1、堆外内存存放位置
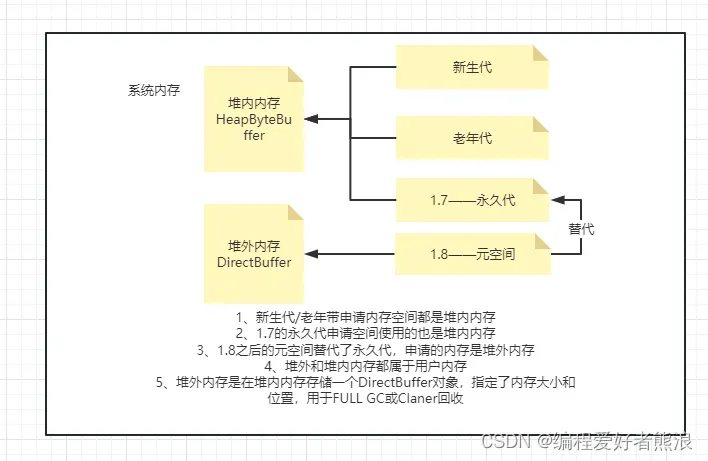
2、为什么需要堆外内存
- 零拷贝:当进行网络I/O 操作、文件读写时,堆内内存都需要转换为堆外内存,然后再与底层设备进行交互。
- 降低JVM GC 对应用程序影响:因为堆外内存不受 JVM 管理。
- 堆外内存可以实现进程之间、JVM 多实例之间的数据共享。
- 因为堆外内存需要手动释放(它的缺点)
一份JVM配置信息,MaxDirectMemorySize就是堆外内存
-Xms6144m -Xmx8192m:最小堆内存和最大堆内存
-XX:SurvivorRatio=8:新生代的 E:S:S= 8:1:1
-XX:NewRatio=1:新生代:老年代 = 1:1
-XX:MetaspaceSize=512m:元空间大小
-XX:MaxMetaspaceSize=512m:元空间最大大小
-XX:MaxDirectMemorySize=512m:最大堆外内存大小
-XX:+UseConcMarkSweepGC:启动CMS垃圾回收
-XX:+PrintGC:打印GC信息
-XX:+PrintGCDetails:GC详情信息
-XX:+PrintGCDateStamps:打印GC时间戳
-Xloggc:/home/admin/logs/vehicle-admin/gc.log:GC文件路径
XX:+UseGCLogFileRotation:GC Log 的滚动功能,需要配置Xloggc
-XX:NumberOfGCLogFiles:GC文件个数
XX:GCLogFileSize:GC文件大小
-XX:+HeapDumpOnOutOfMemoryError:内存溢出,生成headDump文件
XX:HeapDumpPath:堆Dump文件路径,需要配置HeapDumpOnOutOfMemoryError
-Xms6144m -Xmx8192m -XX:SurvivorRatio=8 -XX:NewRatio=1 -XX:MetaspaceSize=512m -XX:MaxMetaspaceSize=512m -XX:MaxDirectMemorySize=512m -XX:+UseConcMarkSweepGC -XX:+PrintGC -XX:+PrintGCDetails -XX:+PrintGCDateStamps -Xloggc:/home/admin/logs/vehicle-admin/gc.log -XX:+UseGCLogFileRotation -XX:NumberOfGCLogFiles=1 -XX:GCLogFileSize=100m -XX:+HeapDumpOnOutOfMemoryError -XX:HeapDumpPath=/home/admin/logs/vehicle-admin/heapDump.bin
3、申请堆外内存
通过Unsafe对象调用allocateMemory方法
Unsafe对象不能直接获得,它申请的内存,需要手动回收,很不安全,但可以通过反射获取
private static Unsafe unsafe = null;
static {
try {
Field getUnsafe = Unsafe.class.getDeclaredField("theUnsafe");
getUnsafe.setAccessible(true);
unsafe = (Unsafe) getUnsafe.get(null);
} catch (NoSuchFieldException | IllegalAccessException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws UnsupportedEncodingException {
//申请10M堆外内存,申请的内存需要手动回收
unsafe.allocateMemory(10 * 1024 * 1024L);
//回收堆外内存
unsafe.freeMemory();
}
netty申请堆外内存做法
public static void main(String[] args) throws UnsupportedEncodingException {
//申请10M堆外内存
ByteBuffer.allocateDirect(10 * 1024 * 1024L);
}
public static ByteBuffer allocateDirect(int capacity) {
return new DirectByteBuffer(capacity);
}
DirectByteBuffer初始化
什么时候抛出堆外内存溢出
系统主动调用FCLL GC,并且在最大时间内(尝试次数和每次尝试时间),还是不能申请到足够的对外内存的时候
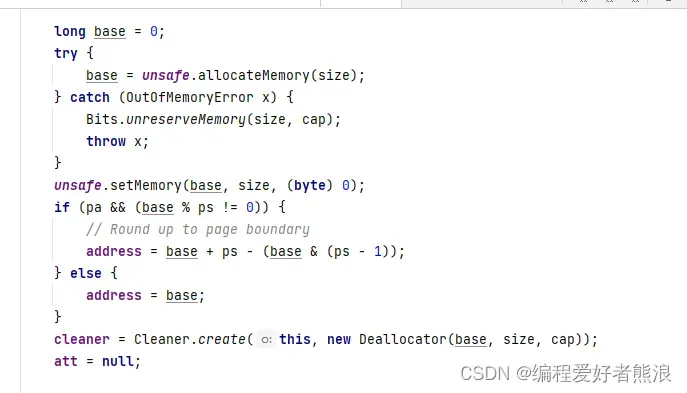
DirectByteBuffer(int cap) { // package-private
super(-1, 0, cap, cap);
//用以判断JVM是否需要对堆外内存进行对齐
boolean pa = VM.isDirectMemoryPageAligned();
//需要连续的也大小进行申请缓存
int ps = Bits.pageSize();
long size = Math.max(1L, (long)cap + (pa ? ps : 0));
//判断能否申请到内存,如果不能,调用一次System.gc()回收一次内存,如果还是不能申请到内存,抛出堆外内存溢出异常。
Bits.reserveMemory(size, cap);
long base = 0;
try {
//真正申请堆外内存
base = unsafe.allocateMemory(size);
} catch (OutOfMemoryError x) {
Bits.unreserveMemory(size, cap);
throw x;
}
//申请到的内存空间
unsafe.setMemory(base, size, (byte) 0);
if (pa && (base % ps != 0)) {
// Round up to page boundary
address = base + ps - (base & (ps - 1));
} else {
address = base;
}
//定义cleaner对象,用于回收堆外内存
cleaner = Cleaner.create(this, new Deallocator(base, size, cap));
att = null;
}
static void reserveMemory(long size, int cap) {
//系统是否设置最大堆外内存
if (!memoryLimitSet && VM.isBooted()) {
maxMemory = VM.maxDirectMemory();
memoryLimitSet = true;
}
// 尝试申请堆外内存,申请成功,直接返回
if (tryReserveMemory(size, cap)) {
return;
}
final JavaLangRefAccess jlra = SharedSecrets.getJavaLangRefAccess();
// retry while helping enqueue pending Reference objects
// which includes executing pending Cleaner(s) which includes
// Cleaner(s) that free direct buffer memory
while (jlra.tryHandlePendingReference()) {
if (tryReserveMemory(size, cap)) {
return;
}
}
// 申请失败,触发一次FULL GC,回收内存,顺带会调用Cleaner回收堆外内存,但并非立即就触发,存在一定的触发和回收时间,下面会判断在最大时间是否能申请到足够的堆外内存
System.gc();
// a retry loop with exponential back-off delays
// (this gives VM some time to do it's job)
boolean interrupted = false;
try {
long sleepTime = 1;
int sleeps = 0;
while (true) {
// 再次尝试申请堆外内存,申请成功,直接返回
if (tryReserveMemory(size, cap)) {
return;
}
// 如果在最大sleep时间还是申请不到,(GC回收完成,还是不能申请到足够的堆外内存),跳出循环,抛出堆外内存溢出
if (sleeps >= MAX_SLEEPS) {
break;
}
if (!jlra.tryHandlePendingReference()) {
try {
Thread.sleep(sleepTime);
sleepTime <<= 1;
sleeps++;
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
interrupted = true;
}
}
}
// no luck
throw new OutOfMemoryError("Direct buffer memory");
} finally {
if (interrupted) {
// don't swallow interrupts
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
}
}
}
VM.isDirectMemoryPageAligned()用以判断JVM是否需要对堆外内存进行对齐,什么是内存页,什么是对齐参考:
内存分页大小对性能的提升原理
内存对齐详解
此参数可以通过-Dsun.nio.PageAlignDirectMemory进行指定,默认是关闭的,在64位Windows JDK上实践证明-XX:[+|-]PageAlignDirectMemory不能用,提示未识别的参数
4、直接内存写入和获取的都是相对系统空间的位置和长度信息
通过position定位byte位置,从0开始
存入byte
public ByteBuffer put(byte x) {
unsafe.putByte(ix(nextPutIndex()), ((x)));
return this;
}
final int nextPutIndex() { // package-private
int p = position;
//前一个写入的位置
if (p >= limit)
throw new BufferOverflowException();
position = p + 1;
//获取当前需要写入的位置
return p;
}
获取byte
public byte get() {
return ((unsafe.getByte(ix(nextGetIndex()))));
}
final int nextGetIndex() { // package-private
int p = position;
if (p >= limit)
throw new BufferUnderflowException();
position = p + 1;
return p;
}
5、回收堆外内存
在初始化DirectByteBuffer的时候,会初始化一个Cleaner对象,它是一个虚引用对象,初始化了一个Deallocator的Runnable对象
PhantomReference 对象继承了Reference
//静态代码块初始化,
static {
ThreadGroup tg = Thread.currentThread().getThreadGroup();
for (ThreadGroup tgn = tg;
tgn != null;
tg = tgn, tgn = tg.getParent());
Thread handler = new ReferenceHandler(tg, "Reference Handler");
/* If there were a special system-only priority greater than
* MAX_PRIORITY, it would be used here
*/
handler.setPriority(Thread.MAX_PRIORITY);
handler.setDaemon(true);
//启动ReferenceHandler线程
handler.start();
// provide access in SharedSecrets
SharedSecrets.setJavaLangRefAccess(new JavaLangRefAccess() {
@Override
public boolean tryHandlePendingReference() {
return tryHandlePending(false);
}
});
}
private static class ReferenceHandler extends Thread {
private static void ensureClassInitialized(Class<?> clazz) {
try {
Class.forName(clazz.getName(), true, clazz.getClassLoader());
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
throw (Error) new NoClassDefFoundError(e.getMessage()).initCause(e);
}
}
static {
ensureClassInitialized(InterruptedException.class);
ensureClassInitialized(Cleaner.class);
}
ReferenceHandler(ThreadGroup g, String name) {
super(g, name);
}
public void run() {
while (true) {
//执行回收方法
tryHandlePending(true);
}
}
}
static boolean tryHandlePending(boolean waitForNotify) {
Reference<Object> r;
Cleaner c;
try {
//对象锁
synchronized (lock) {
if (pending != null) {
r = pending;
//这里获取了Cleaner,前面DirectByteBuffer定义的Cleaner对象
c = r instanceof Cleaner ? (Cleaner) r : null;
pending = r.discovered;
r.discovered = null;
} else {
if (waitForNotify) {
lock.wait();
}
return waitForNotify;
}
}
} catch (OutOfMemoryError x) {
//如果抛出内存溢出错误,当前线程转为就绪状态
Thread.yield();
// retry
return true;
} catch (InterruptedException x) {
// retry
return true;
}
if (c != null) {
//如果存在Cleaner,调用clean方法
c.clean();
return true;
}
ReferenceQueue<? super Object> q = r.queue;
//对象加入排队队列汇总
if (q != ReferenceQueue.NULL) q.enqueue(r);
return true;
}
调用Clean()方法,执行Cleaner对象初始化的Deallocator(Runnable)方法
public void clean() {
if (remove(this)) {
//移除当前对象
try {
//传入的Runnable调用run方法,就是前面的Deallocator对象
this.thunk.run();
} catch (final Throwable var2) {
AccessController.doPrivileged(new PrivilegedAction<Void>() {
public Void run() {
if (System.err != null) {
(new Error("Cleaner terminated abnormally", var2)).printStackTrace();
}
System.exit(1);
return null;
}
});
}
}
}
private static class Deallocator
implements Runnable
{
private static Unsafe unsafe = Unsafe.getUnsafe();
private long address;
private long size;
private int capacity;
private Deallocator(long address, long size, int capacity) {
assert (address != 0);
this.address = address;
this.size = size;
this.capacity = capacity;
}
public void run() {
if (address == 0) {
// Paranoia
return;
}
//回收当前DirectByteBuffer对象使用的堆外内存
unsafe.freeMemory(address);
address = 0;
//更新可用的堆外内存大小
Bits.unreserveMemory(size, capacity);
}
}
6、产生堆外内存溢出的原因
- 设置了最大堆外内存数量,但分配值太小,一次申请的堆外内存数量过大,抛出堆外内存溢出错误,初始化抛出;
- 系统能够申请的堆外内存不足,虽然设置了堆外内存为512M,但如果系统本身只有300M内存给堆外内存,也会抛出堆外内存溢出;
- 堆外内存回收时FullGC触发的Cleaner回收,直到在申请堆外内存的时候通过申请堆外内存的System.gc()触发FULL GC,但这个System.gc()不是立即触发,如果超过了最大时间还没有触发,或者触发回收的内存还不够申请的内存,也会抛出堆外内存溢出;
7、总结
1、定义了DirectByteBuffer的操作byte的都是申请了堆外内存,申请的堆外内存需要手动回收,重置最大可用堆外内存大小;
2、堆外内存泄露并不会提现在JVM内存使用上,排查方式可以通过JConsole检测堆外内存是否一直增长,之后查询系统中使用了DirectByteBuffer的地方;
文章出处登录后可见!
