其实取标题一直以来都是一件麻烦的事,但是如果你要看下去,我想你得有一点语义分割的见解。
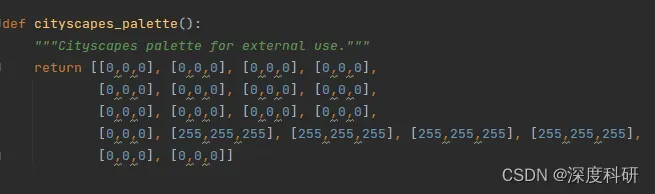
用平常的语言描述该问题就是:语义分割出我们感兴趣的目标物,然后输出该目标物的轮廓点。做语义分割其实有很多种方法,你可以用不同的模型去train你的dataset,但是刚接触语义分割的朋友们可能会说,我该怎么分割出我想要的目标物,而不对其它部分的像素做修改?其实这件事并不复杂,一个很直觉的想法是:修改像素对应的RGB值。那怎么修改对应像素的RGB值呢?举例来说,假设你在mmsegmentation框架下用的是SegFormer模型,你应该在class_names.py文件中修改cityscapes中palette(如上图)
问题的前半段很好解决,那如何解决输出目标物轮廓点这件事情呢?一种比较直觉的想法是:将分割好的图片转为二值图,然后在转为灰度图,之后利用cv2.findContours()函数寻找轮廓点,为了验证轮廓点的准确性,再用cv2.drawContours()函数做可视化处理。这样的处理对一些简单的图片是一种策略,但是对于已经语义分割好的图片,再这样处理会不会有一些“脱裤子放屁——多此一举”呢?答案是肯定的。你想想看,你是怎么将一幅图片语义分割出来的呢?是根据每个像素的类别逐一“上色”的对吧。那这么说来,其实要做输出轮廓点这件事,只要让模型输出一张分割后的二maskt图片,然后转为灰度图,再重复上面说的cv2.findContours()、cv2.drawContours()的操作就可以了吧?
那这里有一个前提,什么前提呢?前提是你已经知道如何修改像素值这件事情。所以在SegFormer里面,你可以在base.py文件中进行修改,一些注释我已经写在代码里面:
def show_result(self,
img,
result, # 这里的result就是每个像素的类别,它的大小应该与你的图片大小有关
palette=None,
win_name='',
show=False,
wait_time=0,
out_file=None):
"""Draw `result` over `img`.
Args:
img (str or Tensor): The image to be displayed.
result (Tensor): The semantic segmentation results to draw over
`img`.
palette (list[list[int]]] | np.ndarray | None): The palette of
segmentation map. If None is given, random palette will be
generated. Default: None
win_name (str): The window name.
wait_time (int): Value of waitKey param.
Default: 0.
show (bool): Whether to show the image.
Default: False.
out_file (str or None): The filename to write the image.
Default: None.
Returns:
img (Tensor): Only if not `show` or `out_file`
"""
img = mmcv.imread(img)
img = img.copy()
seg = result[0]
if palette is None:
if self.PALETTE is None:
palette = np.random.randint(
0, 255, size=(len(self.CLASSES), 3))
else:
palette = self.PALETTE
palette = np.array(palette)
assert palette.shape[0] == len(self.CLASSES)
assert palette.shape[1] == 3
assert len(palette.shape) == 2
color_seg = np.zeros((seg.shape[0], seg.shape[1], 3), dtype=np.uint8)
for label, color in enumerate(palette):
color_seg[seg == label, :] = color # 注意数组的特别用法
# convert to BGR
color_seg = color_seg[..., ::-1]
# from IPython import embed; embed(header='debug vis')
# img = img * 0.5 + color_seg * 0.5 # 这两步是修改的地方
# img = img.astype(np.uint8)
# if out_file specified, do not show image in window
if out_file is not None:
show = False
if show:
mmcv.imshow(img, win_name, wait_time)
if out_file is not None:
mmcv.imwrite(img, out_file)
if not (show or out_file):
warnings.warn('show==False and out_file is not specified, only '
'result image will be returned')
return color_seg #这一步也是修改的地方,原来是return img,这样就是分割出输出,为不是mask后的图输出
有了输出的mask图像(与原始图片的一一对应),就可以很方便的在原图进行可视化操作:
result = inference_segmentor(model_seg, p) # 前向推理,得到每个像素的类别
img_seg = show_result_pyplot(model_seg, p, result, get_palette(opt.palette)) # 得到分割后的mask
img = cv2.imread(p) # 这一步是为了轮廓在原图中显示,我这里的p实际上是我的图片路径
gray_img = cv2.cvtColor(img_seg, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY) # 转为灰度图
contours, _ = cv2.findContours(gray_img, cv2.RETR_TREE, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_NONE) # 寻找轮廓点
res = cv2.drawContours(img, contours, -1, (0, 0, 255), 1) # 绘制轮廓点
可视化后的效果(mask——原图——轮廓):
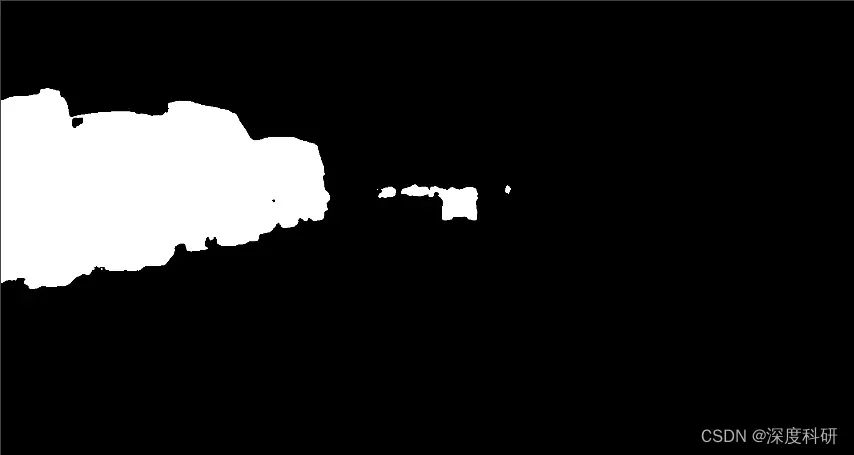
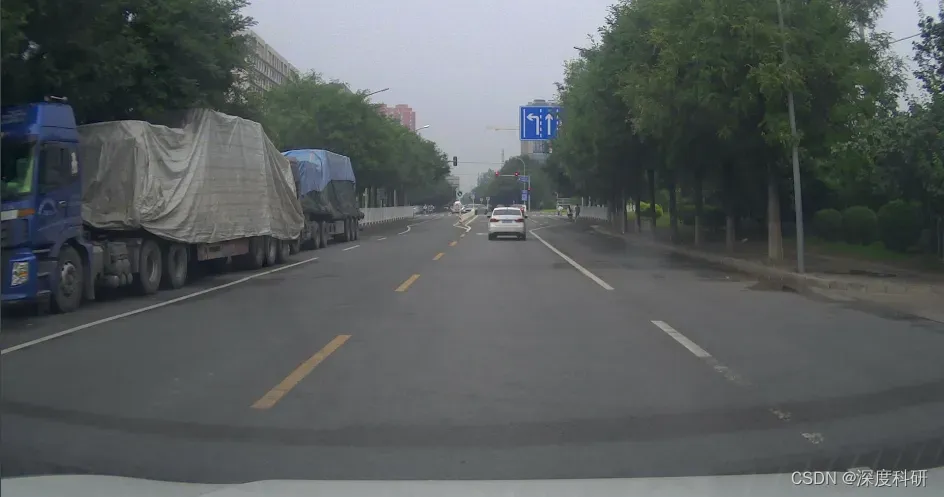



当然,轮廓检测的方法还有很多,希望你不会因此局限。
文章出处登录后可见!
