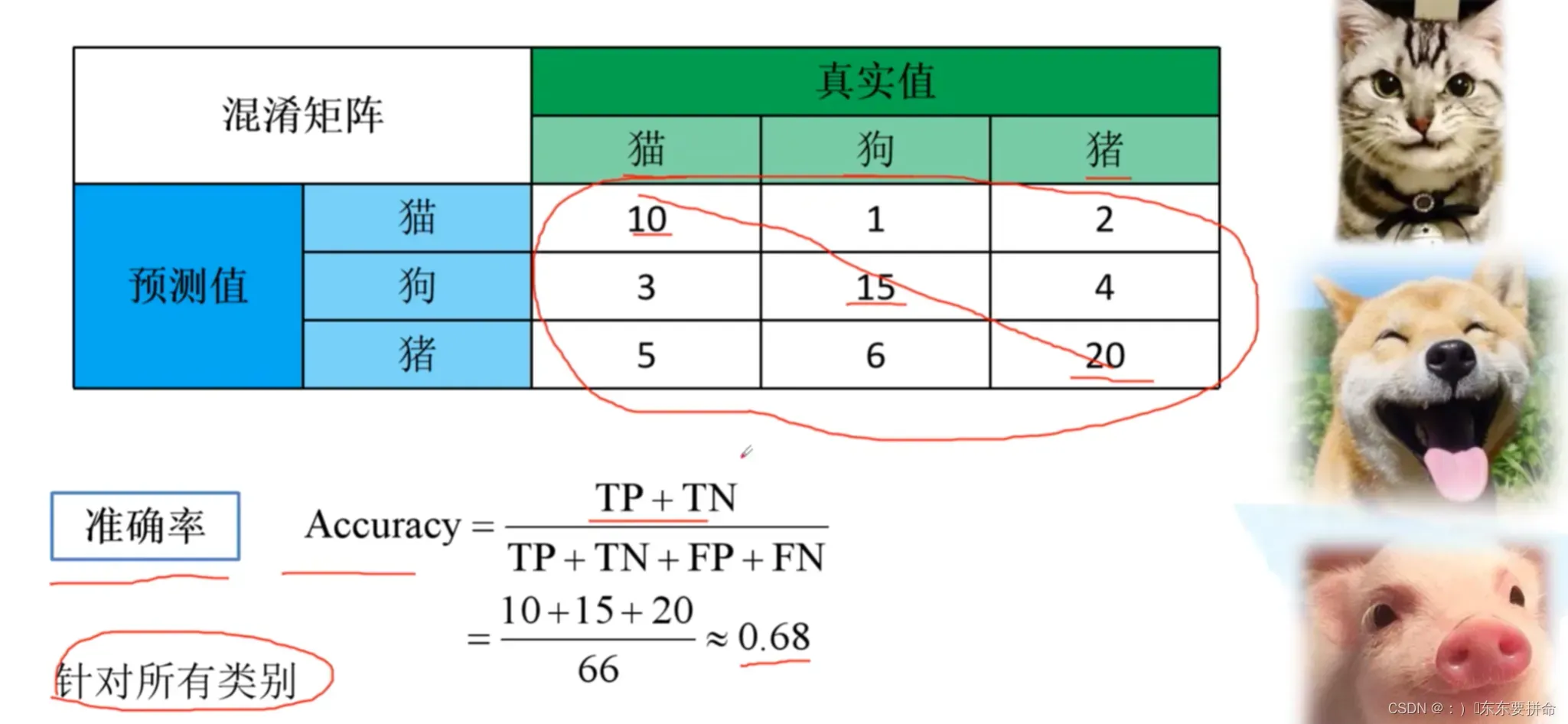
混淆矩阵是评估模型结果的一种指标 用来判断分类模型的好坏
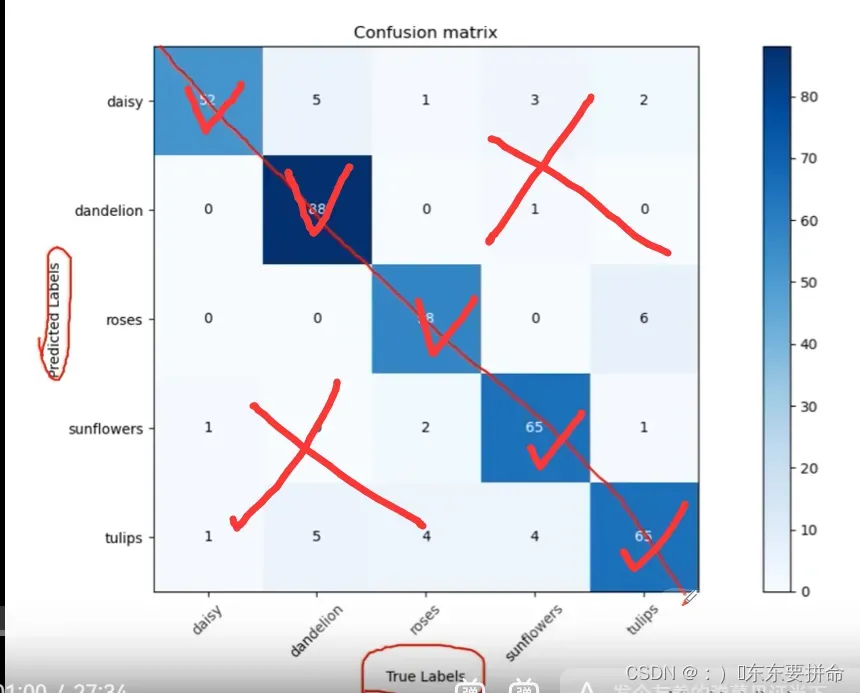
预测对了 为对角线
还可以通过矩阵的上下角发现哪些容易出错
从这个 矩阵出发 可以得到 acc != precision recall 特异度?
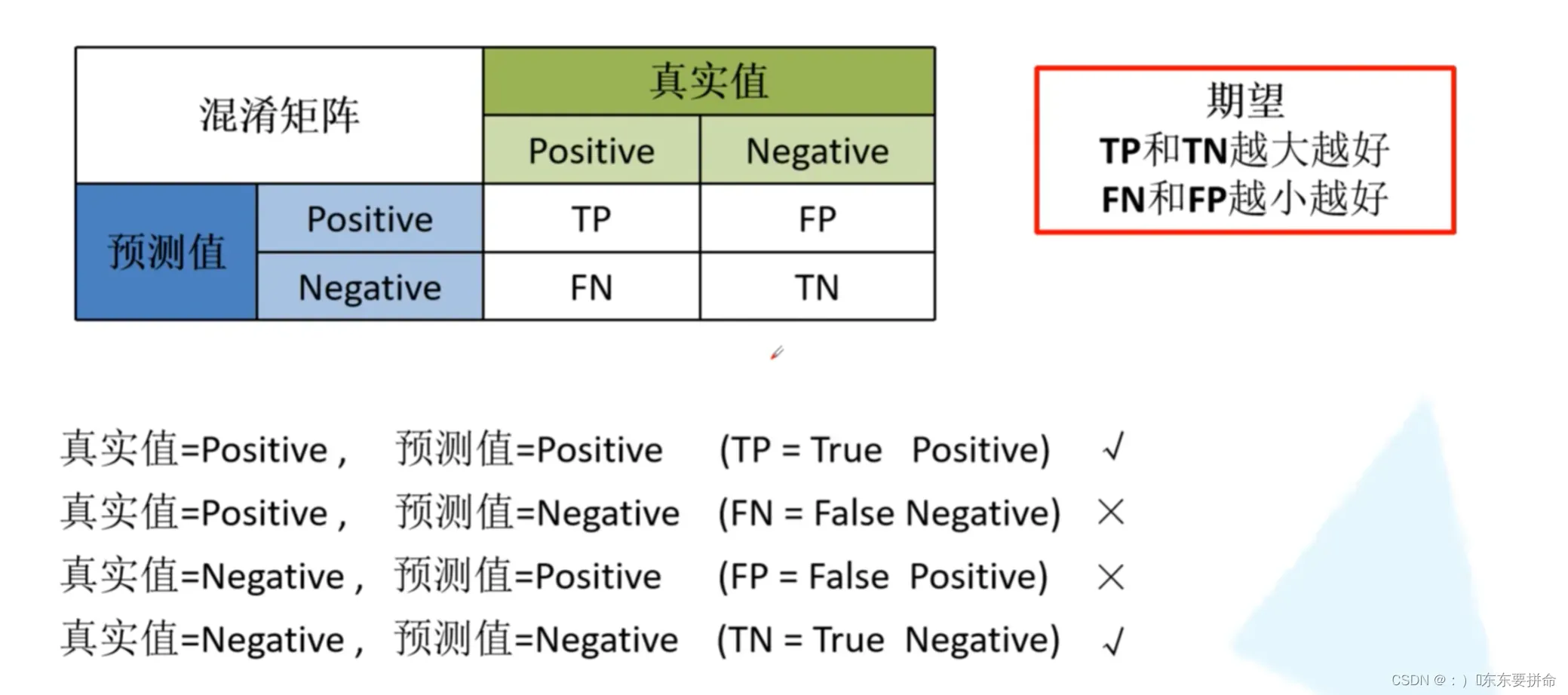
目标检测01笔记AP mAP recall precision是什么 查全率是什么 查准率是什么 什么是准确率 什么是召回率_:)�东东要拼命的博客-CSDN博客
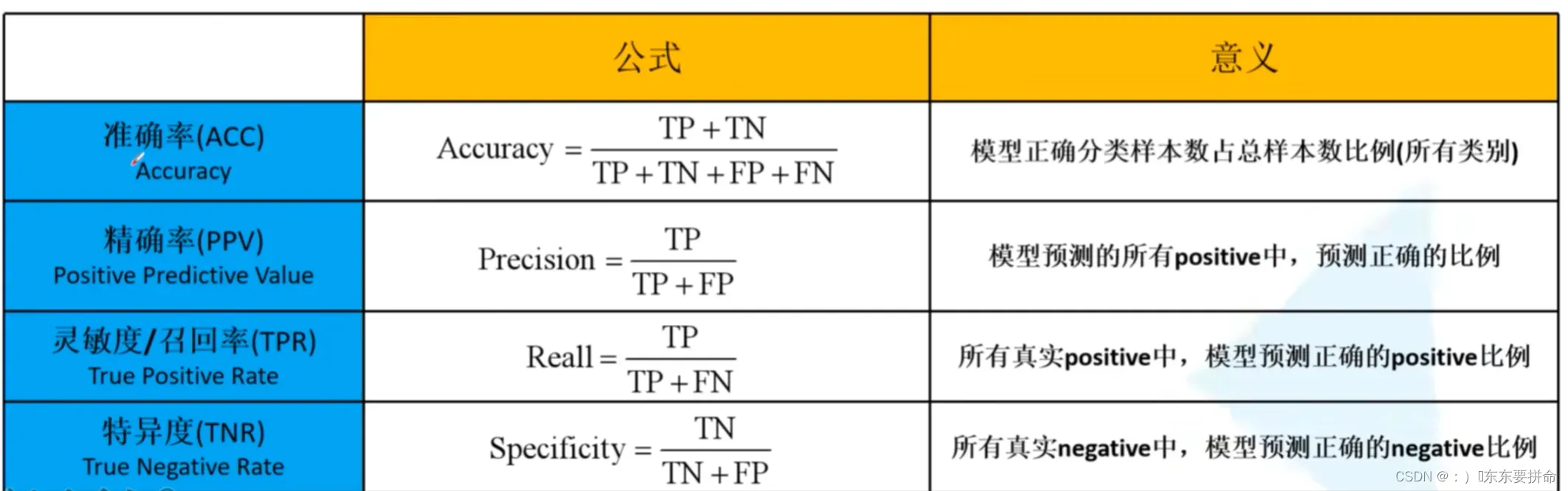
acc 是对所有类别来说的
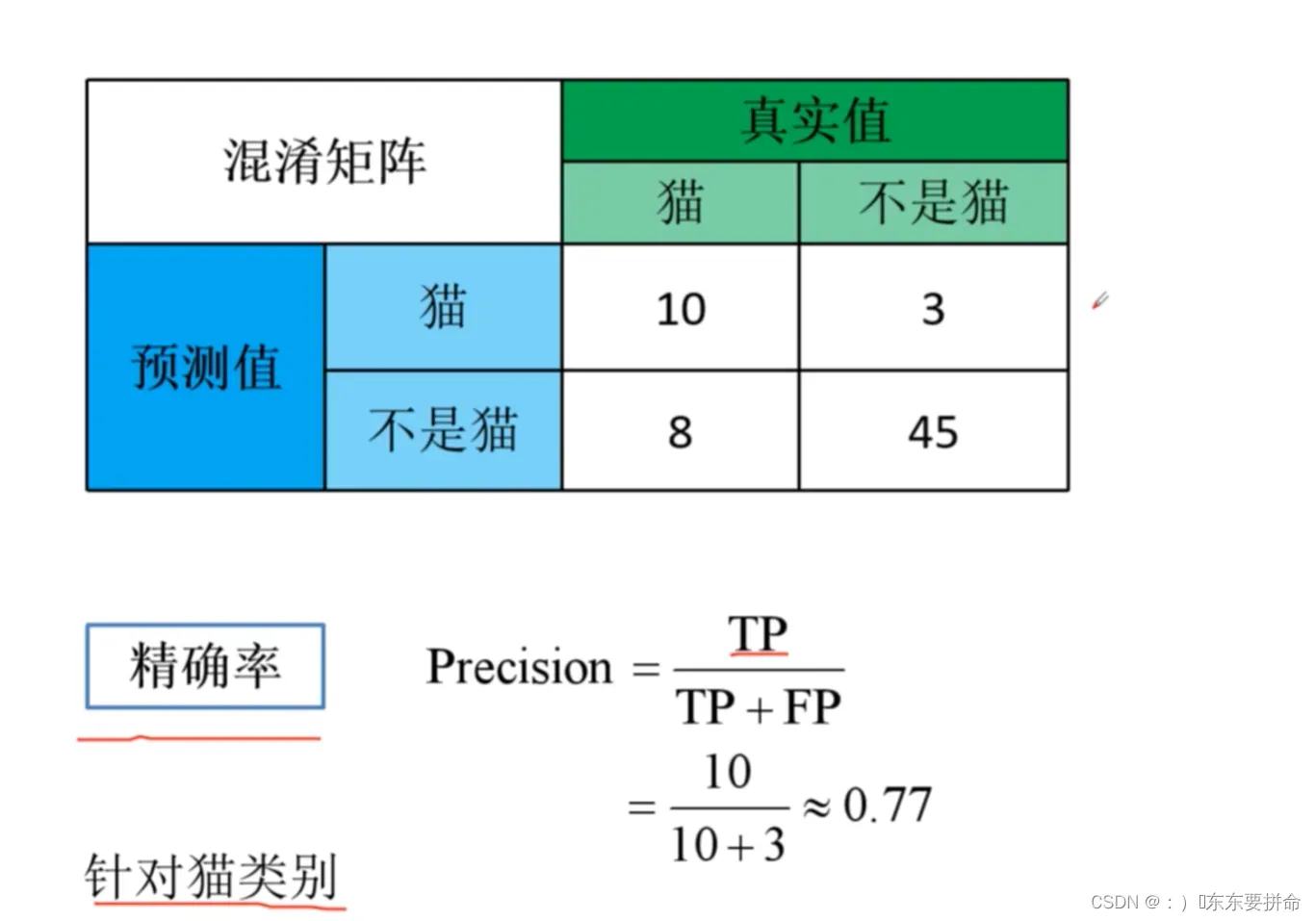
其他三个都是 对于类别来说的
下面给出源码
import json
import os
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import torch
from prettytable import PrettyTable
from torchvision import datasets
from torchvision.models import MobileNetV2
from torchvision.transforms import transforms
class ConfusionMatrix(object):
"""
注意版本问题,使用numpy来进行数值计算的
"""
def __init__(self, num_classes: int, labels: list):
self.matrix = np.zeros((num_classes, num_classes))
self.num_classes = num_classes
self.labels = labels
def update(self, preds, labels):
for p, t in zip(preds, labels):
self.matrix[t, p] += 1
# 行代表预测标签 列表示真实标签
def summary(self):
# calculate accuracy
sum_TP = 0
for i in range(self.num_classes):
sum_TP += self.matrix[i, i]
acc = sum_TP / np.sum(self.matrix)
print("acc is", acc)
# precision, recall, specificity
table = PrettyTable()
table.fields_names = ["", "pre", "recall", "spec"]
for i in range(self.num_classes):
TP = self.matrix[i, i]
FP = np.sum(self.matrix[i, :]) - TP
FN = np.sum(self.matrix[:, i]) - TP
TN = np.sum(self.matrix) - TP - FP - FN
pre = round(TP / (TP + FP), 3) # round 保留三位小数
recall = round(TP / (TP + FN), 3)
spec = round(TN / (FP + FN), 3)
table.add_row([self.labels[i], pre, recall, spec])
print(table)
def plot(self):
matrix = self.matrix
print(matrix)
plt.imshow(matrix, cmap=plt.cm.Blues) # 颜色变化从白色到蓝色
# 设置 x 轴坐标 label
plt.xticks(range(self.num_classes), self.labels, rotation=45)
# 将原来的 x 轴的数字替换成我们想要的信息 self.num_classes x 轴旋转45度
# 设置 y 轴坐标 label
plt.yticks(range(self.num_classes), self.labels)
# 显示 color bar 可以通过颜色的密度看出数值的分布
plt.colorbar()
plt.xlabel("true_label")
plt.ylabel("Predicted_label")
plt.title("ConfusionMatrix")
# 在图中标注数量 概率信息
thresh = matrix.max() / 2
# 设定阈值来设定数值文本的颜色 开始遍历图像的时候一般是图像的左上角
for x in range(self.num_classes):
for y in range(self.num_classes):
# 这里矩阵的行列交换,因为遍历的方向 第y行 第x列
info = int(matrix[y, x])
plt.text(x, y, info,
verticalalignment='center',
horizontalalignment='center',
color="white" if info > thresh else "black")
plt.tight_layout()
# 图形显示更加的紧凑
plt.show()
if __name__ ==' __main__':
device = torch.device("cuda:0" if torch.cuda.is_available()else "cpu")
print(device)
# 使用验证集的预处理方式
data_transform = transforms.Compose([transforms.Resize(256),
transforms.CenterCrop(224),
transforms.ToTensor()
transforms.Normalize([0.485, 0.456, 0.406], [0.229, 0.224, 0.225])])
data_loot = os.path.abspath(os.path.join(os.getcwd(), "../.."))
# get data root path
image_path = data_loot + "/data_set/flower_data/"
# flower data set path
validate_dataset = datasets.ImageFolder(root=image_path +"val",
transform=data_transform)
batch_size = 16
validate_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoder(validate_dataset,
batch_size=batch_size,
shuffle=False,
num_workers=2)
net = MobileNetV2(num_classes=5)
#加载预训练的权重
model_weight_path = "./MobileNetV2.pth"
net.load_state_dict(torch.load(model_weight_path, map_location=device))
net.to(device)
#read class_indict
try:
json_file = open('./class_indicts.json', 'r')
class_indict = json.load(json_file)
except Exception as e:
print(e)
exit(-1)
labels = [label for _, label in class_indict.item()]
# 通过json文件读出来的label
confusion = ConfusionMatrix(num_classes=5, labels=labels)
net.eval()
# 启动验证模式
# 通过上下文管理器 no_grad 来停止pytorch的变量对梯度的跟踪
with torch.no_grad():
for val_data in validate_loader:
val_images, val_labels = val_data
outputs = net(val_images.to(device))
outputs = torch.softmax(outputs, dim=1)
outputs = torch.argmax(outputs, dim=1)
# 获取概率最大的元素
confusion.update(outputs.numpy(), val_labels.numpy())
# 预测值和标签值
confusion.plot()
# 绘制混淆矩阵
confusion.summary()
# 来打印各个指标信息
是这样的 这篇算是一个学习笔记,其中的基础图都源于我的导师

霹雳吧啦Wz的个人空间_哔哩哔哩_bilibili
欢迎无依无靠的CV同学加入
讲的非常好 代码其实也是导师给的
我能做的就是读懂每一行加点注释
给不想看视频的同学留点时间
文章出处登录后可见!
已经登录?立即刷新
