-
在使用 Kubernetes Python Client 之前,需要先加载本地计算机的 Kubernetes 配置文件。可以使用
config.load_kube_config()方法来加载这个文件。这个方法默认会从本地计算机的$HOME/.kube/config文件中读取配置信息,并将其存储到 Python 运行时环境中。 -
如果 Kubernetes 配置文件存储在其他位置,或者你需要连接多个 Kubernetes 集群,可以使用以下方式来加载配置文件:
pip install kubernetes
- 指定配置文件路径:
from kubernetes import client, config
# 指定配置文件路径
config.load_kube_config(config_file='/path/to/config')
# 创建 Kubernetes API 客户端
v1 = client.CoreV1Api()
# 获取 Pod 列表
pod_list = v1.list_pod_for_all_namespaces(watch=False)
# 遍历 Pod 列表
for pod in pod_list.items:
print(f'{pod.metadata.namespace}/{pod.metadata.name}')
使用 config.load_kube_config() 方法来加载指定路径下的 Kubernetes 配置文件。
- 指定多个配置文件:
from kubernetes import client, config
# 指定多个配置文件
config.load_kube_config(config_file=['/path/to/config1', '/path/to/config2'])
# 创建 Kubernetes API 客户端
v1 = client.CoreV1Api()
# 获取 Pod 列表
pod_list = v1.list_pod_for_all_namespaces(watch=False)
# 遍历 Pod 列表
for pod in pod_list.items:
print(f'{pod.metadata.namespace}/{pod.metadata.name}')
-
要获取某个命名空间下的 Pod 列表,可以使用 v1.list_namespaced_pod() 方法。以下是示例代码:
from kubernetes import client, config
# 加载 Kubernetes 配置
config.load_kube_config()
# 创建 Kubernetes API 客户端
v1 = client.CoreV1Api()
# 指定命名空间
namespace = 'your-namespace'
# 获取 Pod 列表
pod_list = v1.list_namespaced_pod(namespace)
# 遍历 Pod 列表
for pod in pod_list.items:
print(f'{pod.metadata.namespace}/{pod.metadata.name}')
#使用 config.load_kube_config() 方法加载 Kubernetes 配置文件,然后使用 client.CoreV1Api() 方法创建 Kubernetes API 客户端。接着,指定了要获取 Pod 列表的命名空间,并使用 v1.list_namespaced_pod(namespace) 方法获取该命名空间下的 Pod 列表。最后,遍历 Pod 列表,并输出每个 Pod 的命名空间和名称。
-
要重启一个 Pod,可以使用 v1.patch_namespaced_pod() 方法。以下是示例代码:
from kubernetes import client, config
# 加载 Kubernetes 配置
config.load_kube_config()
# 创建 Kubernetes API 客户端
v1 = client.CoreV1Api()
# 指定 Pod 的命名空间和名称
namespace = 'your-namespace'
name = 'your-pod-name'
# 重启 Pod
body = {'spec': {'containers': [{'name': 'your-container-name', 'restartCount': 0}]}}
v1.patch_namespaced_pod(name, namespace, body)
-
首先使用
config.load_kube_config()方法加载 Kubernetes 配置文件,然后使用client.CoreV1Api()方法创建 Kubernetes API 客户端。接着,指定要重启的 Pod 的命名空间和名称,并使用v1.patch_namespaced_pod(name, namespace, body)方法来重启该 Pod。 -
需要注意的是,重启 Pod 操作将会杀死该 Pod 中的容器,并重新启动一个新的容器。因此,在执行重启操作之前,请确保你已经备份了相关数据,并且已经确认该操作不会对应用程序产生不良影响。另外,需要注意在
body中指定要重启的容器名称和重启次数,以确保重启操作能够正确执行。
要删除一个 Pod,可以使用 v1.delete_namespaced_pod() 方法。以下是示例代码:
from kubernetes import client, config
# 加载 Kubernetes 配置
config.load_kube_config()
# 创建 Kubernetes API 客户端
v1 = client.CoreV1Api()
# 指定 Pod 的命名空间和名称
namespace = 'your-namespace'
name = 'your-pod-name'
# 删除 Pod
v1.delete_namespaced_pod(name, namespace)
- 使用
config.load_kube_config()方法加载 Kubernetes 配置文件,然后使用client.CoreV1Api()方法创建 Kubernetes API 客户端。接着,我们指定要删除的 Pod 的命名空间和名称,并使用v1.delete_namespaced_pod(name, namespace)方法来删除该 Pod。
需要注意的是,删除 Pod 操作是不可逆的,一旦删除了一个 Pod,将无法恢复。因此,在执行删除操作之前,请确保你已经备份了相关数据,并且已经确认该操作不会对应用程序产生不良影响。
创建一个pods
from kubernetes import client, config
config.load_kube_config(config_file='/tmp/config')
v1 = client.CoreV1Api()
api_instance = client.CoreV1Api()
namespace = 'my-test'
# 创建 Pod
pod_manifest = {
'apiVersion': 'v1',
'kind': 'Pod',
'metadata': {
'name': 'mypod'
},
'spec': {
'containers': [{
'name': 'mycontainer',
'image': 'nginx:latest',
'ports': [{
'containerPort': 80,
'hostPort': 80
}]
}]
}
}
resp = v1.create_namespaced_pod(body=pod_manifest, namespace=namespace)
print("Pod created. status='%s'" % resp.status.phase)
# 创建 Service
service_manifest = {
'apiVersion': 'v1',
'kind': 'Service',
'metadata': {
'name': 'myservice'
},
'spec': {
'selector': {
'app': 'myapp'
},
'ports': [{
'protocol': 'TCP',
'port': 80,
'targetPort': 80,
'nodePort': 30001
}],
'type': 'NodePort'
}
}
resp = api_instance.create_namespaced_service(
body=service_manifest,
namespace=namespace)
print("Service created. status='%s'" % resp)
查看某2个命名空间下的pods
from datetime import datetime
import pytz
from kubernetes import client, config
# 指定配置文件路径
config.load_kube_config(config_file='config')
# 创建 Kubernetes API 客户端
v1 = client.CoreV1Api()
namespaces = ['my-test', 'opx'] # 命名空间名称列表
# 遍历每个命名空间下的 Pod 列表
for namespace in namespaces:
pod_list = v1.list_namespaced_pod(namespace, watch=False)
# 输出命名空间名称
print(f'NAMESPACE: {namespace}')
print(f'{"NAME":30} {"READY":10} {"STATUS":15} {"RESTARTS":>12} {"AGE":>5}')
# 遍历 Pod 列表
for pod in pod_list.items:
# 获取所有容器状态信息
container_statuses = pod.status.container_statuses
if container_statuses is not None:
ready_count = 0
for status in container_statuses:
if status.ready:
ready_count += 1
if status.state.waiting is not None or status.state.terminated is not None:
pod_status = 'Error'
break
else:
pod_status = 'Running'
restart_count = container_statuses[0].restart_count if container_statuses else 0
else:
ready_count = 0
pod_status = 'Pending'
restart_count = 0
created_at = pod.metadata.creation_timestamp.timestamp()
current_time = datetime.now(pytz.utc)
age = round((current_time.timestamp() - created_at) / 3600, 1)
# 打印输出每个 Pod 的名称、状态、重启次数和年龄
print(f'{pod.metadata.name:30} {ready_count}/{len(container_statuses):<4} {pod_status:15} {restart_count:>12} {age:>3.1f}h')
# 输出分隔符
print('-' * 80)
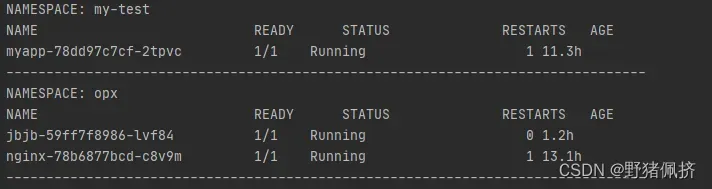
查询所有的pods
from kubernetes import client, config
# 指定配置文件路径
config.load_kube_config(config_file='/tmp/config')
# 创建 Kubernetes API 客户端
v1 = client.CoreV1Api()
# 输出表头
print(f'{"NAMESPACE":15} {"NAME":30} {"READY":10} {"STATUS":15} {"RESTARTS":10} {"AGE":15}')
# 遍历每个命名空间下的 Pod 列表
for namespace in v1.list_namespace().items:
pod_list = v1.list_namespaced_pod(namespace.metadata.name, watch=False)
# 输出命名空间名称
print(f'{namespace.metadata.name}')
# 遍历 Pod 列表
for pod in pod_list.items:
# 获取所有容器状态信息
container_statuses = [status.state for status in pod.status.container_statuses]
# 获取容器状态
if len(container_statuses) > 0:
state = container_statuses[0]
# 检查状态类型
if state.running is not None:
status = 'Running'
elif state.waiting is not None:
status = f'Waiting ({state.waiting.reason})'
elif state.terminated is not None:
status = f'Terminated ({state.terminated.reason})'
else:
status = 'Unknown'
else:
status = 'Unknown'
# 获取重启次数和年龄
restart_count = pod.status.container_statuses[0].restart_count
age = pod.metadata.creation_timestamp
# 打印输出每个 Pod 的名称、状态、重启次数和年龄
print(f' {pod.metadata.name:30} {pod.status.phase:10} {status:15} {restart_count:10} {age:15}')
# 输出命名空间的分隔符
print('+' * 80)
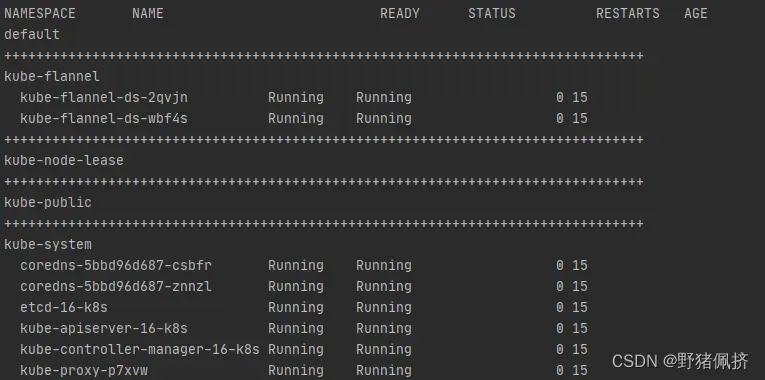
查看service
from kubernetes import client, config
# 指定配置文件路径
config.load_kube_config(config_file='/tmp/config')
# 创建 Kubernetes API 客户端
v1 = client.CoreV1Api()
namespaces = ['my-test', 'opx', 'default'] # 命名空间名称列表
# 遍历每个命名空间下的 Service 列表,并输出分隔行和表头
for namespace in namespaces:
print('-' * 80)
print(f'Namespace: {namespace}\n')
print(f'{"NAME":30} {"TYPE":10} {"CLUSTER-IP":20} {"EXTERNAL-IP(S)":20} {"PORT(S)":20} {"AGE":15}')
service_list = v1.list_namespaced_service(namespace, watch=False)
# 遍历 Service 列表
for service in service_list.items:
# 获取 Cluster IP 和 Node Port
cluster_ip = service.spec.cluster_ip or ''
node_port = ''
if service.spec.type == 'NodePort':
ports = [f'{port.node_port}/{port.protocol}' for port in service.spec.ports]
node_port = ', '.join(ports)
# 获取 External IPs
external_ips = []
if service.spec.external_name:
external_ips.append(service.spec.external_name)
if service.spec.load_balancer_ip:
external_ips.append(service.spec.load_balancer_ip)
if service.spec.load_balancer_source_ranges:
external_ips.extend(service.spec.load_balancer_source_ranges)
external_ips = ', '.join(external_ips)
# 获取年龄
age = service.metadata.creation_timestamp
# 打印输出每个 Service 的名称、类型、Cluster IP、External IPs、Ports 和年龄
print(
f'{service.metadata.name:30} {service.spec.type:10} {cluster_ip:20} {external_ips:20} {node_port:20} {age:15}')
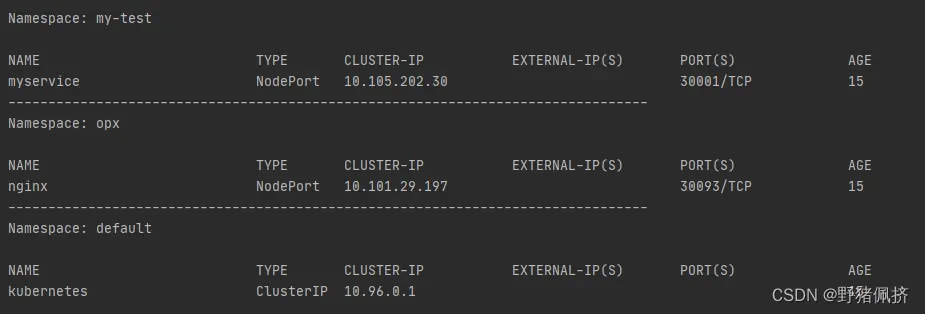
查看deployments
from datetime import datetime
import pytz
from kubernetes import client, config
# 指定配置文件路径
config.load_kube_config(config_file='config')
# 创建 Kubernetes API 客户端
api_instance = client.AppsV1Api()
namespaces = ['my-test', 'opx'] # 命名空间名称列表
# 遍历每个命名空间下的 Deployment 列表
for namespace in namespaces:
deployment_list = api_instance.list_namespaced_deployment(namespace)
# 输出命名空间名称
print(f'NAMESPACE: {namespace}')
# 打印表头
print(f'{"NAME":10} {"READY":8} {"UP-TO-DATE":12} {"AVAILABLE":10} {"AGE":>5} {"CREATED AT":26}')
# 遍历 Deployment 列表
for deployment in deployment_list.items:
name = deployment.metadata.name
ready_replicas = deployment.status.ready_replicas or 0
up_to_date_replicas = deployment.status.updated_replicas or 0
available_replicas = deployment.status.available_replicas or 0
created_at = deployment.metadata.creation_timestamp.timestamp()
age = (datetime.now(pytz.utc).timestamp() - created_at) / 3600
# 打印输出每个 Deployment 的名称、状态和年龄
print(f'{name:10} {ready_replicas}/{deployment.spec.replicas or 0:<8} {up_to_date_replicas:<12} {available_replicas:<10} {age:>3.0f}h {datetime.fromtimestamp(created_at, pytz.utc).strftime("%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S %Z%z"):26}')
# 输出分隔符
print('-' * 100)
输出
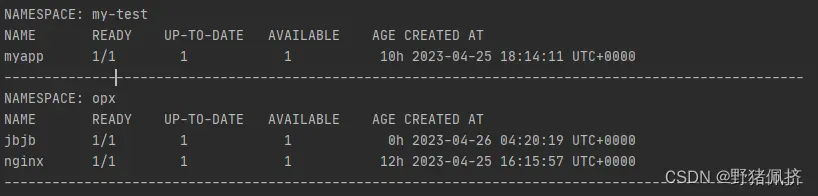
最后还是创建一个Deployment控制器。修一下上面的一个小bug.不过代码超过100行了,感谢理解
from kubernetes import client, config
config.load_kube_config(config_file='config')
v1 = client.CoreV1Api()
api_instance = client.AppsV1Api()
namespace = 'my-test'
# 创建 Deployment
deployment_manifest = {
'apiVersion': 'apps/v1',
'kind': 'Deployment',
'metadata': {
'name': 'myapp'
},
'spec': {
'replicas': 1,
'selector': {
'matchLabels': {
'app': 'myapp'
}
},
'template': {
'metadata': {
'labels': {
'app': 'myapp'
}
},
'spec': {
'containers': [{
'name': 'mycontainer',
'image': 'nginx:latest',
'ports': [{
'containerPort': 80,
'hostPort': 80
}]
}]
}
}
}
}
# 检查 Deployment 是否已存在
try:
api_instance.read_namespaced_deployment(name=deployment_manifest['metadata']['name'], namespace=namespace)
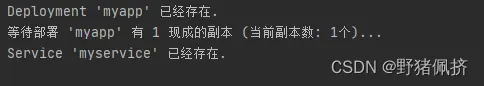
print(f"Deployment '{deployment_manifest['metadata']['name']}' 已经存在.")
except client.exceptions.ApiException as e:
if e.status == 404:
resp = api_instance.create_namespaced_deployment(body=deployment_manifest, namespace=namespace)
print("Deployment created. status='%s'" % resp.status)
else:
raise e
# 获取 Deployment 的名称和 Pod Selector
deployment_name = deployment_manifest['metadata']['name']
pod_selector = deployment_manifest['spec']['selector']['matchLabels']
# 检查 Deployment 是否成功创建
ready_replicas = 0
while ready_replicas < deployment_manifest['spec']['replicas']:
deployments = api_instance.list_namespaced_deployment(namespace=namespace).items
for deployment in deployments:
if deployment.metadata.name == deployment_name:
ready_replicas = deployment.status.ready_replicas or 0
print(
f"等待部署 '{deployment_name}' 有 {deployment_manifest['spec']['replicas']} 现成的副本 (当前副本数: {ready_replicas}个)...")
break
else:
print(f"Deployment '{deployment_name}' not found, waiting...")
# 创建 Service
service_manifest = {
'apiVersion': 'v1',
'kind': 'Service',
'metadata': {
'name': 'myservice'
},
'spec': {
'selector': pod_selector,
'ports': [{
'protocol': 'TCP',
'port': 80,
'targetPort': 80,
'nodePort': 30001
}],
'type': 'NodePort'
}
}
# 检查 Service 是否已存在
try:
v1.read_namespaced_service(name=service_manifest['metadata']['name'], namespace=namespace)
print(f"Service '{service_manifest['metadata']['name']}' 已经存在.")
except client.exceptions.ApiException as e:
if e.status == 404:
resp = v1.create_namespaced_service(body=service_manifest, namespace=namespace)
print("Service created. status='%s'" % resp)
else:
raise e
结果如下:
文章出处登录后可见!
已经登录?立即刷新
