Pytorch: 全连接神经网络-解决 Boston 房价回归问题
Copyright: Jingmin Wei, Pattern Recognition and Intelligent System, School of Artificial and Intelligence, Huazhong University of Science and Technology
MLP 回归模型
使用sklearn库的fetch_california_housing()函数。数据集共包含20640个样本,有8个自变量。
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.metrics import mean_squared_error, mean_absolute_error
from sklearn.datasets import fetch_california_housing
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
from torch.optim import SGD
import torch.utils.data as Data
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import seaborn as sns
房价数据准备
# 导入数据
housedata = fetch_california_housing()
# 切分训练集和测试集
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(housedata.data, housedata.target,
test_size = 0.3, random_state = 42)
70% 训练集,30%测试集。
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test
(array([[ 4.1312 , 35. , 5.88235294, ..., 2.98529412,
33.93 , -118.02 ],
[ 2.8631 , 20. , 4.40120968, ..., 2.0141129 ,
32.79 , -117.09 ],
[ 4.2026 , 24. , 5.61754386, ..., 2.56491228,
34.59 , -120.14 ],
...,
[ 2.9344 , 36. , 3.98671727, ..., 3.33206831,
34.03 , -118.38 ],
[ 5.7192 , 15. , 6.39534884, ..., 3.17889088,
37.58 , -121.96 ],
[ 2.5755 , 52. , 3.40257649, ..., 2.10869565,
37.77 , -122.42 ]]),
array([[ 1.6812 , 25. , 4.19220056, ..., 3.87743733,
36.06 , -119.01 ],
[ 2.5313 , 30. , 5.03938356, ..., 2.67979452,
35.14 , -119.46 ],
[ 3.4801 , 52. , 3.97715472, ..., 1.36033229,
37.8 , -122.44 ],
...,
[ 3.512 , 16. , 3.76228733, ..., 2.36956522,
33.67 , -117.91 ],
[ 3.65 , 10. , 5.50209205, ..., 3.54751943,
37.82 , -121.28 ],
[ 3.052 , 17. , 3.35578145, ..., 2.61499365,
34.15 , -118.24 ]]),
array([1.938, 1.697, 2.598, ..., 2.221, 2.835, 3.25 ]),
array([0.477 , 0.458 , 5.00001, ..., 2.184 , 1.194 , 2.098 ]))
# 数据标准化处理
scale = StandardScaler()
X_train_s = scale.fit_transform(X_train)
X_test_s = scale.transform(X_test)
# 将训练数据转为数据表
housedatadf = pd.DataFrame(data=X_train_s, columns = housedata.feature_names)
housedatadf['target'] = y_train
housedatadf
| MedInc | HouseAge | AveRooms | AveBedrms | Population | AveOccup | Latitude | Longitude | target | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0.133506 | 0.509357 | 0.181060 | -0.273850 | -0.184117 | -0.010825 | -0.805682 | 0.780934 | 1.93800 |
| 1 | -0.532218 | -0.679873 | -0.422630 | -0.047868 | -0.376191 | -0.089316 | -1.339473 | 1.245270 | 1.69700 |
| 2 | 0.170990 | -0.362745 | 0.073128 | -0.242600 | -0.611240 | -0.044800 | -0.496645 | -0.277552 | 2.59800 |
| 3 | -0.402916 | -1.155565 | 0.175848 | -0.008560 | -0.987495 | -0.075230 | 1.690024 | -0.706938 | 1.36100 |
| 4 | -0.299285 | 1.857152 | -0.259598 | -0.070993 | 0.086015 | -0.066357 | 0.992350 | -1.430902 | 5.00001 |
| … | … | … | … | … | … | … | … | … | … |
| 14443 | 1.308827 | 0.509357 | 0.281603 | -0.383849 | -0.675265 | -0.007030 | -0.875918 | 0.810891 | 2.29200 |
| 14444 | -0.434100 | 0.350793 | 0.583037 | 0.383154 | 0.285105 | 0.063443 | -0.763541 | 1.075513 | 0.97800 |
| 14445 | -0.494787 | 0.588640 | -0.591570 | -0.040978 | 0.287736 | 0.017201 | -0.758858 | 0.601191 | 2.22100 |
| 14446 | 0.967171 | -1.076283 | 0.390149 | -0.067164 | 0.306154 | 0.004821 | 0.903385 | -1.186252 | 2.83500 |
| 14447 | -0.683202 | 1.857152 | -0.829656 | -0.087729 | 1.044630 | -0.081672 | 0.992350 | -1.415923 | 3.25000 |
14448 rows × 9 columns
使用相关系数热力图分析数据集中9个变量的相关性
datacor = np.corrcoef(housedatadf.values, rowvar=0)
datacor = pd.DataFrame(data = datacor, columns = housedatadf.columns,
index = housedatadf.columns)
plt.figure(figsize=(8, 6))
ax = sns.heatmap(datacor, square = True, annot = True, fmt = '.3f',
linewidths = .5, cmap = 'YlGnBu',
cbar_kws = {'fraction': 0.046, 'pad': 0.03})
plt.show()
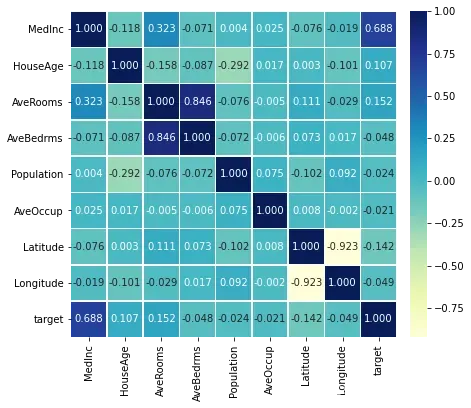
从图像可以看出,和目标函数相关性最大的是MedInc(收入中位数)变量。而且AveRooms和AveBedrms两个变量的正相关性较强。
# 将数据集转为张量
X_train_t = torch.from_numpy(X_train_s.astype(np.float32))
y_train_t = torch.from_numpy(y_train.astype(np.float32))
X_test_t = torch.from_numpy(X_test_s.astype(np.float32))
y_test_t = torch.from_numpy(y_test.astype(np.float32))
# 将训练数据处理为数据加载器
train_data = Data.TensorDataset(X_train_t, y_train_t)
test_data = Data.TensorDataset(X_test_t, y_test_t)
train_loader = Data.DataLoader(dataset = train_data, batch_size = 64,
shuffle = True, num_workers = 1)
搭建网络预测房价
# 搭建全连接神经网络回归
class MLPregression(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(MLPregression, self).__init__()
# 第一个隐含层
self.hidden1 = nn.Linear(in_features=8, out_features=100, bias=True)
# 第二个隐含层
self.hidden2 = nn.Linear(100, 100)
# 第三个隐含层
self.hidden3 = nn.Linear(100, 50)
# 回归预测层
self.predict = nn.Linear(50, 1)
# 定义网络前向传播路径
def forward(self, x):
x = F.relu(self.hidden1(x))
x = F.relu(self.hidden2(x))
x = F.relu(self.hidden3(x))
output = self.predict(x)
# 输出一个一维向量
return output[:, 0]
# 输出网络结构
from torchsummary import summary
testnet = MLPregression()
summary(testnet, input_size=(1, 8)) # 表示1个样本,每个样本有8个特征
----------------------------------------------------------------
Layer (type) Output Shape Param #
================================================================
Linear-1 [-1, 1, 100] 900
Linear-2 [-1, 1, 100] 10,100
Linear-3 [-1, 1, 50] 5,050
Linear-4 [-1, 1, 1] 51
================================================================
Total params: 16,101
Trainable params: 16,101
Non-trainable params: 0
----------------------------------------------------------------
Input size (MB): 0.00
Forward/backward pass size (MB): 0.00
Params size (MB): 0.06
Estimated Total Size (MB): 0.06
----------------------------------------------------------------
# 输出网络结构
from torchviz import make_dot
testnet = MLPregression()
x = torch.randn(1, 8).requires_grad_(True)
y = testnet(x)
myMLP_vis = make_dot(y, params=dict(list(testnet.named_parameters()) + [('x', x)]))
myMLP_vis
然后使用训练集对网络进行训练
# 定义优化器
optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(testnet.parameters(), lr = 0.01)
loss_func = nn.MSELoss() # 均方根误差损失函数
train_loss_all = []
# 对模型迭代训练,总共epoch轮
for epoch in range(30):
train_loss = 0
train_num = 0
# 对训练数据的加载器进行迭代计算
for step, (b_x, b_y) in enumerate(train_loader):
output = testnet(b_x) # MLP在训练batch上的输出
loss = loss_func(output, b_y) # 均方根损失函数
optimizer.zero_grad() # 每次迭代梯度初始化0
loss.backward() # 反向传播,计算梯度
optimizer.step() # 使用梯度进行优化
train_loss += loss.item() * b_x.size(0)
train_num += b_x.size(0)
train_loss_all.append(train_loss / train_num)
# 可视化损失函数的变换情况
plt.figure(figsize = (8, 6))
plt.plot(train_loss_all, 'ro-', label = 'Train loss')
plt.legend()
plt.grid()
plt.xlabel('epoch')
plt.ylabel('Loss')
plt.show()
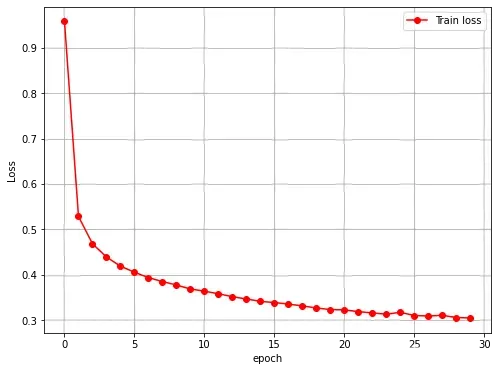
对网络预测,并使用平均绝对值误差来表示预测效果
y_pre = testnet(X_test_t)
y_pre = y_pre.data.numpy()
mae = mean_absolute_error(y_test, y_pre)
print('在测试集上的绝对值误差为:', mae)
在测试集上的绝对值误差为: 0.39334159455403034
真实集和预测值可视化,查看之间的差异
index = np.argsort(y_test)
plt.figure(figsize=(8, 6))
plt.plot(np.arange(len(y_test)), y_test[index], 'r', label = 'Original Y')
plt.scatter(np.arange(len(y_pre)), y_pre[index], s = 3, c = 'b', label = 'Prediction')
plt.legend(loc = 'upper left')
plt.grid()
plt.xlabel('Index')
plt.ylabel('Y')
plt.show()
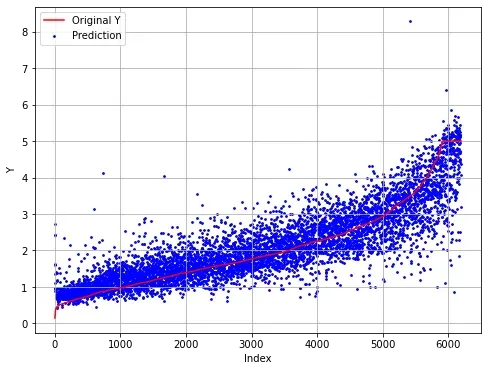
在测试集上,MLP回归正确地预测处理原始数据的变化趋势,但部分样本的预测差异较大。
文章出处登录后可见!
已经登录?立即刷新
