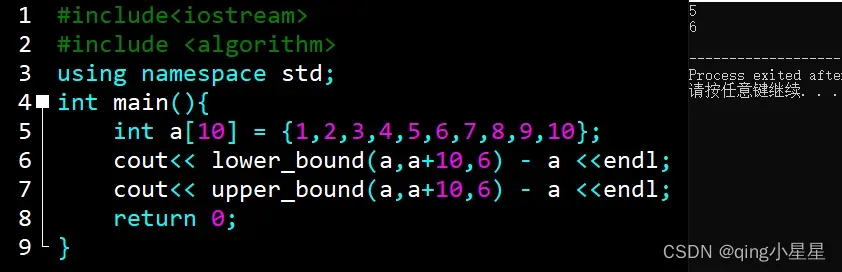
若无合法答案:返回的是[first, last)的last

二、具体到题目中如何应用
1、数的范围


AC代码:
思路分析:
这道题要分别找到区间第一个k和最后一个k。
方法是用lower_bound()函数找到第一个>=k的下标x1,这是第一个k
用upper_bound()函数找到第一个>k的下标,并-1得到x2,这是最后一个k
特判一下:如果不存在,输出-1 -1。如果存在,输出x1, x2。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int n,q,k,x1,x2,t;
int a[100010];
int main(){
cin >> n >> q;
for(int i = 0;i < n;i++){
cin >> a[i];
}
while(q--){
cin >> k;
x1 = lower_bound(a,a + n,k) - a;
x2 = upper_bound(a,a + n,k) - a - 1;
if(x1 == x2 + 1)
cout << -1 << ' ' << -1 << endl;
else
cout << x1 << ' '<< x2 << endl;
}
return 0;
}
2、递增三元组
AcWing蓝桥杯辅导课——递增三元组


AC代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
typedef long long lld;
const int N = 100005;
int a[N], b[N], c[N];
int n;
lld sum;
int main()
{
scanf("%d", &n);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
scanf("%d", &a[i]);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
scanf("%d", &b[i]);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
scanf("%d", &c[i]);
//由于二分的前提是单调序列 所以预先对a b c排序 直接sort
sort(a + 1, a + 1 + n);
sort(b + 1, b + 1 + n);
sort(c + 1, c + 1 + n);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
//直接用STL中的两个二分函数解决
lld x = ( lower_bound(a + 1, a + 1 + n, b[i]) - a ) - 1;
//在数组a中找比b[i]小的数
lld y = n - ( upper_bound( c + 1, c + 1 + n, b[i]) - c ) + 1;
//在数组c中找比b[i]大的数
sum += x * y;
}
printf("%lld", sum);
return 0;
}
这里分析一下为什么x, y 这样写:
x=( lower_bound(a+1, a+1+n, b[i] ) – a )-1;
①lower_bound(a + 1, a + 1 + n, b[i] ) 返回a数组中第一个大于等于b[i]的地址
② lower_bound(a + 1, a + 1 + n, b[i] ) – a 返回a数组中第一个大于等于b[i]的下标
③因为要找的是a数组中第一个小于b[i]的,所以下标应当-1
④下标从1开始,找到的下标 = 这一段的元素个数
y=n-( upper_bound(c+1,c+1+n,b[i] )-c)+1;
①upper_bound( c + 1, c + 1 + n, b[i] ) 返回c数组中第一个大于b[i]的地址
②upper_bound( c + 1, c + 1 + n, b[i] ) – c 返回c数组中第一个大于b[i]的下标
③n – ( upper_bound( c + 1, c + 1 + n, b[i] ) – c ) + 1
把返回的下标记作x,则后一段的元素个数为n-x+1
3、数组元素的目标和


思路分析:
既然要找两个和为x的数,那么我们可以转换成确定了一个数y的值为 ai,然后快速在 b中找出 x−y的问题。显然我们可以二分查找,算法复杂度为 O(nlogn),可以AC。
二分版AC代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int N = 100010;
int a[N], b[N];
int main()
{
int n, m, x;
cin>> n >> m >> x;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
cin>> a[i];
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++)
cin>> b[i];
for (int i = 0; a[i] < x; i++) // a[i] < x剪枝
{
int k = lower_bound(b, b+m, x-a[i]) - b;
if(a[i] + b[k] == x)
{
cout<< i << " " << k << endl;
return 0;
}
}
return 0;
}
祝大家天天快乐AC~
版权声明:本文为博主作者:qing小星星原创文章,版权归属原作者,如果侵权,请联系我们删除!
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_64565994/article/details/129966610
