数据结构:栈
1.1栈的概念以及结构
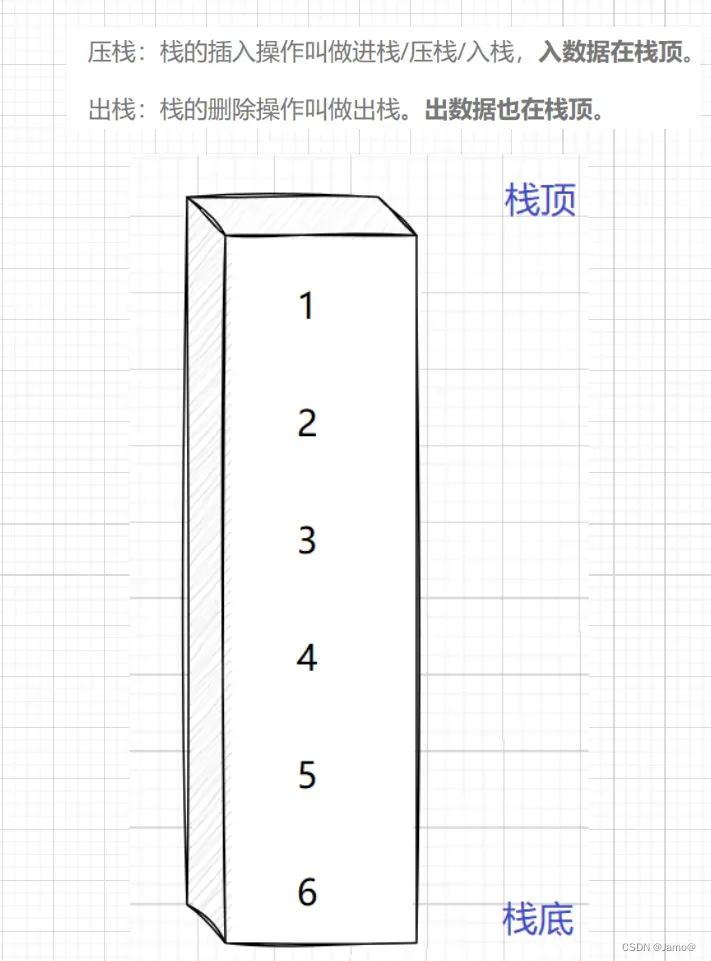
栈(stack)是一种基于数组或者链表实现的一种特殊的数据结构,它具有的特点是先进后出,只允许在固定的一端进行插入和删除操作,进行数据插入和删除操作的一端称为栈顶,另一端称为栈底。
1.2栈的实现
栈的实现一般可以使用数组或者链表实现,相对而言数组的结构实现更优一些。因为数组在尾上插入数据的
代价比较小
如下是基于数组实现的栈(能动态增长空间)的代码:
- Stack.h(声明文件)
#pragma once
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<assert.h>
#include<stdbool.h>
// 支持动态增长的栈(基于数组实现)
typedef int STDataType;
typedef struct Stack//类似于顺序表创建一个结构体来实现 栈表(线性表)
{
STDataType* parray;
int top; // 栈顶
int capacity; // 容量
}Stack;
// 初始化栈
void Init(Stack* ps);
// 入栈
void Push(Stack* ps, STDataType data);
// 出栈
void Pop(Stack* ps);
// 获取栈顶元素
STDataType Peek(Stack* ps);
// 获取栈中有效元素个数
int Size(Stack* ps);
// 检测栈是否为空,如果为空返回非零结果,如果不为空返回0
bool Empty(Stack* ps);
// 销毁栈
void Destroy(Stack* ps);
// 打印栈元素
void Print(Stack* ps);
- Stack.c(栈的具体接口实现)
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include"Stack.h"
//最初的栈空间大小
#define initcapacity 4
// 初始化栈(给一定空间)
void Init(Stack* ps)
{
ps->capacity = initcapacity;//栈的容量
ps->parray = (STDataType*)malloc(sizeof(STDataType) * initcapacity);//动态开辟的栈的空间
ps->top = 0;//表示栈顶元素的下一个位置
}
// 入栈
void Push(Stack* ps, STDataType data)
{
assert(ps);
// 入栈前需要检查容量是否已经满了。满了则需要扩容
if (ps->top == ps->capacity)
{
//防止最初容量为0 后续无法扩容
if (ps->capacity == 0)
ps->capacity = 4;
//每次扩容为之前容量的两倍
int newcapacity = 2 * (ps->capacity);
STDataType* newparray = (STDataType*)realloc(ps->parray, sizeof(STDataType) * newcapacity);
if (newparray == NULL)
{
perror("realloc");
return;
}
ps->parray = newparray;
ps->capacity = newcapacity;
}
//正式入栈
ps->parray[ps->top] = data;
(ps->top)++;
}
// 出栈
void Pop(Stack* ps)
{
//防止栈不存在
assert(ps);
//防止栈为空,栈空了就不能继续删除了
assert(ps->top > 0);
(ps->top)--;
}
// 获取栈顶元素
STDataType Peek(Stack* ps)
{
assert(ps);
assert(ps->top > 0);
return ps->parray[(ps->top) - 1];
}
// 获取栈中有效元素个数
int Size(Stack* ps)
{
assert(ps);
return ps->top;
}
// 检测栈是否为空,如果为空返回非零结果,如果不为空返回0
bool Empty(Stack* ps)
{
assert(ps);
if (ps->top == 0)
{
return true;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
// 销毁栈
void Destroy(Stack* ps)
{
assert(ps);
free(ps->parray);
ps->parray = NULL;
ps->parray = 0;
ps->top = 0;
}
// 打印栈元素
void Print(Stack* ps)
{
assert(ps);
int i = 0;
for (i = 0; i < (ps->top); i++)
{
printf("%d ", ps->parray[i]);
}
printf("\n");
}
- test.c(接口测试)
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include"Stack.h"
// 入栈测试
void test1()
{
//初始化Stack
Stack st;
Init(&st);
Push(&st, 1);
Push(&st, 2);
Push(&st, 3);
Push(&st, 4);
Push(&st, 5);
Print(&st);
}
// 出栈测试
void test2()
{
//初始化Stack
Stack st;
Init(&st);
Push(&st, 1);
Push(&st, 2);
Push(&st, 3);
Push(&st, 4);
Push(&st, 5);
Pop(&st);
Print(&st);
}
// 获取栈顶元素测试
void test3()
{
//初始化Stack
Stack st;
Init(&st);
Push(&st, 1);
Push(&st, 2);
Push(&st, 3);
Push(&st, 4);
Push(&st, 5);
printf("%d\n", Peek(&st));
}
int main()
{
// 入栈测试
// test1();
//出栈测试
//test2();
// 获取栈顶元素测试
test3();
return 0;
}
版权声明:本文为博主作者:Jamo@原创文章,版权归属原作者,如果侵权,请联系我们删除!
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/AlanTZT/article/details/134903132
