内容
1.写在前面
2. 数据
3. 代码 – 多元线性回归
3.1 导入库
3.2 导入数据
3.3 多元线性回归模型
3.3.1 多元线性回归-OLS
3.3.2 多元线性回归模型预测值相对误差
3.3.3 残差图
3.3.4 预测值与真实值分布图
4. 代码 – 响应面
4.1 多元二次回归算法
4.2 响应曲面绘制代码
4.3 调用matching_3D绘制响应曲面
1.写在前面
多项式回归与响应面分析法相结合,可以利用响应面图直观地反映复杂的三维关系,从而清晰地表现出两个自变量与一个因变量之间关系的技术方法。
Frontiers | Saturated Dissolved Oxygen Concentration in in situ Fragmentation Bioleaching of Copper Sulfide Ores | Microbiology
本文根据本文数据绘制相关图片。
2. 数据
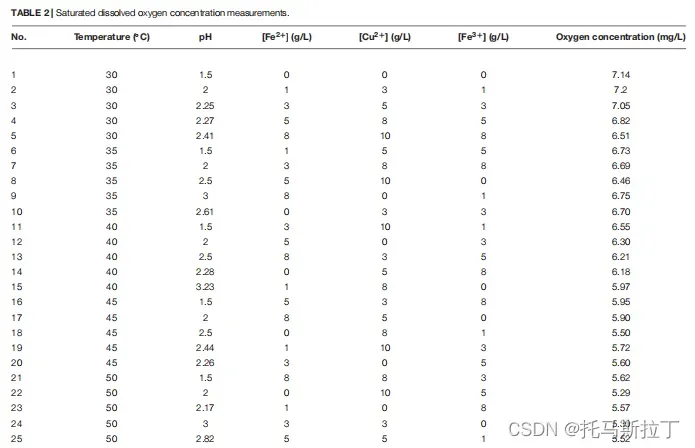
除25组数据外,还加一组自然情况下的基准数据 :
| No. | Temperature | pH | Fe2+ | Cu2+ | Fe3+ | Y |
| 0 | 30 | 6.5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 7.55 |
3. 代码 – 多元线性回归
3.1 导入库
from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d.axes3d import Axes3D
from matplotlib import cm
from pylab import *
from numpy import *
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import pandas as pd
import math
import numpy as np
import copy
plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus']=False #用于解决不能显示负号的问题
mpl.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['SimHei']
3.2 导入数据
#26
xArr = [
[1,30,6.5,0,0,0],
[1,30,1.5,0,0,0],
[1,30,2,1,3,1],
[1,30,2.25,3,5,3],
[1,30,2.27,5,8,5],
[1,30,2.41,8,10,8],
[1,35,1.5,1,5,5],
[1,35,2,3,8,8],
[1,35,2.5,5,10,0],
[1,35,3,8,0,1],
[1,35,2.61,0,3,3],
[1,40,1.5,3,10,1],
[1,40,2,5,0,3],
[1,40,2.5,8,3,5],
[1,40,2.28,0,5,8],
[1,40,3.23,1,8,0],
[1,45,1.5,5,3,8],
[1,45,2,8,5,0],
[1,45,2.5,0,8,1],
[1,45,2.44,1,10,3],
[1,45,2.26,3,0,5],
[1,50,1.5,8,8,3],
[1,50,2,0,10,5],
[1,50,2.17,1,0,8],
[1,50,3,3,3,0],
[1,50,2.82,5,5,1]
]
#26
yArr = [
7.55,
7.14,
7.2,
7.05,
6.82,
6.51,
6.73,
6.69,
6.46,
6.75,
6.70,
6.55,
6.3,
6.21,
6.18,
5.97,
5.95,
5.9,
5.5,
5.72,
5.6,
5.62,
5.29,
5.57,
5.30,
5.21
]
# print(len(xArr),len(yArr))3.3 多元线性回归模型
3.3.1 多元线性回归-OLS
这里插一点和题目不相关的东西,像这种有许多X与对应的Y的数据,可以考虑进行多元线性回归
回归代码如下:(最小二乘)
#最小二乘法 OLS
def standRegres(xArr,yArr):
xMat = mat(xArr)
yMat = mat(yArr).T
xTx = xMat.T*xMat
if linalg.det(xTx) == 0.0:
print("This matrix is singular, cannot do inverse")
return
ws = xTx.I * (xMat.T*yMat)
# print(ws)
return ws3.3.2 多元线性回归模型预测值相对误差
使用多元线性回归方程验证每组数据的相对误差:
mySum = 0
sse = 0
yPerList = []
#采用全部数据进行训练
ws = standRegres(xArr,yArr) #ws即为方程系数
print(ws)
for index,x in enumerate(xArr):
yPer = float(x*ws) #yPer即为预测值
yPerList.append(yPer)
mySum += abs(yPer-yArr[index])*100
sse = (yPer-yArr[index])**2
error = abs(yPer-yArr[index])/yArr[index]*100 #相对误差
# print(yArr[index],round(yPer,2),str(round(error,2))+"%")
plt.plot(index,error,"o")
plt.title(" ",fontsize=13) #图片上方留白
plt.rc('font',family='Arial') #设置字体
plt.rcParams['xtick.direction'] = 'in' #刻度线朝内
plt.rcParams['ytick.direction'] = 'in'
plt.tick_params(labelsize=18) #刻度大小
plt.xlabel("Test No.",fontsize=18)
plt.ylabel("Relative Error/%",fontsize=18)
plt.savefig("线性回归模型各拟合值相对误差",dpi=500,bbox_inches = 'tight') #dpi-清晰度
plt.show()
print("SSE=",sse,"平均相对误差=",round(mySum/sum(yArr),2))
print(corrcoef(yPerList,yArr)[0][1])影响:
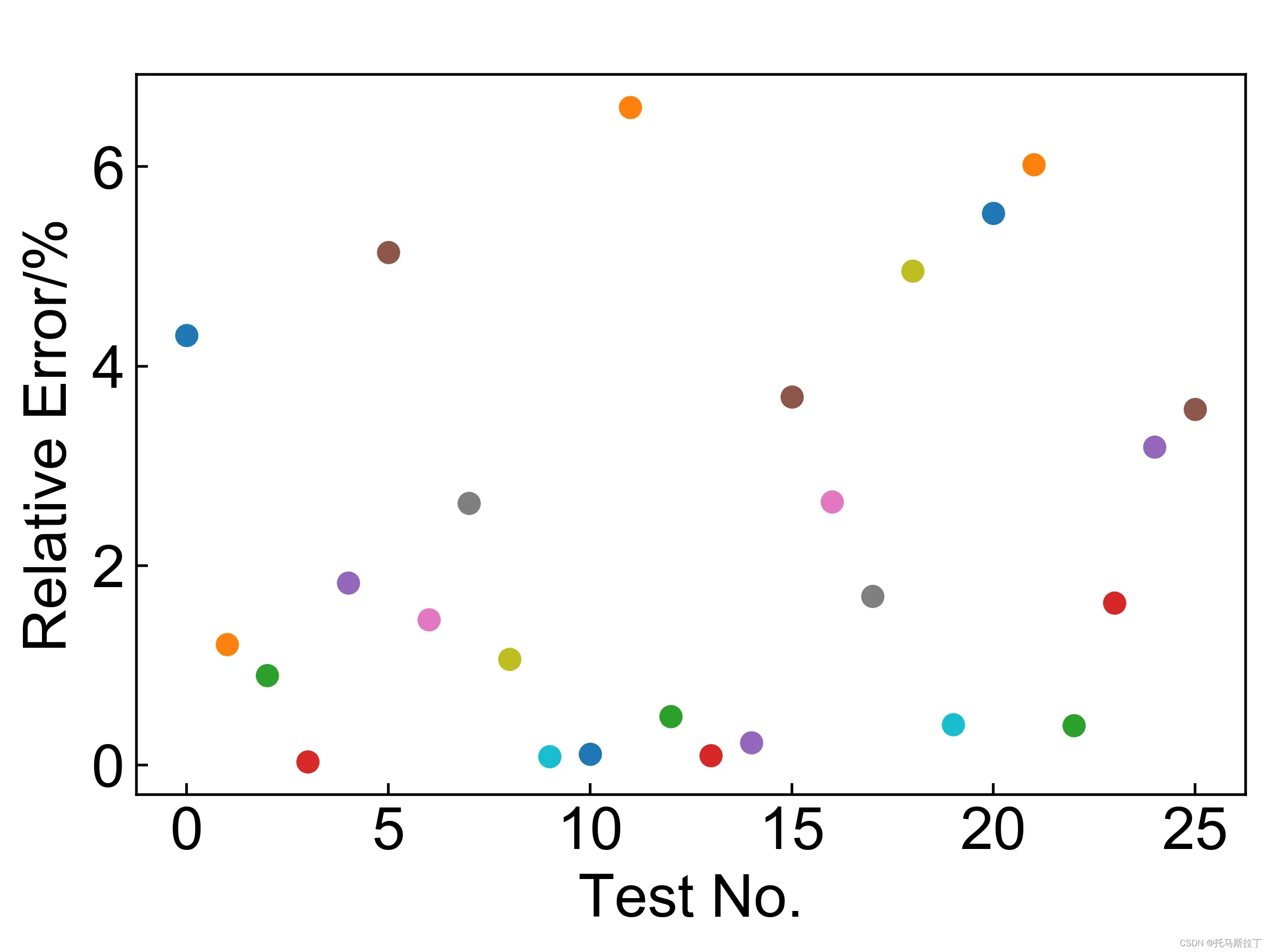
3.3.3 残差图
相关代码:
#残差图
mySum = 0
sse = 0
yPerList = []
#采用全部数据进行训练
ws = standRegres(xArr,yArr)
# print(ws)
for index,x in enumerate(xArr):
yPer = float(x*ws)
residua = yArr[index] - yPer
plt.plot(index,residua,"bo")
x = np.linspace(0,25,100)
plt.plot(x,np.zeros(len(x)),"r")
plt.title(" ",fontsize=13)
plt.rcParams['xtick.direction'] = 'in'
plt.rcParams['ytick.direction'] = 'in'
plt.rc('font',family='Arial')
plt.tick_params(labelsize=18)
plt.xlabel("Test No.",fontsize=18)
plt.ylabel("Residua",fontsize=18)
plt.ylim((-0.5, 0.5))
plt.savefig("残差图.jpg",dpi=500,bbox_inches = 'tight')
plt.show()
影响:
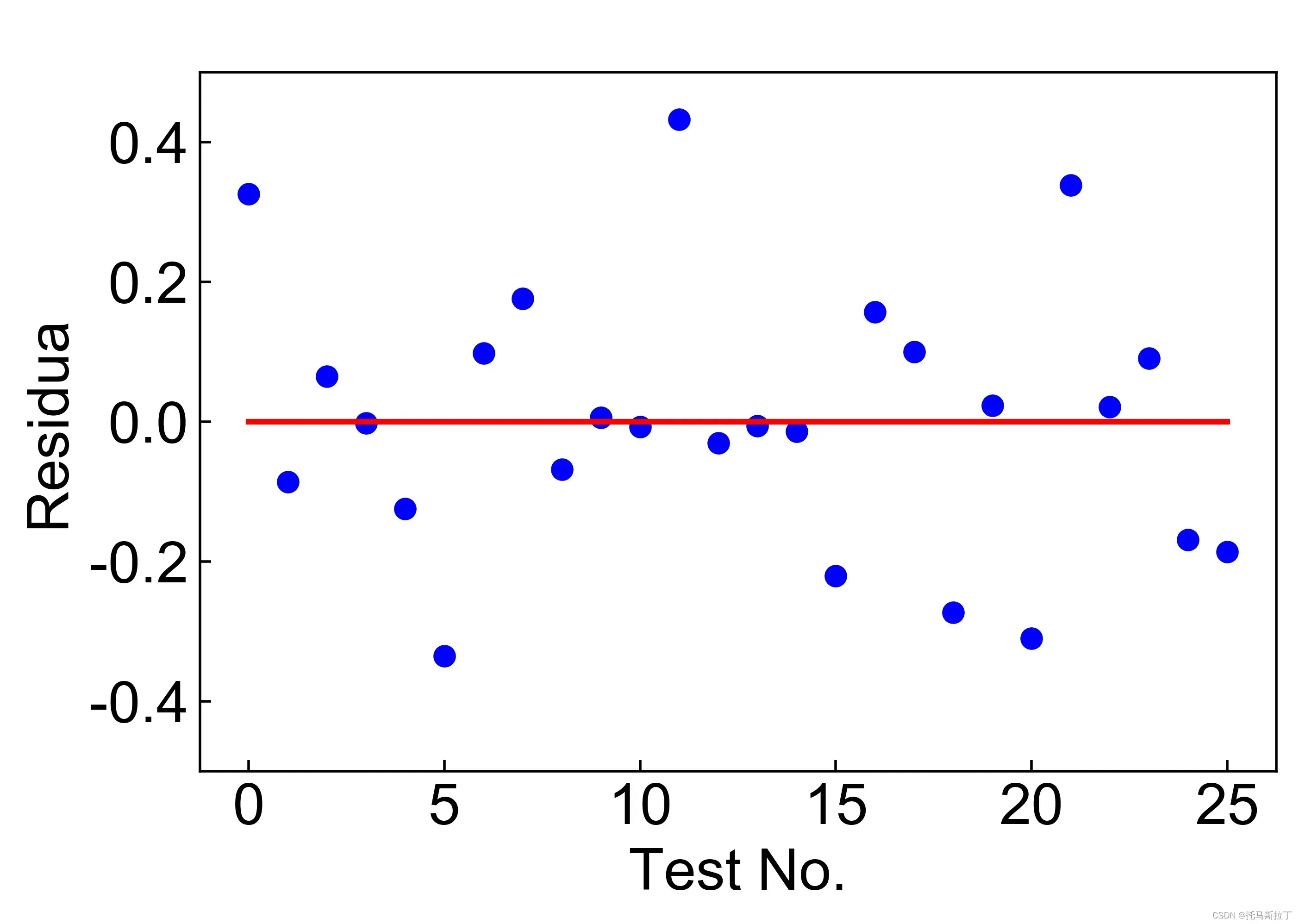
3.3.4 预测值与真实值分布图
相关代码:
#分布图
mySum = 0
sse = 0
yPerList = []
#采用全部数据进行训练
ws = standRegres(xArr,yArr)
# print(ws)
for index,x in enumerate(xArr):
yPer = float(x*ws)
yPerList.append(yPer)
plt.plot(list(range(len(xArr))),yPerList,"bo",label="Fitted value")
plt.plot(list(range(len(xArr))),yArr,"r*",label="Measurement value")
plt.title(" ",fontsize=13)
plt.rc('font',family='Arial')
plt.rcParams['xtick.direction'] = 'in'
plt.rcParams['ytick.direction'] = 'in'
plt.tick_params(labelsize=18)
plt.legend(framealpha=0,loc=(0.45, 0.55),fontsize=15)
plt.xlabel("Test No.",fontsize=18)
plt.ylabel("Oxygen solubility/mg·${{L^-}^1}$",fontsize=18)
plt.savefig("分布图.jpg",dpi=500,bbox_inches = 'tight')
plt.show()
影响:
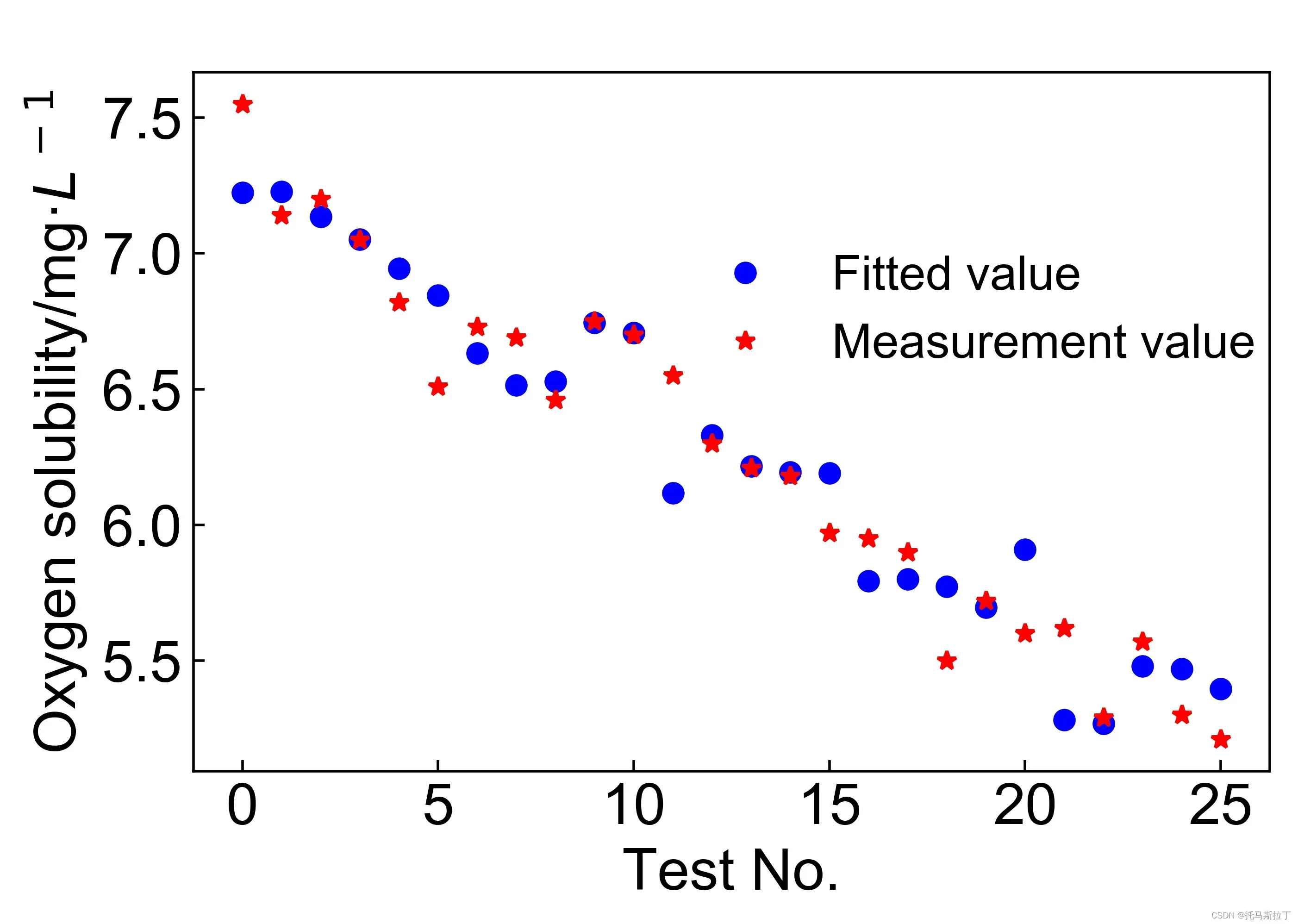
4. 代码 – 响应面
4.1 多元二次回归算法
相关代码:
#最小二乘法曲面拟合
def fun(x):
round(x, 2)
if x >= 0:
return '+'+str(x)
else:
return str(x)
def get_res(X, Y, Z, n):
# 求方程系数
sigma_x = 0
for i in X: sigma_x += i
sigma_y = 0
for i in Y: sigma_y += i
sigma_z = 0
for i in Z: sigma_z += i
sigma_x2 = 0
for i in X: sigma_x2 += i * i
sigma_y2 = 0
for i in Y: sigma_y2 += i * i
sigma_x3 = 0
for i in X: sigma_x3 += i * i * i
sigma_y3 = 0
for i in Y: sigma_y3 += i * i * i
sigma_x4 = 0
for i in X: sigma_x4 += i * i * i * i
sigma_y4 = 0
for i in Y: sigma_y4 += i * i * i * i
sigma_x_y = 0
for i in range(n):
sigma_x_y += X[i] * Y[i]
# print(sigma_xy)
sigma_x_y2 = 0
for i in range(n): sigma_x_y2 += X[i] * Y[i] * Y[i]
sigma_x_y3 = 0
for i in range(n): sigma_x_y3 += X[i] * Y[i] * Y[i] * Y[i]
sigma_x2_y = 0
for i in range(n): sigma_x2_y += X[i] * X[i] * Y[i]
sigma_x2_y2 = 0
for i in range(n): sigma_x2_y2 += X[i] * X[i] * Y[i] * Y[i]
sigma_x3_y = 0
for i in range(n): sigma_x3_y += X[i] * X[i] * X[i] * Y[i]
sigma_z_x2 = 0
for i in range(n): sigma_z_x2 += Z[i] * X[i] * X[i]
sigma_z_y2 = 0
for i in range(n): sigma_z_y2 += Z[i] * Y[i] * Y[i]
sigma_z_x_y = 0
for i in range(n): sigma_z_x_y += Z[i] * X[i] * Y[i]
sigma_z_x = 0
for i in range(n): sigma_z_x += Z[i] * X[i]
sigma_z_y = 0
for i in range(n): sigma_z_y += Z[i] * Y[i]
# print("-----------------------")
# 给出对应方程的矩阵形式
a = np.array([[sigma_x4, sigma_x3_y, sigma_x2_y2, sigma_x3, sigma_x2_y, sigma_x2],
[sigma_x3_y, sigma_x2_y2, sigma_x_y3, sigma_x2_y, sigma_x_y2, sigma_x_y],
[sigma_x2_y2, sigma_x_y3, sigma_y4, sigma_x_y2, sigma_y3, sigma_y2],
[sigma_x3, sigma_x2_y, sigma_x_y2, sigma_x2, sigma_x_y, sigma_x],
[sigma_x2_y, sigma_x_y2, sigma_y3, sigma_x_y, sigma_y2, sigma_y],
[sigma_x2, sigma_x_y, sigma_y2, sigma_x, sigma_y, n]])
b = np.array([sigma_z_x2, sigma_z_x_y, sigma_z_y2, sigma_z_x, sigma_z_y, sigma_z])
# 高斯消元解线性方程
res = np.linalg.solve(a, b)
return res
labelName = ["Oxygen solubility/mg·${{L^-}^1}$",
"T/$^\circ$C",
"pH",
"c(${{Fe^2}^+}$)/g·${{L^-}^1}$",
"c(${{Cu^2}^+}$)/g·${{L^-}^1}$",
"c(${{Fe^3}^+}$)/g·${{L^-}^1}$",]
print(labelName)4.2 响应曲面绘制代码
绘图的核心代码在这里,有兴趣的可以自己研究
变量res的系数就是用4.1节的多元二次回归算法生成的系数
def matching_3D(X, Y, Z,xLabelIndex,yLabelIndex,name,arg1=37,arg2=-72):
n = len(X)
res = get_res(X, Y, Z, n)
# 输出方程形式
print("z=%.6s*x^2%.6s*xy%.6s*y^2%.6s*x%.6s*y%.6s" % (
fun(res[0]), fun(res[1]), fun(res[2]), fun(res[3]), fun(res[4]), fun(res[5])))
# 画曲面图和离散点
fig = plt.figure() # 建立一个空间
ax = fig.add_subplot(111, projection='3d') # 3D坐标
xgrid = np.linspace(min(X),max(X),100)
ygrid = np.linspace(min(Y),max(Y),100)
x,y = np.meshgrid(xgrid,ygrid)
# 给出方程
z = res[0] * x * x + res[1] * x * y + res[2] * y * y + res[3] * x + res[4] * y + res[5]
# 画出曲面
sp = ax.plot_surface(x, y, z, rstride=3, cstride=3, cmap=cm.jet)
ax.contourf(x,y,z,zdir='z',offset=5,cmap = plt.get_cmap('rainbow'))
# 画出点
ax.scatter(X, Y, Z, c='r',label="实测点",alpha=0)
plt.rc('font',family='Arial')
plt.xlabel(labelName[xLabelIndex])
plt.xticks(rotation=30,fontsize=9)
plt.ylabel(labelName[yLabelIndex])
ax.set_zlabel(labelName[0])
# show_text(ax)
# ax.legend()
fig.colorbar(sp)
ax.view_init(elev=arg1, azim=arg2)
plt.rcParams['xtick.direction'] = 'in'
plt.rcParams['ytick.direction'] = 'in'
plt.savefig(name,dpi=500,bbox_inches = 'tight')
fig.show()4.3 调用matching_3D绘制响应曲面
代码:
和4.2节matching_3D的参数对照看:
X与Y为自变量列表-分别为X轴与Y轴
yArr为因变量-Z轴坐标
1、4即为对应4.1节中labelName列表对应的名字 ,用于自动生成响应的坐标名称
T-cu2+即为保存的图片文件名
37,-72用于调整图片视角
%matplotlib notebook
X = []
Y = []
for x,y in zip(xArrMat[:,1],xArrMat[:,4]):
X.append(float(x))
Y.append(float(y))
matching_3D(X,Y,yArr,1,4,"T-cu2+曲面图",37,-72)效果: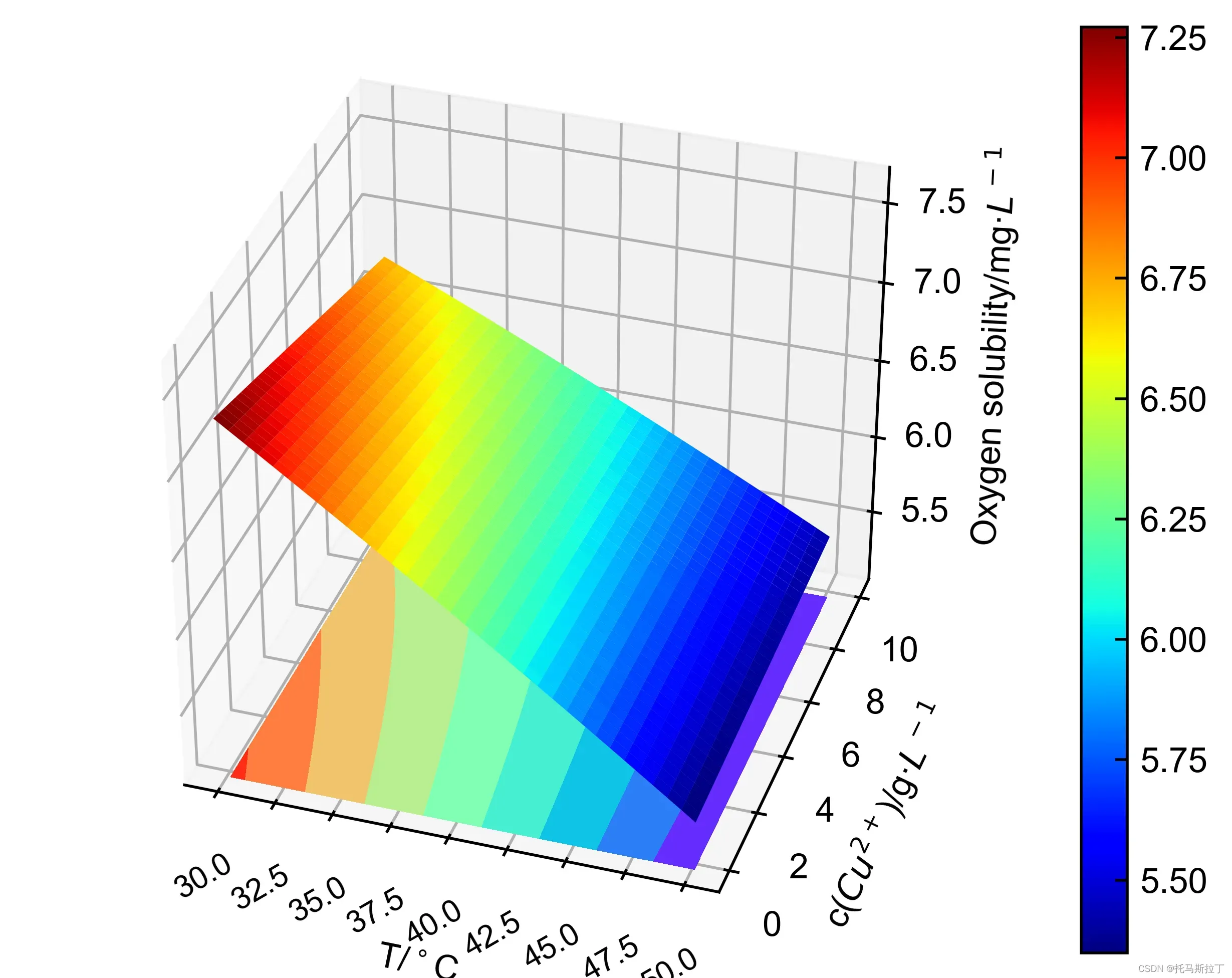
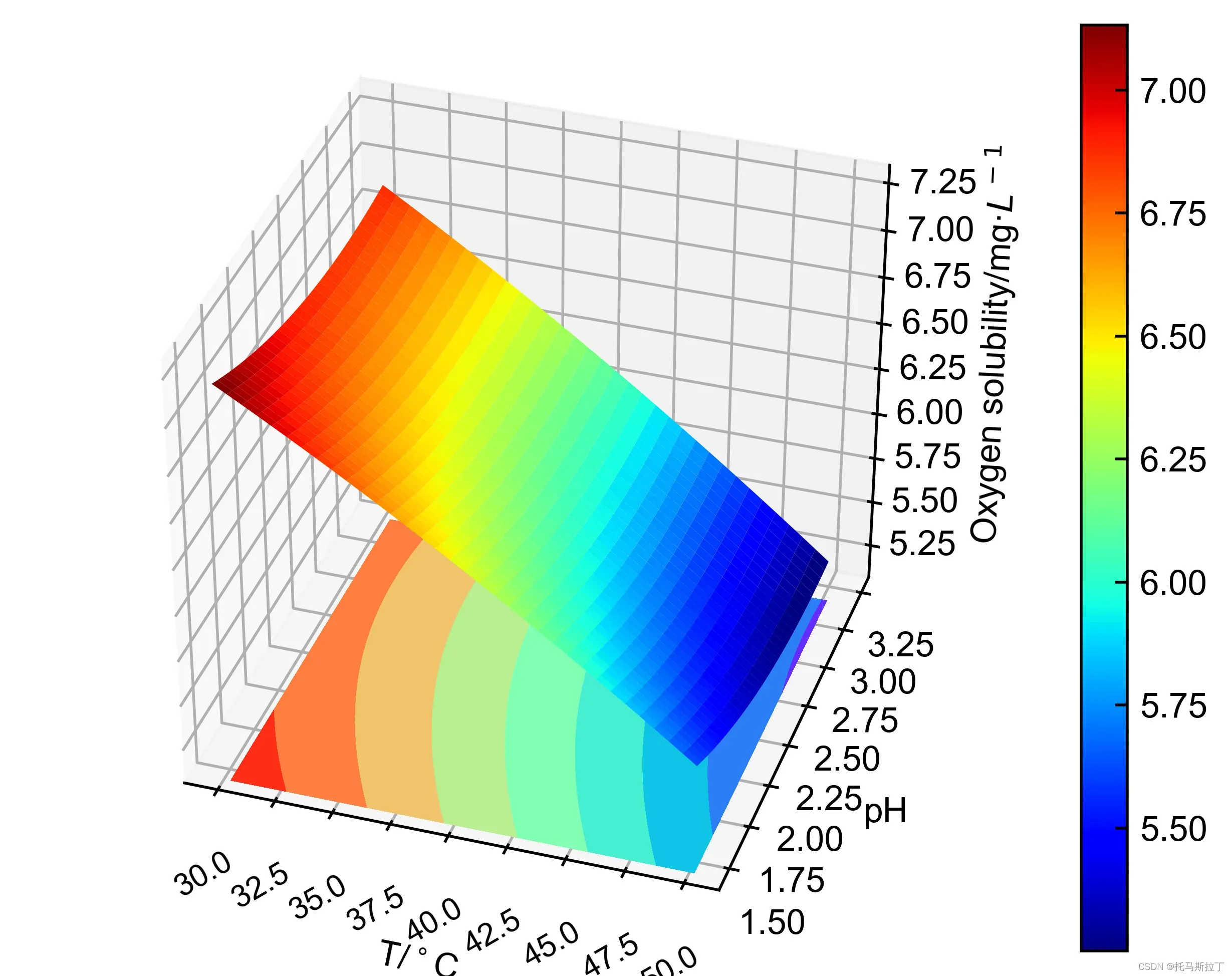
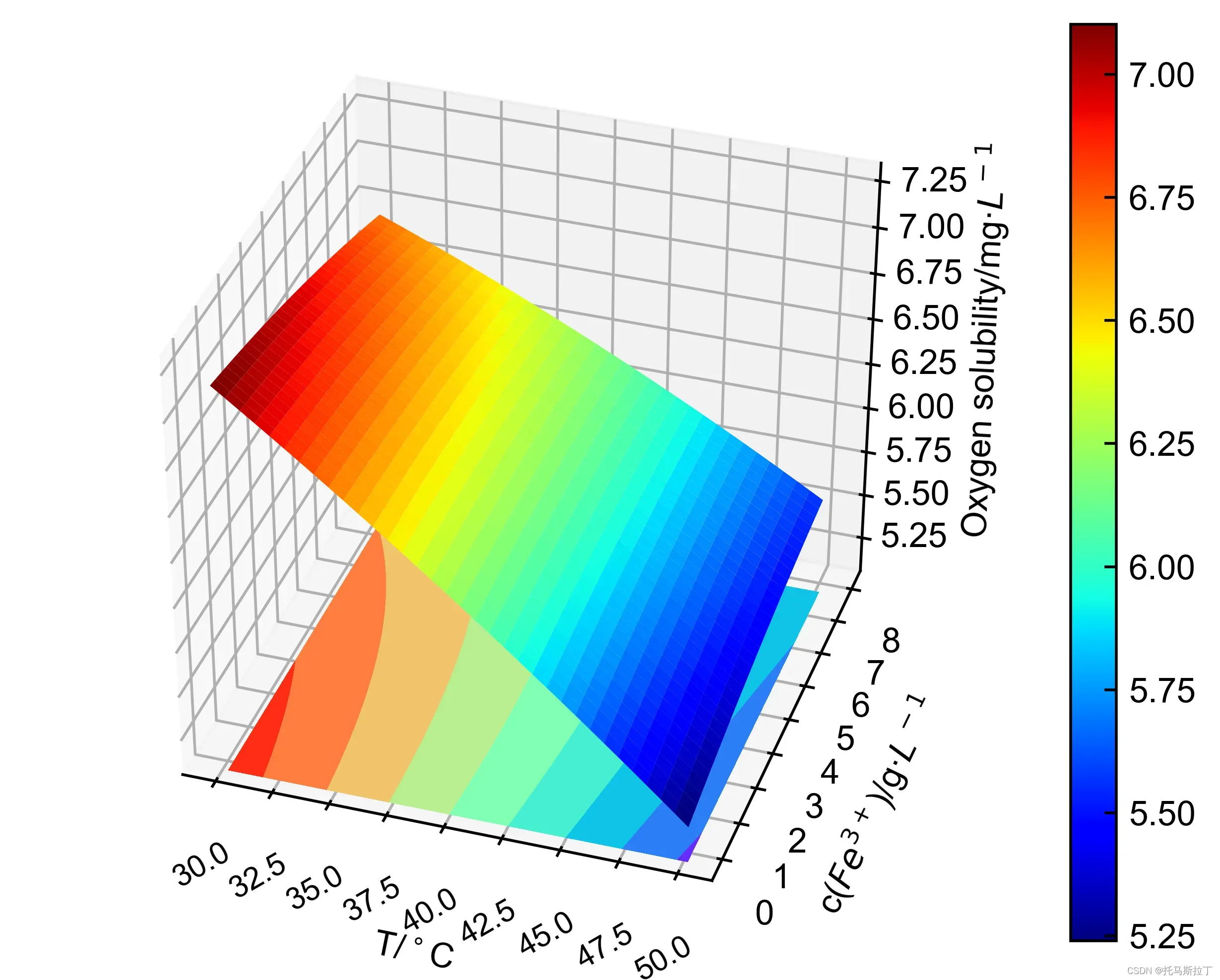
文章出处登录后可见!
已经登录?立即刷新
