前言
系统环境是win10,显卡RTX3080;cuda10.2,cudnn7.1;OpenCV4.5;yolov5用的是5s的模型,2020年8月13日的发布v3.0这个版本; ncnn版本是20210525;C++ IDE vs2019.
1.环境安装
1.anaconda环境
- 创建环境
conda create --name yolov5 python=3.7
activate yolov5
- 退出环境
conda deactivate
查看已安装的环境
conda info --env
- 删除环境
conda env remove -n yolov5
2.安装依赖
git clone https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5.git
cd yolov5
pip install -r requirements.txt
要么
git clone https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5.git
cd yolov5
conda install pytorch torchvision cudatoolkit=10.2 -c pytorch
pip install cython matplotlib tqdm opencv-python tensorboard scipy pillow onnx pyyaml pandas seaborn
win下尽量不要用cuda11,试了几次都是要么找不到GPU,要么跑到一半崩了。
2.数据处理
1.数据标注用labelme,身份证的数据我从网上找了一些公开的模板数据,然后用对抗生成了一批数据进行标注,300张样本左右。
2.在yolo/data 目录下创建一个存放数据集的目录,目录下再分两个目录,JPEGImages存放原始图像,Annotations存在放标签文件。
3.数据标注用labelme标注成.xml,但yolo要的标签格式是.txt,所以要把数据转换过来。
- 数据生成训练集与验证集,在data/xxxx目录下会 train.txt 和val.txt,输出所有标注的类名,并在JPEGImages下生成与文件名对应的.txt文件。
执行订单:
python generate_txt.py --img_path data/XXXXX/JPEGImages --xml_path data/XXXXX/Annotations --out_path data/XXXXX
- 输出标注的类名样例:如[‘ida’, ‘idb’]。
- 生成的.txt文件
类名 归一化目标坐标点
0 0.518 0.7724887556221889 0.296 0.15367316341829085
3 0.4475 0.7694902548725637 0.089 0.08620689655172414
- 数据处理代码
import os
import glob
import argparse
import random
import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET
from PIL import Image
from tqdm import tqdm
def get_all_classes(xml_path):
xml_fns = glob.glob(os.path.join(xml_path, '*.xml'))
class_names = []
for xml_fn in xml_fns:
tree = ET.parse(xml_fn)
root = tree.getroot()
for obj in root.iter('object'):
cls = obj.find('name').text
class_names.append(cls)
return sorted(list(set(class_names)))
def convert_annotation(img_path, xml_path, class_names, out_path):
output = []
im_fns = glob.glob(os.path.join(img_path, '*.jpg'))
for im_fn in tqdm(im_fns):
if os.path.getsize(im_fn) == 0:
continue
xml_fn = os.path.join(xml_path, os.path.splitext(os.path.basename(im_fn))[0] + '.xml')
if not os.path.exists(xml_fn):
continue
img = Image.open(im_fn)
height, width = img.height, img.width
tree = ET.parse(xml_fn)
root = tree.getroot()
anno = []
xml_height = int(root.find('size').find('height').text)
xml_width = int(root.find('size').find('width').text)
if height != xml_height or width != xml_width:
print((height, width), (xml_height, xml_width), im_fn)
continue
for obj in root.iter('object'):
cls = obj.find('name').text
cls_id = class_names.index(cls)
xmlbox = obj.find('bndbox')
xmin = int(xmlbox.find('xmin').text)
ymin = int(xmlbox.find('ymin').text)
xmax = int(xmlbox.find('xmax').text)
ymax = int(xmlbox.find('ymax').text)
cx = (xmax + xmin) / 2.0 / width
cy = (ymax + ymin) / 2.0 / height
bw = (xmax - xmin) * 1.0 / width
bh = (ymax - ymin) * 1.0 / height
anno.append('{} {} {} {} {}'.format(cls_id, cx, cy, bw, bh))
if len(anno) > 0:
output.append(im_fn)
with open(im_fn.replace('.jpg', '.txt'), 'w') as f:
f.write('\n'.join(anno))
random.shuffle(output)
train_num = int(len(output) * 0.9)
with open(os.path.join(out_path, 'train.txt'), 'w') as f:
f.write('\n'.join(output[:train_num]))
with open(os.path.join(out_path, 'val.txt'), 'w') as f:
f.write('\n'.join(output[train_num:]))
def parse_args():
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser('generate annotation')
parser.add_argument('--img_path', type=str, help='input image directory')
parser.add_argument('--xml_path', type=str, help='input xml directory')
parser.add_argument('--out_path', type=str, help='output directory')
args = parser.parse_args()
return args
if __name__ == '__main__':
args = parse_args()
class_names = get_all_classes(args.xml_path)
print(class_names)
convert_annotation(args.img_path, args.xml_path, class_names, args.out_path)
3.模型训练
1.model/yolov5s.yaml,更改nc数目。
# parameters
nc: 2 # 检测总类别
depth_multiple: 0.33 # model depth multiple 网络的深度系数
width_multiple: 0.50 # layer channel multiple 卷积核的系数
# anchors 候选框,可以改成自己目标的尺寸,也可以增加候选框
anchors:
- [10,13, 16,30, 33,23] # P3/8
- [30,61, 62,45, 59,119] # P4/16
- [116,90, 156,198, 373,326] # P5/32
# YOLOv5 backbone
backbone: #特征提取模块
# [from, number, module, args]
# from - 输入是什么,-1:上一层的输出结果;
# number - 该层的重复的次数,要乘以系数,小于1则等于1 源码( n = max(round(n * gd), 1) if n > 1 else n)
# module - 层的名字
# args - 卷积核的个数
[[-1, 1, Focus, [64, 3]], # 0-P1/2 # 64要乘以卷积核的个数 64*0.5 = 32个特征图
[-1, 1, Conv, [128, 3, 2]], # 1-P2/4
[-1, 3, BottleneckCSP, [128]],
[-1, 1, Conv, [256, 3, 2]], # 3-P3/8
[-1, 9, BottleneckCSP, [256]],
[-1, 1, Conv, [512, 3, 2]], # 5-P4/16
[-1, 9, BottleneckCSP, [512]],
[-1, 1, Conv, [1024, 3, 2]], # 7-P5/32
[-1, 1, SPP, [1024, [5, 9, 13]]],
[-1, 3, BottleneckCSP, [1024, False]], # 9
]
# YOLOv5 head
head:
[[-1, 1, Conv, [512, 1, 1]],
[-1, 1, nn.Upsample, [None, 2, 'nearest']],
[[-1, 6], 1, Concat, [1]], # cat backbone P4
[-1, 3, BottleneckCSP, [512, False]], # 13
[-1, 1, Conv, [256, 1, 1]],
[-1, 1, nn.Upsample, [None, 2, 'nearest']],
[[-1, 4], 1, Concat, [1]], # cat backbone P3
[-1, 3, BottleneckCSP, [256, False]], # 17 (P3/8-small)
[-1, 1, Conv, [256, 3, 2]],
[[-1, 14], 1, Concat, [1]], # cat head P4
[-1, 3, BottleneckCSP, [512, False]], # 20 (P4/16-medium)
[-1, 1, Conv, [512, 3, 2]],
[[-1, 10], 1, Concat, [1]], # cat head P5
[-1, 3, BottleneckCSP, [1024, False]], # 23 (P5/32-large)
[[17, 20, 23], 1, Detect, [nc, anchors]], # Detect(P3, P4, P5) [17,20,23] #17层、20层、23层;
]
2.在data目录下添加一个xxx.yaml训练数据配置文件。
# download command/URL (optional)
download: bash data/scripts/get_voc.sh
# 训练集txt与验证集txt路径
train: data/xxx/train.txt
val: data/xxx/val.txt
# 总类别数
nc: 2
# 类名
names: ['ida', 'idb']
3.训练参数
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
parser.add_argument('--weights', type=str, default='yolov5s.pt', help='initial weights path') # 权重文件,是否在使用预训练权重文件
parser.add_argument('--cfg', type=str, default='', help='model.yaml path') # 网络配置文件
parser.add_argument('--data', type=str, default='data/coco128.yaml', help='data.yaml path') # 训练数据集目录
parser.add_argument('--hyp', type=str, default='data/hyp.scratch.yaml', help='hyperparameters path') #超参数配置文件
parser.add_argument('--epochs', type=int, default=300) # 训练迭代次数
parser.add_argument('--batch-size', type=int, default=32, help='total batch size for all GPUs') # batch-size大小
parser.add_argument('--img-size', nargs='+', type=int, default=[640, 640], help='[train, test] image sizes') # 训练图像大小
parser.add_argument('--rect', action='store_true', help='rectangular training') #矩形训练
parser.add_argument('--resume', nargs='?', const=True, default=False, help='resume most recent training') # 是否接着上一次的日志权重继续训练
parser.add_argument('--nosave', action='store_true', help='only save final checkpoint') # 不保存
parser.add_argument('--notest', action='store_true', help='only test final epoch') # 不测试
parser.add_argument('--noautoanchor', action='store_true', help='disable autoanchor check')
parser.add_argument('--evolve', action='store_true', help='evolve hyperparameters') #超参数范围
parser.add_argument('--bucket', type=str, default='', help='gsutil bucket')
parser.add_argument('--cache-images', action='store_true', help='cache images for faster training') #是否缓存图像
parser.add_argument('--image-weights', action='store_true', help='use weighted image selection for training')
parser.add_argument('--device', default='', help='cuda device, i.e. 0 or 0,1,2,3 or cpu') # 用GPU或者CPU进行训练
parser.add_argument('--multi-scale', action='store_true', help='vary img-size +/- 50%%') #是否多尺度训练
parser.add_argument('--single-cls', action='store_true', help='train as single-class dataset') # 是否一个类别
parser.add_argument('--adam', action='store_true', help='use torch.optim.Adam() optimizer') # 优化器先择
parser.add_argument('--sync-bn', action='store_true', help='use SyncBatchNorm, only available in DDP mode')
parser.add_argument('--local_rank', type=int, default=-1, help='DDP parameter, do not modify')
parser.add_argument('--log-imgs', type=int, default=16, help='number of images for W&B logging, max 100')
parser.add_argument('--workers', type=int, default=8, help='maximum number of dataloader workers') #win不能改,win上改不改都容易崩
parser.add_argument('--project', default='runs/train', help='save to project/name')
parser.add_argument('--name', default='exp', help='save to project/name')
parser.add_argument('--exist-ok', action='store_true', help='existing project/name ok, do not increment')
opt = parser.parse_args()
4.训练命令
- 单卡:
python train.py --cfg models/yolov5s.yaml --data data/ODID.yaml --hyp data/hyps/hyp.scratch.yaml --epochs 100 --multi-scale --device 0
- Doka:
python train.py --cfg models/yolov5s.yaml --data data/ODID.yaml --hyp data/hyps/hyp.scratch.yaml --epochs 100 --multi-scale --device 0,1
5.测试模型
python test.py --weights runs/train/exp/weights/best.pt --data data/ODID.yaml --device 0 --verbose
--weights: 训练得到的模型
--data:数据配置文件.txt
--device:选择gpu进行评测
--verbose:是否打印每一类的评测指标
OpenCV DNN C++ 推理
1.由于OpenCV DNN中的slice层不支持step为2,所以在转换模型时需要修改代码,修改的地方在models/common.py中Focus类
- 修复前:
class Focus(nn.Module):
# Focus wh information into c-space
def __init__(self, c1, c2, k=1, s=1, p=None, g=1, act=True): # ch_in, ch_out, kernel, stride, padding, groups
super(Focus, self).__init__()
self.conv = Conv(c1 * 4, c2, k, s, p, g, act)
def forward(self, x): # x(b,c,w,h) -> y(b,4c,w/2,h/2)
return self.conv(torch.cat([x[..., ::2, ::2], x[..., 1::2, ::2], x[..., ::2, 1::2], x[..., 1::2, 1::2]], 1))
- 修改后
class Focus(nn.Module):
# Focus wh information into c-space
def __init__(self, c1, c2, k=1, s=1, p=None, g=1, act=True): # ch_in, ch_out, kernel, stride, padding, groups
super(Focus, self).__init__()
self.conv = Conv(c1 * 4, c2, k, s, p, g, act)
def forward(self, x): # x(b,c,w,h) -> y(b,4c,w/2,h/2)
#return self.conv(torch.cat([x[..., ::2, ::2], x[..., 1::2, ::2], x[..., ::2, 1::2], x[..., 1::2, 1::2]], 1))
return self.conv(x)
2.转换模型
python models/export.py --weights runs/exp/weights/best.pt
# --weights: 训练得到的模型
运行后,onnx模型保存为了runs/exp/weights/best.onnx,这个模型就可以用OpenCV DNN进行推理。
3.DNN C++推理
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <fstream>
#include <sstream>
#include <opencv2/opencv.hpp>
#include <opencv2/dnn.hpp>
void imshow(std::string name, const cv::Mat& cv_src)
{
cv::namedWindow(name, 0);
int max_rows = 800;
int max_cols = 800;
if (cv_src.rows >= cv_src.cols && cv_src.rows > max_rows)
{
cv::resizeWindow(name, cv::Size(cv_src.cols * max_rows / cv_src.rows, max_rows));
}
else if (cv_src.cols >= cv_src.rows && cv_src.cols > max_cols)
{
cv::resizeWindow(name, cv::Size(max_cols, cv_src.rows * max_cols / cv_src.cols));
}
cv::imshow(name, cv_src);
}
inline float sigmoid(float x)
{
return 1.f / (1.f + exp(-x));
}
void sliceAndConcat(cv::Mat& img, cv::Mat* input)
{
const float* srcData = img.ptr<float>();
float* dstData = input->ptr<float>();
using Vec12f = cv::Vec<float, 12>;
for (int i = 0; i < input->size[2]; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < input->size[3]; j++)
{
for (int k = 0; k < 3; ++k)
{
dstData[k * input->size[2] * input->size[3] + i * input->size[3] + j] =
srcData[k * img.size[2] * img.size[3] + 2 * i * img.size[3] + 2 * j];
}
for (int k = 0; k < 3; ++k)
{
dstData[(3 + k) * input->size[2] * input->size[3] + i * input->size[3] + j] =
srcData[k * img.size[2] * img.size[3] + (2 * i + 1) * img.size[3] + 2 * j];
}
for (int k = 0; k < 3; ++k)
{
dstData[(6 + k) * input->size[2] * input->size[3] + i * input->size[3] + j] =
srcData[k * img.size[2] * img.size[3] + 2 * i * img.size[3] + 2 * j + 1];
}
for (int k = 0; k < 3; ++k)
{
dstData[(9 + k) * input->size[2] * input->size[3] + i * input->size[3] + j] =
srcData[k * img.size[2] * img.size[3] + (2 * i + 1) * img.size[3] + 2 * j + 1];
}
}
}
}
std::vector<cv::String> getOutputNames(const cv::dnn::Net& net)
{
static std::vector<cv::String> names;
if (names.empty())
{
std::vector<int> outLayers = net.getUnconnectedOutLayers();
std::vector<cv::String> layersNames = net.getLayerNames();
names.resize(outLayers.size());
for (size_t i = 0; i < outLayers.size(); i++)
{
names[i] = layersNames[outLayers[i] - 1];
}
}
return names;
}
void drawPred(int classId, float conf, int left, int top, int right, int bottom, cv::Mat& frame,
const std::vector<std::string> &classes)
{
cv::rectangle(frame, cv::Point(left, top), cv::Point(right, bottom), cv::Scalar(0, 255, 0), 3);
std::string label = cv::format("%.2f", conf);
if (!classes.empty()) {
CV_Assert(classId < (int)classes.size());
label = classes[classId] + ": " + label;
}
int baseLine;
cv::Size labelSize = cv::getTextSize(label, cv::FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.5, 1, &baseLine);
top = std::max(top, labelSize.height);
cv::rectangle(frame, cv::Point(left, top - round(1.5 * labelSize.height)), cv::Point(left + round(1.5 * labelSize.width), top + baseLine), cv::Scalar(0, 255, 0), cv::FILLED);
cv::putText(frame, label, cv::Point(left, top), cv::FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.75, cv::Scalar(), 2);
}
void postprocess(cv::Mat& cv_src, std::vector<cv::Mat>& outs, const std::vector<std::string>& classes, int net_size)
{
float confThreshold = 0.4f;
float nmsThreshold = 0.5f;
std::vector<int> classIds;
std::vector<float> confidences;
std::vector<cv::Rect> boxes;
int strides[] = { 8, 16, 32 };
std::vector<std::vector<int> > anchors =
{
{ 10,13, 16,30, 33,23 },
{ 30,61, 62,45, 59,119 },
{ 116,90, 156,198, 373,326 }
};
for (size_t k = 0; k < outs.size(); k++)
{
float* data = outs[k].ptr<float>();
int stride = strides[k];
int num_classes = outs[k].size[4] - 5;
for (int i = 0; i < outs[k].size[2]; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < outs[k].size[3]; j++)
{
for (int a = 0; a < outs[k].size[1]; ++a)
{
float* record = data + a * outs[k].size[2] * outs[k].size[3] * outs[k].size[4] +
i * outs[k].size[3] * outs[k].size[4] + j * outs[k].size[4];
float* cls_ptr = record + 5;
for (int cls = 0; cls < num_classes; cls++)
{
float score = sigmoid(cls_ptr[cls]) * sigmoid(record[4]);
if (score > confThreshold)
{
float cx = (sigmoid(record[0]) * 2.f - 0.5f + (float)j) * (float)stride;
float cy = (sigmoid(record[1]) * 2.f - 0.5f + (float)i) * (float)stride;
float w = pow(sigmoid(record[2]) * 2.f, 2) * anchors[k][2 * a];
float h = pow(sigmoid(record[3]) * 2.f, 2) * anchors[k][2 * a + 1];
float x1 = std::max(0, std::min(cv_src.cols, int((cx - w / 2.f) * (float)cv_src.cols / (float)net_size)));
float y1 = std::max(0, std::min(cv_src.rows, int((cy - h / 2.f) * (float)cv_src.rows / (float)net_size)));
float x2 = std::max(0, std::min(cv_src.cols, int((cx + w / 2.f) * (float)cv_src.cols / (float)net_size)));
float y2 = std::max(0, std::min(cv_src.rows, int((cy + h / 2.f) * (float)cv_src.rows / (float)net_size)));
classIds.push_back(cls);
confidences.push_back(score);
boxes.push_back(cv::Rect(cv::Point(x1, y1), cv::Point(x2, y2)));
}
}
}
}
}
}
std::vector<int> indices;
cv::dnn::NMSBoxes(boxes, confidences, confThreshold, nmsThreshold, indices);
for (size_t i = 0; i < indices.size(); i++)
{
int idx = indices[i];
cv::Rect box = boxes[idx];
drawPred(classIds[idx], confidences[idx], box.x, box.y,
box.x + box.width, box.y + box.height, cv_src, classes);
}
}
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
std::string path = "images";
std::vector<std::string> filenames;
cv::glob(path, filenames, false);
for (auto name : filenames)
{
cv::Mat cv_src = cv::imread(name);
if (cv_src.empty())
{
continue;
}
std::vector<std::string> class_names{ "ida","idb" };
int net_size = 640;
cv::Mat blob = cv::dnn::blobFromImage(cv_src, 1.0 / 255, cv::Size(net_size, net_size),
cv::Scalar(0, 0, 0), true, false);
cv::dnn::Net net = cv::dnn::readNet("model/ODID_DNN.onnx");
const int sz[] = { 1, 12, net_size / 2, net_size / 2 };
cv::Mat input = cv::Mat(4, sz, blob.type());
sliceAndConcat(blob, &input);
net.setInput(input);
auto t0 = cv::getTickCount();
std::vector<cv::Mat> outs;
net.forward(outs, getOutputNames(net));
postprocess(cv_src, outs, class_names, net_size);
auto t1 = cv::getTickCount();
std::cout << "elapsed time: " << (t1 - t0) * 1000.0 / cv::getTickFrequency() << "ms" << std::endl;
imshow("img", cv_src);
cv::waitKey();
}
return 0;
}
输出结果:
4.模型以上传csdn.
四、NCNN推理
NCNN是目前我用到过最好用,也是最容易白嫖的推理加速库,特别是在移动端部署的时候,真的不能更好的了,在些万分感激nihui大佬的无私贡献。这里用的是ncnn编好的ncnn-20210525-windows-vs2019这个版本。
关于yolov5 ncnn推理可以看nihui大佬的知乎。
1.模型简化
https://github.com/daquexian/onnx-simplifier
2 .onnx转ncnn模型
onnx2ncnn yolov5s-sim.onnx yolov5s.param yolov5s.bin
- onnx转为 ncnn 模型,会输出很多 Unsupported slice step!,这是focus模块转换的报错.
- Focus模块在v5中是图片进入backbone前,对图片进行切片操作,具体操作是在一张图片中每隔一个像素拿到一个值,类似于邻近下采样,这样就拿到了四张图片,四张图片互补,长的差不多,但是没有信息丢失,这样一来,将W、H信息就集中到了通道空间,输入通道扩充了4倍,即拼接起来的图片相对于原先的RGB三通道模式变成了12个通道,最后将得到的新图片再经过卷积操作,最终得到了没有信息丢失情况下的二倍下采样特征图。以yolov5s为例,原始的640 × 640 × 3的图像输入Focus结构,采用切片操作,先变成320 × 320 × 12的特征图,再经过一次卷积操作,最终变成320 × 320 × 64的特征图。
- yolov5 Focus模块实现
class Focus(Layer):
def __init__(self, filters, kernel_size, strides=1, padding='SAME'):
super(Focus, self).__init__()
self.conv = Conv(filters, kernel_size, strides, padding)
def call(self, x):
return self.conv(tf.concat([x[..., ::2, ::2, :],
x[..., 1::2, ::2, :],
x[..., ::2, 1::2, :],
x[..., 1::2, 1::2, :]],
axis=-1))
对应的模型结构:
Split splitncnn_input0 1 4 images images_splitncnn_0 images_splitncnn_1 images_splitncnn_2 images_splitncnn_3
Crop Slice_4 1 1 images_splitncnn_3 171 -23309=1,0 -23310=1,2147483647 -23311=1,1
Crop Slice_9 1 1 171 176 -23309=1,0 -23310=1,2147483647 -23311=1,2
Crop Slice_14 1 1 images_splitncnn_2 181 -23309=1,1 -23310=1,2147483647 -23311=1,1
Crop Slice_19 1 1 181 186 -23309=1,0 -23310=1,2147483647 -23311=1,2
Crop Slice_24 1 1 images_splitncnn_1 191 -23309=1,0 -23310=1,2147483647 -23311=1,1
Crop Slice_29 1 1 191 196 -23309=1,1 -23310=1,2147483647 -23311=1,2
Crop Slice_34 1 1 images_splitncnn_0 201 -23309=1,1 -23310=1,2147483647 -23311=1,1
Crop Slice_39 1 1 201 206 -23309=1,1 -23310=1,2147483647 -23311=1,2
Concat Concat_40 4 1 176 186 196 206 207 0=0
可视化: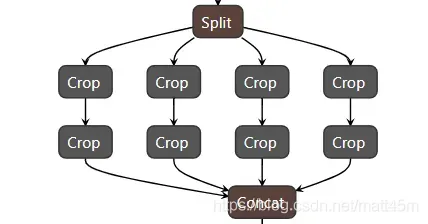
- Focus模块的优点:
Focus的作用无非是使图片在下采样的过程中,不带来信息丢失的情况下,将W、H的信息集中到通道上,再使用3 × 3的卷积对其进行特征提取,使得特征提取得更加的充分。
3 . 替换Focus模块
- 更改.param文件
更改前:
Input images 0 1 images
Split splitncnn_input0 1 4 images images_splitncnn_0 images_splitncnn_1 images_splitncnn_2 images_splitncnn_3
Crop Slice_4 1 1 images_splitncnn_3 171 -23309=1,0 -23310=1,2147483647 -23311=1,1
Crop Slice_9 1 1 171 176 -23309=1,0 -23310=1,2147483647 -23311=1,2
Crop Slice_14 1 1 images_splitncnn_2 181 -23309=1,1 -23310=1,2147483647 -23311=1,1
Crop Slice_19 1 1 181 186 -23309=1,0 -23310=1,2147483647 -23311=1,2
Crop Slice_24 1 1 images_splitncnn_1 191 -23309=1,0 -23310=1,2147483647 -23311=1,1
Crop Slice_29 1 1 191 196 -23309=1,1 -23310=1,2147483647 -23311=1,2
Crop Slice_34 1 1 images_splitncnn_0 201 -23309=1,1 -23310=1,2147483647 -23311=1,1
Crop Slice_39 1 1 201 206 -23309=1,1 -23310=1,2147483647 -23311=1,2
Concat Concat_40 4 1 176 186 196 206 207 0=0
Convolution Conv_41 1 1 207 208 0=32 1=3 11=3 2=1 12=1 3=1 13=1 4=1 14=1 15=1 16=1 5=1 6=3456
更改后:
Input images 0 1 images
YoloV5Focus focus 1 1 images 207
Convolution Conv_41 1 1 207 208 0=32 1=3 11=3 2=1 12=1 3=1 13=1 4=1 14=1 15=1 16=1 5=1 6=3456
4.动态尺寸推理更改
- 静态尺寸推理:按长边缩放到 640xH 或 Wx640,padding 到 640×640 再检测,如果 H/W 比较小,会在 padding 上浪费大量运算。
- 动态尺寸推理:按长边缩放到 640xH 或 Wx640,padding 到 640xH2 或 W2x640 再检测,其中 H2/W2 是 H/W 向上取32倍数,计算量少,速度更快。
- yolov5支持动态尺寸推理, 但这里Reshape 层把输出grid数写死了,不把这三个参数更改成-1的话,则检测的时候会检测不到目标或者检测到满图像都是框。
更改前: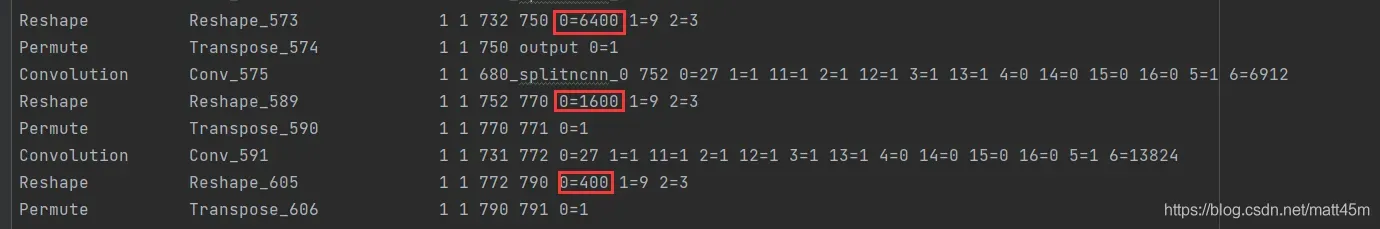
更改后: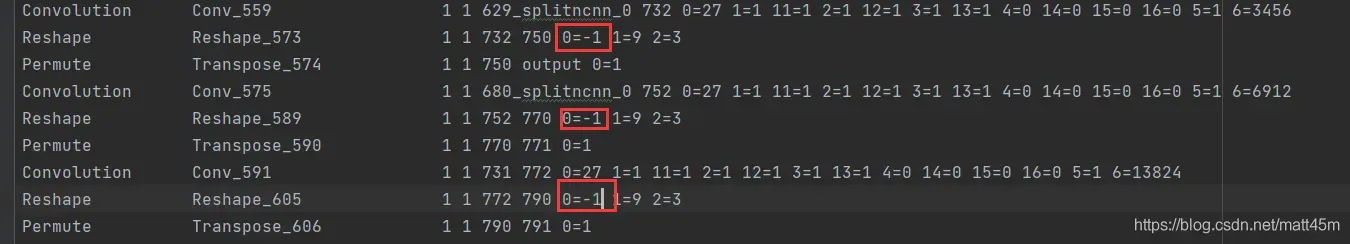
5.更改部层数,改到跟当前层数一样大小。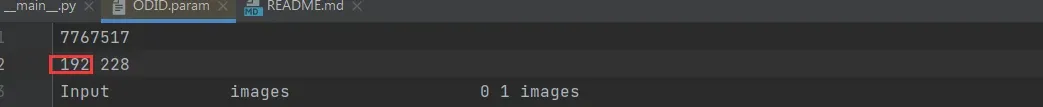
6.转成FP16模型
ncnnoptimize yolov5s.param yolov5s.bin yolov5s-opt.param yolov5s-opt.bin 65536
6.yolov5s模型输出
anchor(先验框)的信息在 yolov5/models/yolov5s.yaml文件里,pytorch的后处理在 yolov5/models/yolo.py Detect类 forward函数,要对着改成c++代码。
模型有3个输出blob,分别对应于 stride 8/16/32 的输出。
每个输出shape的格式是WHC:
- w=n+5,对应于bbox的dx,dy,dw,dh,bbox置信度,n种分类的置信度。
- h=6400,对应于整个图片里全部anchor的xy,这个1600是stride=8的情况,输入640的图片,宽高划分为640/8=80块,80×80即6400
- c=3,对应于三种anchor。
7.NCNN推理代码,动态注册了YoloV5Focus层。
#include "YoloV5Detect.h"
class YoloV5Focus : public ncnn::Layer
{
public:
YoloV5Focus()
{
one_blob_only = true;
}
virtual int forward(const ncnn::Mat& bottom_blob, ncnn::Mat& top_blob, const ncnn::Option& opt) const
{
int w = bottom_blob.w;
int h = bottom_blob.h;
int channels = bottom_blob.c;
int outw = w / 2;
int outh = h / 2;
int outc = channels * 4;
top_blob.create(outw, outh, outc, 4u, 1, opt.blob_allocator);
if (top_blob.empty())
return -100;
#pragma omp parallel for num_threads(opt.num_threads)
for (int p = 0; p < outc; p++)
{
const float* ptr = bottom_blob.channel(p % channels).row((p / channels) % 2) + ((p / channels) / 2);
float* outptr = top_blob.channel(p);
for (int i = 0; i < outh; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < outw; j++)
{
*outptr = *ptr;
outptr += 1;
ptr += 2;
}
ptr += w;
}
}
return 0;
}
};
DEFINE_LAYER_CREATOR(YoloV5Focus)
int initYolov5Net(std::string& param_path, std::string& bin_path, ncnn::Net& yolov5_net,bool use_gpu)
{
bool has_gpu = false;
yolov5_net.clear();
//CPU相关设置(只实现了安卓端)
/// 0 = all cores enabled(default)
/// 1 = only little clusters enabled
/// 2 = only big clusters enabled
//ncnn::set_cpu_powersave(2);
//ncnn::set_omp_num_threads(ncnn::get_big_cpu_count());
#if NCNN_VULKAN
ncnn::create_gpu_instance();
has_gpu = ncnn::get_gpu_count() > 0;
#endif
yolov5_net.opt.use_vulkan_compute = (use_gpu && has_gpu);
yolov5_net.opt.use_bf16_storage = true;
//动态注册层
yolov5_net.register_custom_layer("YoloV5Focus", YoloV5Focus_layer_creator);
//读取模型
int rp = yolov5_net.load_param(param_path.c_str());
int rb = yolov5_net.load_model(bin_path.c_str());
if (rp < 0 || rb < 0)
{
return -1;
}
return 0;
}
static inline float sigmoid(float x)
{
return static_cast<float>(1.f / (1.f + exp(-x)));
}
static void generateProposals(const ncnn::Mat& anchors, int stride, const ncnn::Mat& in_pad, const ncnn::Mat& feat_blob, float prob_threshold, std::vector<Object>& objects)
{
const int num_grid = feat_blob.h;
int num_grid_x;
int num_grid_y;
if (in_pad.w > in_pad.h)
{
num_grid_x = in_pad.w / stride;
num_grid_y = num_grid / num_grid_x;
}
else
{
num_grid_y = in_pad.h / stride;
num_grid_x = num_grid / num_grid_y;
}
const int num_class = feat_blob.w - 5;
const int num_anchors = anchors.w / 2;
for (int q = 0; q < num_anchors; q++)
{
const float anchor_w = anchors[q * 2];
const float anchor_h = anchors[q * 2 + 1];
const ncnn::Mat feat = feat_blob.channel(q);
for (int i = 0; i < num_grid_y; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < num_grid_x; j++)
{
const float* featptr = feat.row(i * num_grid_x + j);
// find class index with max class score
int class_index = 0;
float class_score = -FLT_MAX;
for (int k = 0; k < num_class; k++)
{
float score = featptr[5 + k];
if (score > class_score)
{
class_index = k;
class_score = score;
}
}
float box_score = featptr[4];
float confidence = sigmoid(box_score) * sigmoid(class_score);
if (confidence >= prob_threshold)
{
// yolov5/models/yolo.py Detect forward
// y = x[i].sigmoid()
// y[..., 0:2] = (y[..., 0:2] * 2. - 0.5 + self.grid[i].to(x[i].device)) * self.stride[i] # xy
// y[..., 2:4] = (y[..., 2:4] * 2) ** 2 * self.anchor_grid[i] # wh
float dx = sigmoid(featptr[0]);
float dy = sigmoid(featptr[1]);
float dw = sigmoid(featptr[2]);
float dh = sigmoid(featptr[3]);
float pb_cx = (dx * 2.f - 0.5f + j) * stride;
float pb_cy = (dy * 2.f - 0.5f + i) * stride;
float pb_w = pow(dw * 2.f, 2) * anchor_w;
float pb_h = pow(dh * 2.f, 2) * anchor_h;
float x0 = pb_cx - pb_w * 0.5f;
float y0 = pb_cy - pb_h * 0.5f;
float x1 = pb_cx + pb_w * 0.5f;
float y1 = pb_cy + pb_h * 0.5f;
Object obj;
obj.rect.x = x0;
obj.rect.y = y0;
obj.rect.width = x1 - x0;
obj.rect.height = y1 - y0;
obj.label = class_index;
obj.prob = confidence;
objects.push_back(obj);
}
}
}
}
}
static inline float intersectionArea(const Object& a, const Object& b)
{
cv::Rect_<float> inter = a.rect & b.rect;
return inter.area();
}
static void qsortDescentInplace(std::vector<Object>& faceobjects, int left, int right)
{
int i = left;
int j = right;
float p = faceobjects[(left + right) / 2].prob;
while (i <= j)
{
while (faceobjects[i].prob > p)
i++;
while (faceobjects[j].prob < p)
j--;
if (i <= j)
{
// swap
std::swap(faceobjects[i], faceobjects[j]);
i++;
j--;
}
}
#pragma omp parallel sections
{
#pragma omp section
{
if (left < j) qsortDescentInplace(faceobjects, left, j);
}
#pragma omp section
{
if (i < right) qsortDescentInplace(faceobjects, i, right);
}
}
}
static void qsortDescentInplace(std::vector<Object>& faceobjects)
{
if (faceobjects.empty())
return;
qsortDescentInplace(faceobjects, 0, faceobjects.size() - 1);
}
static void nmsSortedBboxes(const std::vector<Object>& faceobjects, std::vector<int>& picked, float nms_threshold)
{
picked.clear();
const int n = faceobjects.size();
std::vector<float> areas(n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
areas[i] = faceobjects[i].rect.area();
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
const Object& a = faceobjects[i];
int keep = 1;
for (int j = 0; j < (int)picked.size(); j++)
{
const Object& b = faceobjects[picked[j]];
// intersection over union
float inter_area = intersectionArea(a, b);
float union_area = areas[i] + areas[picked[j]] - inter_area;
// float IoU = inter_area / union_area
if (inter_area / union_area > nms_threshold)
keep = 0;
}
if (keep)
{
picked.push_back(i);
}
}
}
int targetDetection(cv::Mat& cv_src, ncnn::Net& yolov5_net, std::vector<Object>& objects, int target_size,
float prob_threshold, float nms_threshold)
{
int w = cv_src.cols, h = cv_src.rows;
float scale = 1.0f;
if (w > h)
{
scale = (float)target_size / (float)w;
w = target_size;
h = h * scale;
}
else
{
scale = (float)target_size / (float)h;
h = target_size;
w = w * scale;
}
ncnn::Mat ncnn_in = ncnn::Mat::from_pixels_resize(cv_src.data, ncnn::Mat::PIXEL_BGR2RGB, cv_src.cols, cv_src.rows, w, h);
//边缘扩展检测的尺寸
//源码在 yolov5/utils/datasets.py letterbox方法
int wpad = (w + 31) / 32 * 32 - w;
int hpad = (h + 31) / 32 * 32 - h;
ncnn::Mat in_pad;
ncnn::copy_make_border(ncnn_in, in_pad, hpad / 2, hpad - hpad / 2, wpad / 2, wpad - wpad / 2, ncnn::BORDER_CONSTANT, 114.f);
const float norm_vals[3] = { 1 / 255.f, 1 / 255.f, 1 / 255.f };
in_pad.substract_mean_normalize(0, norm_vals);
//创建一个提取器
ncnn::Extractor ex = yolov5_net.create_extractor();
ex.input("images", in_pad);
std::vector<Object> proposals;
//stride 8
{
ncnn::Mat out;
ex.extract("750", out);
ncnn::Mat anchors(6);
anchors[0] = 10.f;
anchors[1] = 13.f;
anchors[2] = 16.f;
anchors[3] = 30.f;
anchors[4] = 33.f;
anchors[5] = 23.f;
std::vector<Object> objects8;
generateProposals(anchors, 8, in_pad, out, prob_threshold, objects8);
proposals.insert(proposals.end(), objects8.begin(), objects8.end());
}
stride 16
{
ncnn::Mat out;
ex.extract("771", out);
ncnn::Mat anchors(6);
anchors[0] = 30.f;
anchors[1] = 61.f;
anchors[2] = 62.f;
anchors[3] = 45.f;
anchors[4] = 59.f;
anchors[5] = 119.f;
std::vector<Object> objects16;
generateProposals(anchors, 16, in_pad, out, prob_threshold, objects16);
proposals.insert(proposals.end(), objects16.begin(), objects16.end());
}
// stride 32
{
ncnn::Mat out;
ex.extract("791", out);
ncnn::Mat anchors(6);
anchors[0] = 116.f;
anchors[1] = 90.f;
anchors[2] = 156.f;
anchors[3] = 198.f;
anchors[4] = 373.f;
anchors[5] = 326.f;
std::vector<Object> objects32;
generateProposals(anchors, 32, in_pad, out, prob_threshold, objects32);
proposals.insert(proposals.end(), objects32.begin(), objects32.end());
}
// sort all proposals by score from highest to lowest
qsortDescentInplace(proposals);
// apply nms with nms_threshold
std::vector<int> picked;
nmsSortedBboxes(proposals, picked, nms_threshold);
int count = picked.size();
objects.resize(count);
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++)
{
objects[i] = proposals[picked[i]];
// adjust offset to original unpadded
float x0 = (objects[i].rect.x - (wpad / 2)) / scale;
float y0 = (objects[i].rect.y - (hpad / 2)) / scale;
float x1 = (objects[i].rect.x + objects[i].rect.width - (wpad / 2)) / scale;
float y1 = (objects[i].rect.y + objects[i].rect.height - (hpad / 2)) / scale;
// clip
x0 = std::max(std::min(x0, (float)(cv_src.cols - 1)), 0.f);
y0 = std::max(std::min(y0, (float)(cv_src.rows - 1)), 0.f);
x1 = std::max(std::min(x1, (float)(cv_src.cols - 1)), 0.f);
y1 = std::max(std::min(y1, (float)(cv_src.rows - 1)), 0.f);
objects[i].rect.x = x0;
objects[i].rect.y = y0;
objects[i].rect.width = x1 - x0;
objects[i].rect.height = y1 - y0;
}
return 0;
}
void drawObjects(const cv::Mat& cv_src, const std::vector<Object>& objects,std::vector<std::string> & class_names)
{
cv::Mat cv_detect = cv_src.clone();
for (size_t i = 0; i < objects.size(); i++)
{
const Object& obj = objects[i];
std::cout << "Object label:" << obj.label << " Object prod:" << obj.prob
<<" Object rect" << obj.rect << std::endl;
cv::rectangle(cv_detect, obj.rect, cv::Scalar(255, 0, 0));
std::string text = class_names[obj.label] + " " +std::to_string(int(obj.prob * 100)) +"%";
int baseLine = 0;
cv::Size label_size = cv::getTextSize(text, cv::FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.5, 1, &baseLine);
int x = obj.rect.x;
int y = obj.rect.y - label_size.height - baseLine;
if (y < 0)
y = 0;
if (x + label_size.width > cv_detect.cols)
x = cv_detect.cols - label_size.width;
cv::rectangle(cv_detect, cv::Rect(cv::Point(x, y), cv::Size(label_size.width, label_size.height + baseLine)),
cv::Scalar(255, 255, 255), -1);
cv::putText(cv_detect, text, cv::Point(x, y + label_size.height),
cv::FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.5, cv::Scalar(0, 0, 0));
}
cv::imshow("image", cv_detect);
}
int main(void)
{
std::string parma_path = "models/ODIDF16.param";
std::string bin_parh = "models/ODIDF16.bin";
ncnn::Net yolov5_net;
initYolov5Net(parma_path,bin_parh,yolov5_net,true);
std::vector<std::string> class_names{ "ida", "idb", "idback", "idhead" };
std::string path = "images";
std::vector<std::string> filenames;
cv::glob(path, filenames, false);
for (auto name : filenames)
{
cv::Mat cv_src = cv::imread(name);
if (cv_src.empty())
{
continue;
}
std::vector<Object> objects;
double start = static_cast<double>(cv::getTickCount());
targetDetection(cv_src, yolov5_net, objects);
double time = ((double)cv::getTickCount() - start) / cv::getTickFrequency();
std::cout << name <<"Detection time:" << time << "(second) " << std::endl;
drawObjects(cv_src, objects, class_names);
cv::waitKey();
}
return 0;
}
五、 编译NCNN
1.依赖库:
- protobuf-3.4.0
下载地址:https://github.com/google/protobuf/archive/v3.4.0.zip
打开VS2017或者VS2019本机工具命令,切到源码目录
cd protobuf
mkdir build
cd build
cmake -G"NMake Makefiles" -DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=Release -DCMAKE_INSTALL_PREFIX=%cd%/install -Dprotobuf_BUILD_TESTS=OFF -Dprotobuf_MSVC_STATIC_RUNTIME=OFF ../cmake
nmake
nmake install
- Vulkan
https://vulkan.lunarg.com/sdk/home
版本:VulkanSDK-1.2.141.2
直接点击安装,之后验证是否安装成功,运行C:\VulkanSDK\1.2.141.2\Bin\vkcube.exe,出现下面图像代表安装成功。
- glfw
https://www.glfw.org/
把glfw-3.3.2.bin.WIN64复制到VulkanSDK\1.2.141.2\Third-Party - GLM
https://github.com/g-truc/glm/
把GLM复制到VulkanSDK\1.2.141.2\Third-Party - 添加系统路径
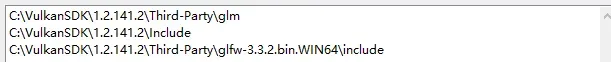
2.NCNN增加自定义层
在代码里面注册自定义层时,用ncnn2mem转换模型之后在移动端推理时会报读入模型错误的问题,ncnn2mem之后的模型是以.h方式全部读入到内存,内存方式注册自定义层的时候,要用 TYPEINDEX 枚举,这里可参考ncnn的增加自定义层。之前用的ncnn库都是下载编译好的库,要增加自定义则要git源码进行重新编译。
2.1 添加自己定义层。 - git 源码
git clone https://github.com/Tencent/ncnn.git
cd ncnn
git submodule update --init
- 在ncnn定义源码添加.h文件:src/layer/YoloV5Focus.h
YoloV5Focus.h
#ifndef LAYER_YOLOOCUS_H
#define LAYER_YOLOOCUS_H
#include "layer.h"
namespace ncnn
{
class YoloV5Focus :public Layer
{
public:
YoloV5Focus();
virtual int forward(const ncnn::Mat& bottom_blob, ncnn::Mat& top_blob, const ncnn::Option& opt) const;
};
}
#endif
- 在ncnn定义源码添加.cpp文件:src/layer/YoloV5Focus.cpp
YoloV5Focus.cpp
#include "YoloV5Focus.h"
namespace ncnn
{
YoloV5Focus::YoloV5Focus()
{
one_blob_only = true;
//support_inplace = true;
}
int YoloV5Focus::forward(const ncnn::Mat& bottom_blob, ncnn::Mat& top_blob, const ncnn::Option& opt) const
{
int w = bottom_blob.w;
int h = bottom_blob.h;
int channels = bottom_blob.c;
int outw = w / 2;
int outh = h / 2;
int outc = channels * 4;
top_blob.create(outw, outh, outc, 4u, 1, opt.blob_allocator);
if (top_blob.empty())
return -100;
#pragma omp parallel for num_threads(opt.num_threads)
for (int p = 0; p < outc; p++)
{
const float* ptr = bottom_blob.channel(p % channels).row((p / channels) % 2) + ((p / channels) / 2);
float* outptr = top_blob.channel(p);
for (int i = 0; i < outh; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < outw; j++)
{
*outptr = *ptr;
outptr += 1;
ptr += 2;
}
ptr += w;
}
}
return 0;
}
}
- 修改 src/CMakeLists.txt 注册 layer/YoloV5Focus
ncnn_add_layer(GroupNorm)
ncnn_add_layer(LayerNorm)
ncnn_add_layer(YoloV5Focus)

- win下OP的名字是大小写不分的,但在别的系统或者移动端要注意层名称的大小写问题。
- 编译ncnn
打开VS2017或者VS2019本机工具命令,切到源码目录
mkdir build
cd build
cmake -G"NMake Makefiles" -DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=Release -DCMAKE_INSTALL_PREFIX=%cd%/install -DProtobuf_INCLUDE_DIR=D:/LIB/protobuf/build/install/include -DProtobuf_LIBRARIES=D:/LIB/protobuf/build/install/lib/libprotobuf.lib -DProtobuf_PROTOC_EXECUTABLE=D:/LIB/protobuf/build/install/bin/protoc.exe -DNCNN_VULKAN=ON ..
nmake
nmake install
六、NCNN Int8量化模型
1.优化模型
./ncnnoptimize yolov5.param yolov5.bin yolov5-opt.param yolov5-opt.bin 0
2.生成校准表
./ncnn2table yolov5s-opt.param yolov5s-opt.bin imagelist.txt yolov5s-opt.table mean=[0,0,0] norm=[0.0039215,0.0039215,0.0039215] shape=[416,416,3] pixel=BGR thread=8 method=kl
3.int8量化模型
./ncnn2int8 yolov5s-opt.param yolov5s-opt.bin yolov5s-int8.param yolov5s-int8.bin yolov5s.table
文章出处登录后可见!
