在我们程序的编写中,有时候我们需要在 Java 程序中对 List 集合进行排序操作。比如获取所有用户的列表,但列表默认是以用户编号从小到大进行排序的,而我们的系统需要按照用户的年龄从大到小进行排序,这个时候,我们就需要对 List 集合进行自定义排序操作了。
List 排序的常见方法有以下 3 种:
-
使用 Comparable 进行排序;
-
使用 Comparator 进行排序;
-
如果是 JDK 8 以上的环境,也可以使用 Stream 流进行排序。
下面我们分别来看各种排序方法的具体实现。
1.使用 Comparable 排序
创建一个包含了用户列表的 List 集合,并按用户的年龄从大到小进行排序,具体实现代码如下:
import com.fasterxml.jackson.core.JsonProcessingException;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.List;
public class ListSortExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建并初始化 List
List<Person> list = new ArrayList<Person>() {{
add(new Person(1, 30, "张三"));
add(new Person(2, 20, "李四"));
add(new Person(3, 40, "王五"));
}};
// 使用 Comparable 自定的规则进行排序
Collections.sort(list);
// 创建ObjectMapper对象
ObjectMapper objectMapper = new ObjectMapper();
// 打印 list 集合
list.forEach(p -> {
// 将JavaBean对象转换为JSON字符串
String jsonStr = null;
try {
jsonStr = objectMapper.writeValueAsString(p);
} catch (JsonProcessingException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(jsonStr);
});
}
}
class Person implements Comparable<Person> {
private int id;
private int age;
private String name;
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name == null ? "" : name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Person(int id, int age, String name) {
this.id = id;
this.age = age;
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Person p) {
return p.getAge() - this.getAge();
}
}
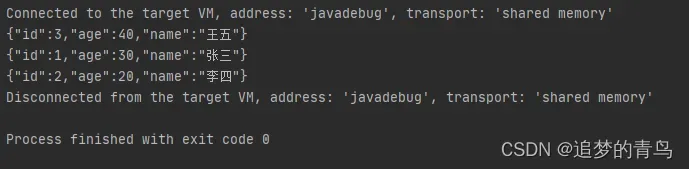
以上代码的执行结果,如下图所示:
2.使用 Comparator 排序
Comparable 是类内部的比较方法,而 Comparator 是排序类外部的比较器。使用 Comparator 比较器,无需修改原 Person 类,只需要扩充一个 Person 类的比较器就行了,Comparator 的实现方法有以下两种:
新建 Comparator 比较器;
使用 Comparator 匿名类比较器。
其中,第二种实现方法要更简洁一些,我们通过下面的具体代码,来观察一下二者的区别。
2.1 新建 Comparator 比较器
import com.fasterxml.jackson.core.JsonProcessingException;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.List;
public class ListSortExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建并初始化 List
List<Person> list = new ArrayList<Person>() {{
add(new Person(1, 30, "张三"));
add(new Person(2, 20, "李四"));
add(new Person(3, 40, "王五"));
}};
// 使用 Comparator 比较器排序
Collections.sort(list, new PersonComparator());
// 创建ObjectMapper对象
ObjectMapper objectMapper = new ObjectMapper();
// 打印 list 集合
list.forEach(p -> {
// 将JavaBean对象转换为JSON字符串
String jsonStr = null;
try {
jsonStr = objectMapper.writeValueAsString(p);
} catch (JsonProcessingException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(jsonStr);
});
}
}
/**
* 新建 Person 比较器
*/
class PersonComparator implements Comparator<Person> {
@Override
public int compare(Person p1, Person p2) {
return p2.getAge() - p1.getAge();
}
}
class Person {
private int id;
private int age;
private String name;
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name == null ? "" : name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Person(int id, int age, String name) {
this.id = id;
this.age = age;
this.name = name;
}
}
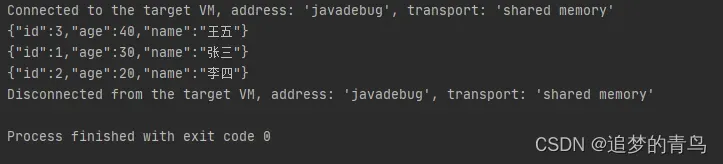
以上代码的执行结果,如下图所示:
2.2 匿名类比较器
比较器 Comparator 可以使用更简洁的匿名类的方式,来实现排序功能,具体实现代码如下:
import com.fasterxml.jackson.core.JsonProcessingException;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.List;
public class ListSortExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建并初始化 List
List<Person> list = new ArrayList<Person>() {{
add(new Person(1, 30, "张三"));
add(new Person(2, 20, "李四"));
add(new Person(3, 40, "王五"));
}};
// 使用匿名比较器排序
Collections.sort(list, new Comparator<Person>() {
@Override
public int compare(Person p1, Person p2) {
return p2.getAge() - p1.getAge();
}
});
// 创建ObjectMapper对象
ObjectMapper objectMapper = new ObjectMapper();
// 打印 list 集合
list.forEach(p -> {
// 将JavaBean对象转换为JSON字符串
String jsonStr = null;
try {
jsonStr = objectMapper.writeValueAsString(p);
} catch (JsonProcessingException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(jsonStr);
});
}
}
class Person {
private int id;
private int age;
private String name;
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name == null ? "" : name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Person(int id, int age, String name) {
this.id = id;
this.age = age;
this.name = name;
}
}
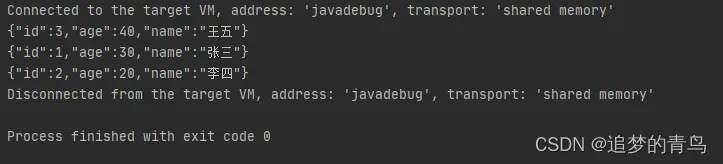
以上代码的执行结果,如下图所示:
 3.使用 Stream 流排序
3.使用 Stream 流排序
在 JDK 8 之后可以使用更加简单的方法 Stream 流来实现排序功能,它的实现只需要一行代码,具体实现如下:
package com.highcom.hc.api;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.core.JsonProcessingException;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
public class ListSortExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建并初始化 List
List<Person> list = new ArrayList<Person>() {{
add(new Person(1, 30, "张三"));
add(new Person(2, 20, "李四"));
add(new Person(3, 40, "王五"));
}};
// 使用 Stream 排序
list = list.stream().sorted(Comparator.comparing(Person::getAge).reversed())
.collect(Collectors.toList());
// 创建ObjectMapper对象
ObjectMapper objectMapper = new ObjectMapper();
// 打印 list 集合
list.forEach(p -> {
// 将JavaBean对象转换为JSON字符串
String jsonStr = null;
try {
jsonStr = objectMapper.writeValueAsString(p);
} catch (JsonProcessingException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(jsonStr);
});
}
}
class Person {
private int id;
private int age;
private String name;
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name == null ? "" : name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Person(int id, int age, String name) {
this.id = id;
this.age = age;
this.name = name;
}
}
其中 reversed() 表示倒序的意思,如果不使用此方法则是正序。
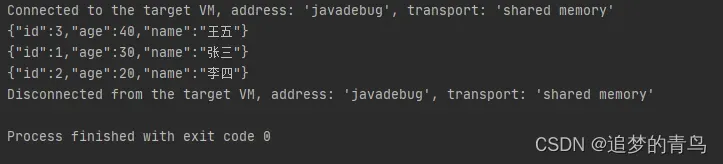
以上代码的执行结果,如下图所示:
扩展:排序字段为 null
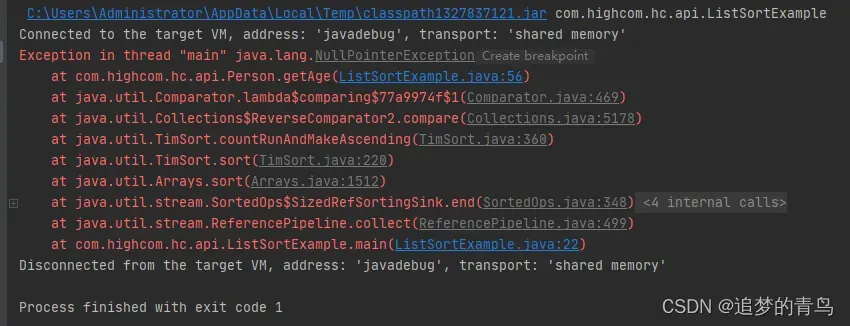
使用 Stream 进行排序时,如果排序的字段出现 null 值就会导致异常发生,具体示例如下:
import com.fasterxml.jackson.core.JsonProcessingException;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
public class ListSortExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建并初始化 List
List<Person> list = new ArrayList<Person>() {{
add(new Person(1, 30, "张三"));
add(new Person(2, 20, "李四"));
add(new Person(3, null, "王五"));
}};
// 使用 Stream 排序
list = list.stream().sorted(Comparator.comparing(Person::getAge).reversed())
.collect(Collectors.toList());
// 创建ObjectMapper对象
ObjectMapper objectMapper = new ObjectMapper();
// 打印 list 集合
list.forEach(p -> {
// 将JavaBean对象转换为JSON字符串
String jsonStr = null;
try {
jsonStr = objectMapper.writeValueAsString(p);
} catch (JsonProcessingException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(jsonStr);
});
}
}
class Person {
private int id;
private Integer age;
private String name;
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name == null ? "" : name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Person(int id, Integer age, String name) {
this.id = id;
this.age = age;
this.name = name;
}
}
以上代码的执行结果,如下图所示:
 想要解决上述问题,需要给 Comparator.comparing 传递第二个参数:Comparator.nullsXXX,如下代码所示:
想要解决上述问题,需要给 Comparator.comparing 传递第二个参数:Comparator.nullsXXX,如下代码所示:
import com.fasterxml.jackson.core.JsonProcessingException;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
public class ListSortExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建并初始化 List
List<Person> list = new ArrayList<Person>() {{
add(new Person(1, 30, "张三"));
add(new Person(2, 20, "李四"));
add(new Person(3, null, "王五"));
}};
// 按照[年龄]排序,但年龄中有一个 null 值
list = list.stream().sorted(Comparator.comparing(Person::getAge,
Comparator.nullsFirst(Integer::compareTo)).reversed())
.collect(Collectors.toList());
// 创建ObjectMapper对象
ObjectMapper objectMapper = new ObjectMapper();
// 打印 list 集合
list.forEach(p -> {
// 将JavaBean对象转换为JSON字符串
String jsonStr = null;
try {
jsonStr = objectMapper.writeValueAsString(p);
} catch (JsonProcessingException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(jsonStr);
});
}
}
class Person {
private int id;
private Integer age;
private String name;
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public Integer getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(Integer age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name == null ? "" : name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Person(int id, Integer age, String name) {
this.id = id;
this.age = age;
this.name = name;
}
}
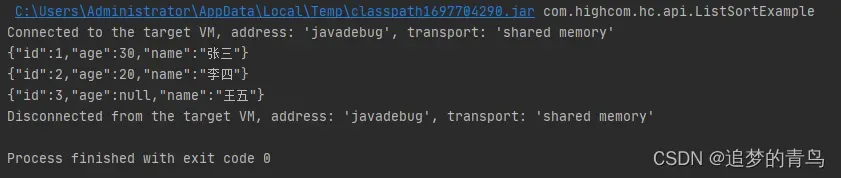
Comparator.nullsFirst 表示将排序字段中的 null 值放到集合最前面,如果想要将 null 值放到集合最后面可以使用 Comparator.nullsLast。
以上代码的执行结果,如下图所示:
总结
本文介绍了 3 种 List 排序的方法,前两种方法常用于 JDK 8 之前的版本,其中比较器 Comparator 有两种实现的写法,而在 JDK 8 之后的版本,就可以使用 Comparator.comparing 实现排序了,如果排序字段中可能出现 null 值,要使用 Comparator.nullsXXX 进行排序处理(否则会报错)
版权声明:本文为博主作者:追梦的青鸟原创文章,版权归属原作者,如果侵权,请联系我们删除!
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/fengchunhua518/article/details/135747174
