A* 算法研究
参考
A*寻路算法详解 #A星 #启发式搜索
路径规划之 A* 算法
最短路搜索-从Dijkstra到Best-First再到A-Star
路径规划算法学习笔记(一):A*算法
A*算法寻路(C++代码实现)
《基于A*算法的自动泊车全局路径规划算法研究》
《基于ROS平台的仓储AGV系统设计及路径规划研究》
理论基础
先去读那两篇论文的笔记
前面已经学习了 Dijkstra 算法和 Best-First-Search 算法,A* 算法可以看作是这两种算法的组合
A* 算法的思想核心是:核心想是:每一步的选择既要考虑离初始点的距离,也要考虑离目标点的距
这里首先定义这两个需要考虑的距离(函数),G 用来表示当前位置离起点的距离(也就是走过的路径),H 用来表示当前位置离终点的距离(和Best-First一样的启发式函数,比如曼哈顿距离),那么 A* 算法每一步考虑的就是
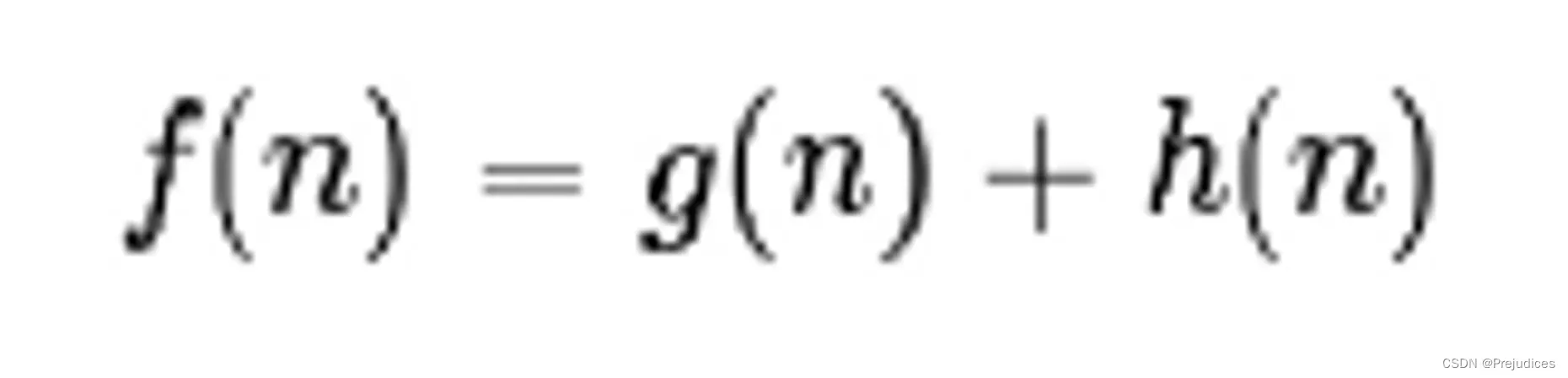
A* 算法在运算过程中,每次从优先队列中选取 f(n) 值最小(优先级最高)的节点作为下一个待遍历的节点
A* 算法使用两个集合来表示待遍历的节点,与已经遍历过的节点,这通常称之为 open_set 和close_set
完整的A*算法描述如下:
- 初始化起始节点和目标节点,并将起始节点添加到 open_set
- 初始化每个节点的代价函数值:g(n) 表示从起始节点到节点 n 的实际代价,h(n) 表示从节点 n 到目标节点的估计代价(启发函数)
- 初始化每个节点的父节点为 null
- 当 open_set 不为空时,重复以下步骤:
- 从 open_set 中选择具有最小 f(n) 值的节点,其中 f(n) = g(n) + h(n)
- 将该节点移出 open_set,并将其添加到 close_set
- 如果选择的节点是目标节点,表示找到了最短路径,可以停止搜索
- 否则,对该节点的相邻节点进行以下操作:
- 如果相邻节点不在 open_set 和 close_set 中,将其添加到 open_set ,并更新其g(n)和h(n)值以及父节点
- 如果相邻节点已经在 open_set 中,检查通过当前节点到达该相邻节点的路径是否更短,如果是,则更新相邻节点的g(n)值和父节点
- 继续下一轮循环
- 如果 open_set 为空,表示没有找到最短路径,搜索失败
- 一旦找到最短路径,可以通过回溯每个节点的父节点来还原整条路径
这里的 open_set 和 close_set 其实就相当于 Dijkstra 算法中的 U 集和 S 集
初始时 S 集中只有起点,U 中是除起点外的其余顶点;open_set 初始时只有顶点,而 close_set 为空
Dijkstra 算法每次迭代时从 U 集中找出路径最短的顶点,并加入 S 集中,同时更新 U 集中顶点的路径及其 parent 节点;A* 算法从 open_set 中选取 f(n) 值最小的节点,加入 close_set,对其相邻节点进行操作,注意如果相邻节点已经在 open_set 中,检查通过当前节点到达该相邻节点的路径是否更短,如果是,则更新相邻节点的 g(n) 值和父节点,这是容易忽略的部分
其实 Dijkstra 算法在更新 U 集时也是更新刚加入 S 集顶点的相邻节点,检查通过当前节点到达该节点相邻节点的路径是否更短,因此 A* 算法也要有相应的操作
启发函数
启发函数对 A* 算法有很重要的影响
- 在极端情况下,当启发函数 h(n) 始终为0,则将由 g(n) 决定节点的优先级,此时算法就退化成了
Dijkstra算法 - 如果 h(n) 始终小于等于节点n到终点的代价,则A*算法保证一定能够找到最短路径。但是当h(n)的值越小,算法将遍历越多的节点,也就导致算法越慢
- 如果h(n)完全等于节点n到终点的代价,则A*算法将找到最佳路径,并且速度很快。可惜并非所有场景下都能做到这一点。因为在没有达到终点之前,很难确切算出距离终点还有多远
- 如果h(n)的值比节点n到终点的代价要大,则A*算法不能保证找到最短路径,不过此时会很快
- 在另外一个极端情况下,如果h(n)相较于g(n)大很多,则此时只有h(n)产生效果,这也就变成了
最佳优先搜索
关于距离
对于网格形式的图,有以下这些启发函数可以使用:
- 如果图形中只允许朝上下左右四个方向移动,则可以使用曼哈顿距离(Manhattan distance)
- 如果图形中允许朝八个方向移动,则可以使用对角距离
- 如果图形中允许朝任何方向移动,则可以使用欧几里得距离(Euclidean distance)
曼哈顿距离
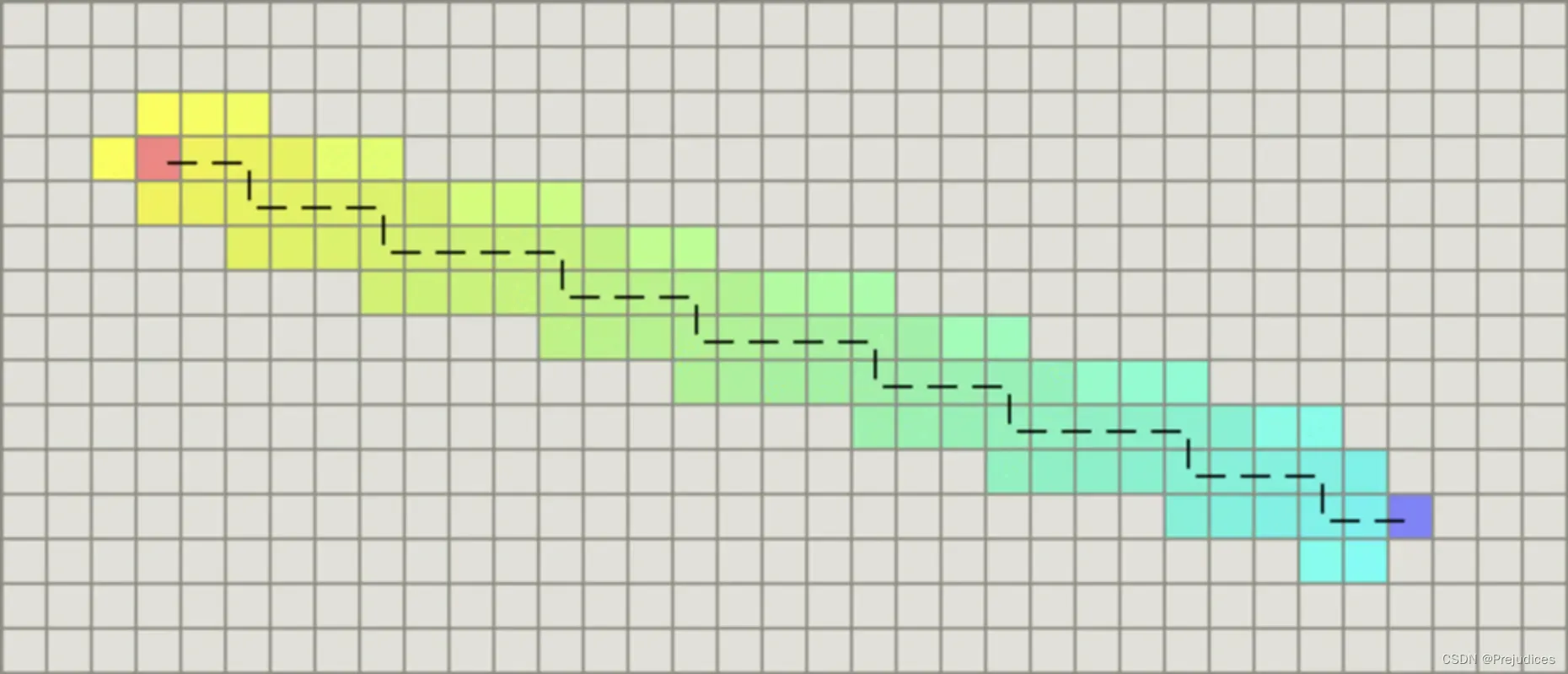
计算曼哈顿距离的函数如下,这里的D是指两个相邻节点之间的移动代价,通常是一个固定的常数
function heuristic(node) =
dx = abs(node.x - goal.x)
dy = abs(node.y - goal.y)
return D * (dx + dy)
对角距离
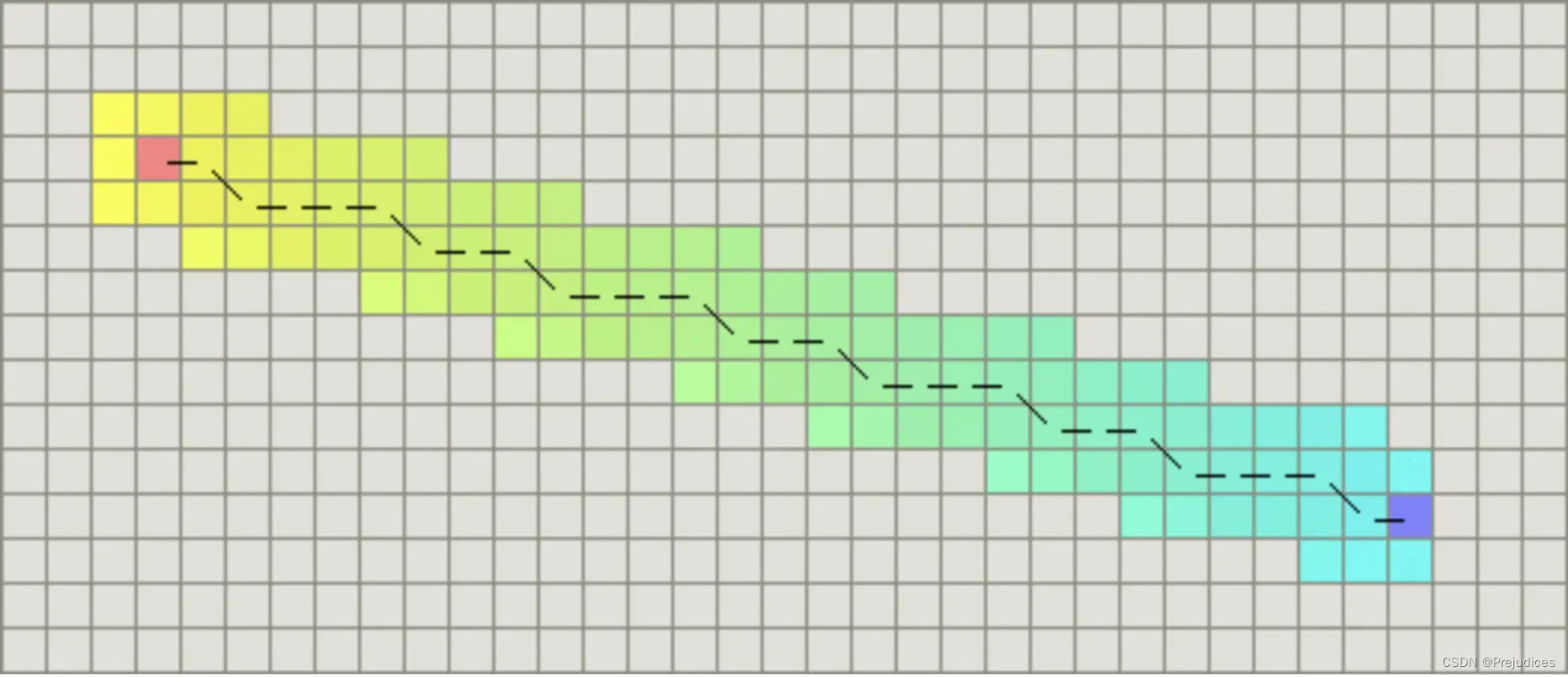
计算对角距离的函数如下,这里的D2指的是两个斜着相邻节点之间的移动代价
function heuristic(node) =
dx = abs(node.x - goal.x)
dy = abs(node.y - goal.y)
return D * (dx + dy) + (D2 - 2 * D) * min(dx, dy)
欧几里得距离
欧几里得距离是指两个节点之间的直线距离,其函数表示如下:
function heuristic(node) =
dx = abs(node.x - goal.x)
dy = abs(node.y - goal.y)
return D * sqrt(dx * dx + dy * dy)
Python 实现
"""
A* grid planning
author: Atsushi Sakai(@Atsushi_twi)
Nikos Kanargias (nkana@tee.gr)
See Wikipedia article (https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/A*_search_algorithm)
"""
import math
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
show_animation = True
class AStarPlanner:
def __init__(self, ox, oy, resolution, rr):
"""
Initialize grid map for a star planning
ox: x position list of Obstacles [m]
oy: y position list of Obstacles [m]
resolution: grid resolution [m]
rr: robot radius[m]
"""
self.resolution = resolution
self.rr = rr
self.min_x, self.min_y = 0, 0
self.max_x, self.max_y = 0, 0
self.obstacle_map = None
self.x_width, self.y_width = 0, 0
self.motion = self.get_motion_model()
self.calc_obstacle_map(ox, oy)
class Node:
def __init__(self, x, y, cost, parent_index):
self.x = x # index of grid
self.y = y # index of grid
self.cost = cost
self.parent_index = parent_index
def __str__(self):
return str(self.x) + "," + str(self.y) + "," + str(
self.cost) + "," + str(self.parent_index)
def planning(self, sx, sy, gx, gy):
"""
A star path search
input:
s_x: start x position [m]
s_y: start y position [m]
gx: goal x position [m]
gy: goal y position [m]
output:
rx: x position list of the final path
ry: y position list of the final path
"""
start_node = self.Node(self.calc_xy_index(sx, self.min_x),
self.calc_xy_index(sy, self.min_y), 0.0, -1)
goal_node = self.Node(self.calc_xy_index(gx, self.min_x),
self.calc_xy_index(gy, self.min_y), 0.0, -1)
open_set, closed_set = dict(), dict()
open_set[self.calc_grid_index(start_node)] = start_node
while True:
if len(open_set) == 0:
print("Open set is empty..")
break
c_id = min(
open_set,
key=lambda o: open_set[o].cost + self.calc_heuristic(goal_node,
open_set[
o]))
current = open_set[c_id]
# show graph
if show_animation: # pragma: no cover
plt.plot(self.calc_grid_position(current.x, self.min_x),
self.calc_grid_position(current.y, self.min_y), "xc")
# for stopping simulation with the esc key.
plt.gcf().canvas.mpl_connect('key_release_event',
lambda event: [exit(
0) if event.key == 'escape' else None])
if len(closed_set.keys()) % 10 == 0:
plt.pause(0.001)
if current.x == goal_node.x and current.y == goal_node.y:
print("Find goal")
goal_node.parent_index = current.parent_index
goal_node.cost = current.cost
break
# Remove the item from the open set
del open_set[c_id]
# Add it to the closed set
closed_set[c_id] = current
# expand_grid search grid based on motion model
for i, _ in enumerate(self.motion):
node = self.Node(current.x + self.motion[i][0],
current.y + self.motion[i][1],
current.cost + self.motion[i][2], c_id)
n_id = self.calc_grid_index(node)
# If the node is not safe, do nothing
if not self.verify_node(node):
continue
if n_id in closed_set:
continue
if n_id not in open_set:
open_set[n_id] = node # discovered a new node
else:
if open_set[n_id].cost > node.cost:
# This path is the best until now. record it
open_set[n_id] = node
rx, ry = self.calc_final_path(goal_node, closed_set)
return rx, ry
def calc_final_path(self, goal_node, closed_set):
# generate final course
rx, ry = [self.calc_grid_position(goal_node.x, self.min_x)], [
self.calc_grid_position(goal_node.y, self.min_y)]
parent_index = goal_node.parent_index
while parent_index != -1:
n = closed_set[parent_index]
rx.append(self.calc_grid_position(n.x, self.min_x))
ry.append(self.calc_grid_position(n.y, self.min_y))
parent_index = n.parent_index
return rx, ry
@staticmethod
def calc_heuristic(n1, n2):
w = 1.0 # weight of heuristic
d = w * math.hypot(n1.x - n2.x, n1.y - n2.y)
return d
def calc_grid_position(self, index, min_position):
"""
calc grid position
:param index:
:param min_position:
:return:
"""
pos = index * self.resolution + min_position
return pos
def calc_xy_index(self, position, min_pos):
return round((position - min_pos) / self.resolution)
def calc_grid_index(self, node):
return (node.y - self.min_y) * self.x_width + (node.x - self.min_x)
def verify_node(self, node):
px = self.calc_grid_position(node.x, self.min_x)
py = self.calc_grid_position(node.y, self.min_y)
if px < self.min_x:
return False
elif py < self.min_y:
return False
elif px >= self.max_x:
return False
elif py >= self.max_y:
return False
# collision check
if self.obstacle_map[node.x][node.y]:
return False
return True
def calc_obstacle_map(self, ox, oy):
self.min_x = round(min(ox))
self.min_y = round(min(oy))
self.max_x = round(max(ox))
self.max_y = round(max(oy))
print("min_x:", self.min_x)
print("min_y:", self.min_y)
print("max_x:", self.max_x)
print("max_y:", self.max_y)
self.x_width = round((self.max_x - self.min_x) / self.resolution)
self.y_width = round((self.max_y - self.min_y) / self.resolution)
print("x_width:", self.x_width)
print("y_width:", self.y_width)
# obstacle map generation
self.obstacle_map = [[False for _ in range(self.y_width)]
for _ in range(self.x_width)]
for ix in range(self.x_width):
x = self.calc_grid_position(ix, self.min_x)
for iy in range(self.y_width):
y = self.calc_grid_position(iy, self.min_y)
for iox, ioy in zip(ox, oy):
d = math.hypot(iox - x, ioy - y)
if d <= self.rr:
self.obstacle_map[ix][iy] = True
break
@staticmethod
def get_motion_model():
# dx, dy, cost
motion = [[1, 0, 1],
[0, 1, 1],
[-1, 0, 1],
[0, -1, 1],
[-1, -1, math.sqrt(2)],
[-1, 1, math.sqrt(2)],
[1, -1, math.sqrt(2)],
[1, 1, math.sqrt(2)]]
return motion
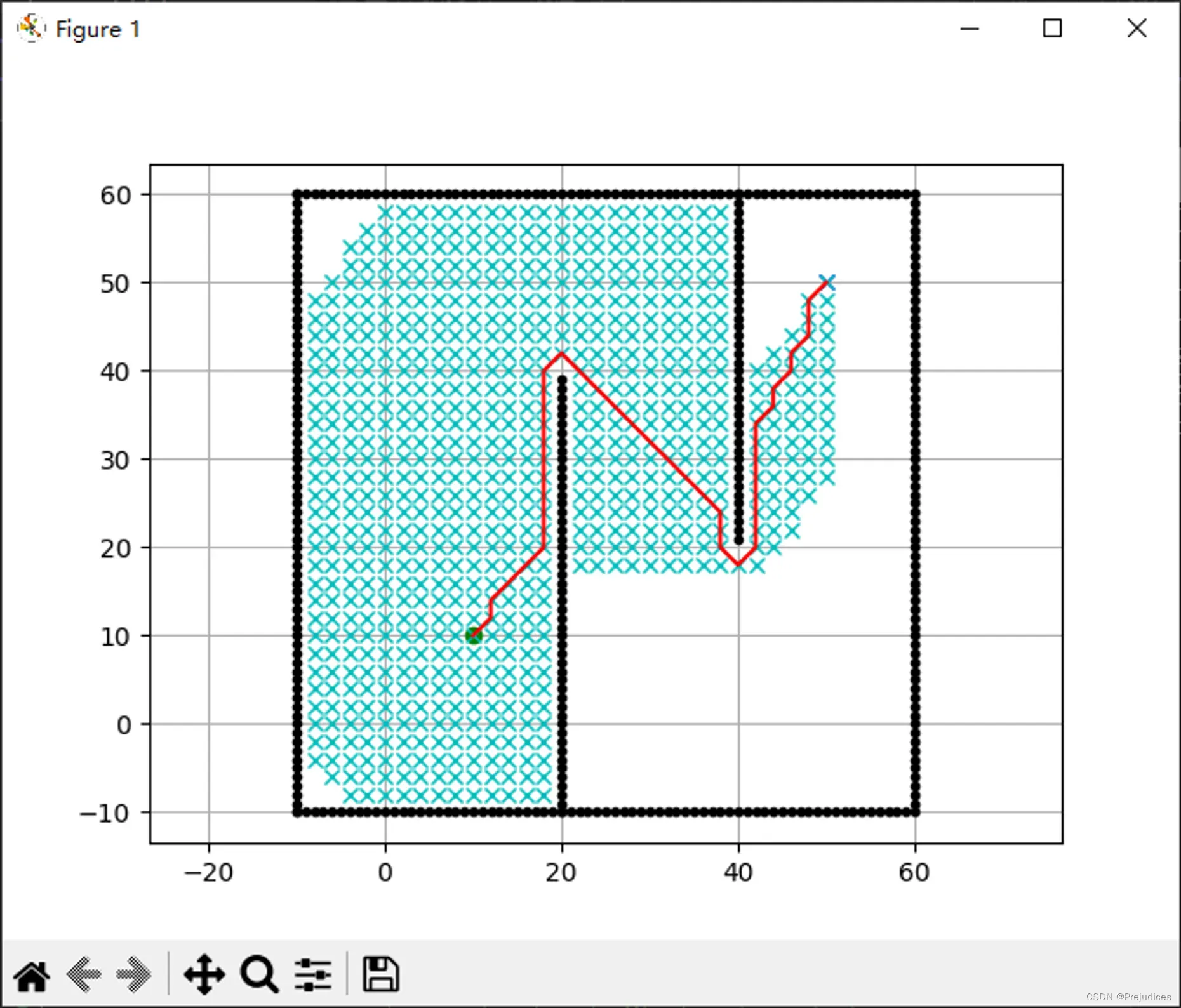
def main():
print(__file__ + " start!!")
# start and goal position
sx = 10.0 # [m]
sy = 10.0 # [m]
gx = 50.0 # [m]
gy = 50.0 # [m]
grid_size = 2.0 # [m]
robot_radius = 1.0 # [m]
# set obstacle positions
ox, oy = [], []
for i in range(-10, 60):
ox.append(i)
oy.append(-10.0)
for i in range(-10, 60):
ox.append(60.0)
oy.append(i)
for i in range(-10, 61):
ox.append(i)
oy.append(60.0)
for i in range(-10, 61):
ox.append(-10.0)
oy.append(i)
for i in range(-10, 40):
ox.append(20.0)
oy.append(i)
for i in range(0, 40):
ox.append(40.0)
oy.append(60.0 - i)
if show_animation: # pragma: no cover
plt.plot(ox, oy, ".k")
plt.plot(sx, sy, "og")
plt.plot(gx, gy, "xb")
plt.grid(True)
plt.axis("equal")
a_star = AStarPlanner(ox, oy, grid_size, robot_radius)
rx, ry = a_star.planning(sx, sy, gx, gy)
if show_animation: # pragma: no cover
plt.plot(rx, ry, "-r")
plt.pause(0.001)
plt.show()
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
输出如下
E:\Junior\Code\path_plan_test\a_star_py\a_star_py\a_star_py.py start!!
min_x: -10
min_y: -10
max_x: 60
max_y: 60
x_width: 35
y_width: 35
Find goal
A* 算法主要体现在 planning() 函数中,过程与 A* 算法的描述是对应的
def planning(self, sx, sy, gx, gy):
"""
A star path search
input:
s_x: start x position [m]
s_y: start y position [m]
gx: goal x position [m]
gy: goal y position [m]
output:
rx: x position list of the final path
ry: y position list of the final path
"""
start_node = self.Node(self.calc_xy_index(sx, self.min_x),
self.calc_xy_index(sy, self.min_y), 0.0, -1)
goal_node = self.Node(self.calc_xy_index(gx, self.min_x),
self.calc_xy_index(gy, self.min_y), 0.0, -1)
open_set, closed_set = dict(), dict()
open_set[self.calc_grid_index(start_node)] = start_node
while True:
if len(open_set) == 0:
print("Open set is empty..")
break
c_id = min(
open_set,
key=lambda o: open_set[o].cost + self.calc_heuristic(goal_node,
open_set[
o]))
current = open_set[c_id]
# show graph
if show_animation: # pragma: no cover
plt.plot(self.calc_grid_position(current.x, self.min_x),
self.calc_grid_position(current.y, self.min_y), "xc")
# for stopping simulation with the esc key.
plt.gcf().canvas.mpl_connect('key_release_event',
lambda event: [exit(
0) if event.key == 'escape' else None])
if len(closed_set.keys()) % 10 == 0:
plt.pause(0.001)
if current.x == goal_node.x and current.y == goal_node.y:
print("Find goal")
goal_node.parent_index = current.parent_index
goal_node.cost = current.cost
break
# Remove the item from the open set
del open_set[c_id]
# Add it to the closed set
closed_set[c_id] = current
# expand_grid search grid based on motion model
for i, _ in enumerate(self.motion):
node = self.Node(current.x + self.motion[i][0],
current.y + self.motion[i][1],
current.cost + self.motion[i][2], c_id)
n_id = self.calc_grid_index(node)
# If the node is not safe, do nothing
if not self.verify_node(node):
continue
if n_id in closed_set:
continue
if n_id not in open_set:
open_set[n_id] = node # discovered a new node
else:
if open_set[n_id].cost > node.cost:
# This path is the best until now. record it
open_set[n_id] = node
rx, ry = self.calc_final_path(goal_node, closed_set)
return rx, ry
1、初始化起始节点和目标节点,并将起始节点添加到 open_set
start_node = self.Node(self.calc_xy_index(sx, self.min_x),
self.calc_xy_index(sy, self.min_y), 0.0, -1)
goal_node = self.Node(self.calc_xy_index(gx, self.min_x),
self.calc_xy_index(gy, self.min_y), 0.0, -1)
open_set, closed_set = dict(), dict()
open_set[self.calc_grid_index(start_node)] = start_node
2、当 open_set 为空时跳出 while 循环
if len(open_set) == 0:
print("Open set is empty..")
break
3、从 open_set 中选择具有最小 f(n) 值的节点
c_id = min(
open_set,
key=lambda o: open_set[o].cost + self.calc_heuristic(goal_node,
open_set[
o]))
current = open_set[c_id]
4、如果选择的节点是目标节点,表示找到了最短路径,可以停止搜索
if current.x == goal_node.x and current.y == goal_node.y:
print("Find goal")
goal_node.parent_index = current.parent_index
goal_node.cost = current.cost
break
5、将该节点移出 open_set,并将其添加到 close_set
# Remove the item from the open set
del open_set[c_id]
# Add it to the closed set
closed_set[c_id] = current
6、对该节点的相邻节点进行操作
# expand_grid search grid based on motion model
for i, _ in enumerate(self.motion):
node = self.Node(current.x + self.motion[i][0],
current.y + self.motion[i][1],
current.cost + self.motion[i][2], c_id)
n_id = self.calc_grid_index(node)
# If the node is not safe, do nothing
if not self.verify_node(node):
continue
if n_id in closed_set:
continue
if n_id not in open_set:
open_set[n_id] = node # discovered a new node
else:
if open_set[n_id].cost > node.cost:
# This path is the best until now. record it
open_set[n_id] = node
7、回溯每个节点的父节点来还原整条路径
rx, ry = self.calc_final_path(goal_node, closed_set)
C++ 实现
- 定义一个三维数组
path,用于存储每个位置的方格对应的“父方格”的坐标 - 二维数组
valF保序每个方格目前情况下最小的 F 值 - 由于每次需要从
open表中弹出的是F值最小的节点,选择使用优先队列来作为 open 表 - 定义
visit二维数组作为 close 表,初始值false,对应位置为true时表示已经加入 close 表
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<string>
#include<vector>
#include<cmath>
#include<queue>
#define N 6 // 棋盘/迷宫 的阶数
using namespace std;
class Node
{
public:
int x, y; // 节点所在位置
int F, G, H; // G:从起点开始,沿着产的路径,移动到网格上指定方格的移动耗费。
// H:从网格上那个方格移动到终点B的预估移动耗费,使用曼哈顿距离。
// F = G + H
Node(int a, int b) :x(a), y(b) {}
// 重载操作符,使优先队列以F值大小为标准维持堆
bool operator < (const Node& a) const
{
return F > a.F;
}
};
// 定义八个方向
int dir[8][2] = { {-1,-1}, {-1, 0}, {-1, 1}, {0, -1},
{0, 1}, {1, -1}, {1, 0}, {1, 1} };
// 优先队列,就相当于open表
priority_queue<Node>que;
// 棋盘
int qp[N][N] = { {0,0,0,0,0,0},
{0,1,1,0,1,1},
{0,0,1,0,0,0},
{0,0,1,1,1,0},
{0,1,1,0,0,0},
{1,1,0,0,0,0} };
bool visit[N][N]; // 访问情况记录,close表
int valF[N][N]; // 记录每个节点对应的F值
int path[N][N][2]; // 存储每个节点的父节点
int Manhuattan(int x, int y, int x1, int y1); // 计算曼哈顿距离
bool NodeIsLegal(int x, int y, int xx, int yy); // 判断位置合法性
void A_start(int x0, int y0, int x1, int y1); // A*算法
void PrintPath(int x1, int y1); // 打印路径
/* ----------------主函数------------------- */
int main()
{
fill(visit[0], visit[0] + N * N, false); // 将visit数组赋初值false
fill(valF[0], valF[0] + N * N, 0); // 初始化F全为0
fill(path[0][0], path[0][0] + N * N * 2, -1); // 路径同样赋初值-1
// // 起点 // 终点
int x0, y0, x1, y1;
cout << "输入起点:";
cin >> x0 >> y0;
cout << "输入终点:";
cin >> x1 >> y1;
x0--; y0--; x1--; y1--;
if (!NodeIsLegal(x0, y0, x0, y0))
{
cout << "非法起点!" << endl;
return 0;
}
A_start(x0, y0, x1, y1); // A*算法
PrintPath(x1, y1); // 打印路径
}
/* ----------------自定义函数------------------ */
void A_start(int x0, int y0, int x1, int y1)
{
// 初始化起点
Node node(x0, y0);
node.G = 0;
node.H = Manhuattan(x0, y0, x1, y1);
node.F = node.G + node.H;
valF[x0][y0] = node.F;
// 起点加入open表
que.push(node);
while (!que.empty())
{
Node node_top = que.top(); que.pop();
visit[node_top.x][node_top.y] = true; // 访问该点,加入closed表
if (node_top.x == x1 && node_top.y == y1) // 到达终点
break;
// 遍历node_top周围的8个位置
for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++)
{
Node node_next(node_top.x + dir[i][0], node_top.y + dir[i][1]); // 创建一个node_top周围的节点
// 该节点坐标合法 且 未加入close表
if (NodeIsLegal(node_next.x, node_next.y, node_top.x, node_top.y) && !visit[node_next.x][node_next.y])
{
// 计算从起点并经过node_top节点到达该节点所花费的代价
node_next.G = node_top.G + int(sqrt(pow(dir[i][0], 2) + pow(dir[i][1], 2)) * 10);
// 计算该节点到终点的曼哈顿距离
node_next.H = Manhuattan(node_next.x, node_next.y, x1, y1);
// 从起点经过node_top和该节点到达终点的估计代价
node_next.F = node_next.G + node_next.H;
// node_next.F < valF[node_next.x][node_next.y] 说明找到了更优的路径,则进行更新
// valF[node_next.x][node_next.y] == 0 说明该节点还未加入open表中,则加入
if (node_next.F < valF[node_next.x][node_next.y] || valF[node_next.x][node_next.y] == 0)
{
// 保存该节点的父节点
path[node_next.x][node_next.y][0] = node_top.x;
path[node_next.x][node_next.y][1] = node_top.y;
valF[node_next.x][node_next.y] = node_next.F; // 修改该节点对应的valF值
que.push(node_next); // 加入open表
}
}
}
}
}
void PrintPath(int x1, int y1)
{
if (path[x1][y1][0] == -1 || path[x1][y1][1] == -1)
{
cout << "没有可行路径!" << endl;
return;
}
int x = x1, y = y1;
int a, b;
while (x != -1 || y != -1)
{
qp[x][y] = 2; // 将可行路径上的节点赋值为2
a = path[x][y][0];
b = path[x][y][1];
x = a;
y = b;
}
// □表示未经过的节点, █表示障碍物, ☆表示可行节点
string s[3] = { "□", "█", "☆" };
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < N; j++)
cout << s[qp[i][j]] << "\t";
cout << endl;
}
}
int Manhuattan(int x, int y, int x1, int y1)
{
return (abs(x - x1) + abs(y - y1)) * 10;
}
bool NodeIsLegal(int x, int y, int xx, int yy)
{
if (x < 0 || x >= N || y < 0 || y >= N) return false; // 判断边界
if (qp[x][y] == 1) return false; // 判断障碍物
// 两节点成对角型且它们的公共相邻节点存在障碍物
if (x != xx && y != yy && (qp[x][yy] == 1 || qp[xx][y] == 1)) return false;
return true;
}
运行输出如下
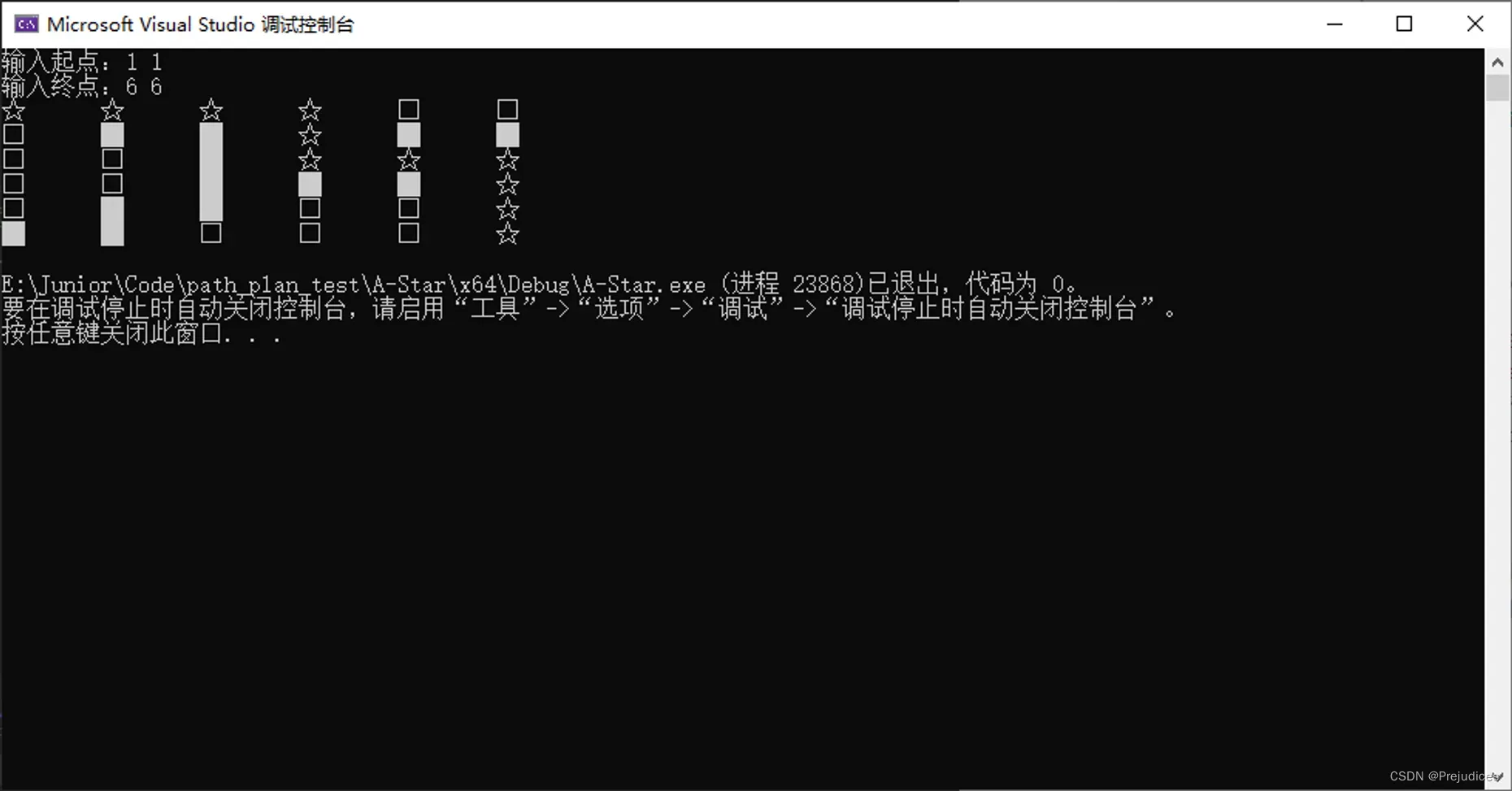
文章出处登录后可见!
