🌈个人主页:秦jh__https://blog.csdn.net/qinjh_?spm=1010.2135.3001.5343
🔥 系列专栏:http://t.csdnimg.cn/eCa5z

目录
前言
💬 hello! 各位铁子们大家好哇。
今日更新了string模拟实现的内容
🎉 欢迎大家关注🔍点赞👍收藏⭐️留言📝
构造

初始化列表部分,要开辟新空间初始化。三次调用strlen效率太低,改进如下图:
我们的构造函数直接写一个全缺省的,这样就不用分开写无参和有参的构造了。上面缺省值不能给nullptr,因为初始化列表那里会报错,str为空,无法strlen。缺省值也不能给’\0’,而要给”\0″,因为’\0’的类型是char,不能给char*。其实给”\0″也是多余的,虽然可以这样写,我们可以直接给空字符串””,系统会在后面自动加上”\0″的。
string(const char* str="")
: _size(strlen(str))
{
_capacity = _size;
_str = new char[_capacity + 1];
strcpy(_str, str);
}析构
~string()
{
delete[] _str;
_str = nullptr;
_size = _capacity = 0;
}遍历
//遍历
size_t size() const
{
return _size;
}
size_t capacity() const
{
return _capacity;
}
char& operator[](size_t pos)
{
assert(pos < _size);
return _str[pos]; //_str[pos]在堆上,可用引用返回,支持修改
}
const char& operator[](size_t pos) const
{
assert(pos < _size);
return _str[pos];
}
void test_string1()
{
string s1("hello world");
string s2;
for (size_t i = 0; i < s1.size(); i++)
{
s1[i]++;
}
cout << endl;
for (size_t i = 0; i < s1.size(); i++)
{
cout << s1[i] << "";
}
cout << endl;
const string s3("xxxx");
for (size_t i = 0; i < s3.size(); i++)
{
//s3[i]++ 错误,可读,但不能写
cout << s3[i] << "";
}
cout << endl;
}operator[]需要重载两个,因为string对象可能是const修饰的。
迭代器
typedef char* iterator;
iterator begin()
{
return _str;
}
iterator end()
{
return _str + _size;
}
void test_string2()
{
string s3("hello world");
string::iterator it3 = s3.begin();
while (it3 != s3.end())
{
//*it3 -= 3;
cout << *it3 << " ";
++it3;
}
cout << endl;
for (auto ch : s3)
{
cout << ch << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}这里迭代器的模拟实现是容易的,不同的容器有不同的迭代器,只是名字相同。
如果string对象有const修饰时,就需要const迭代器,如下方代码:
typedef const char* const_iterator;
const_iterator begin() const
{
return _str;
}
const_iterator end() const
{
return _str + _size;
}
const string s2("hello world");
string::const_iterator it2 = s2.begin();
while (it2 != s2.end())
{
cout << *it2 << " ";
++it2;
}
cout << endl;插入
void reserve(size_t n)
{
if (n > _capacity)
{
char* tmp = new char[n+1];
strcpy(tmp, _str);
delete[] _str;
_str = tmp;
_capacity = n;
}
}
void push_back(char ch)
{
/* if (_size == _capacity)
{
reserve(_capacity == 0 ? 4 : 2 * _capacity);
}
_str[_size] = ch;
++_size;
_str[_size] = '\0';*/
insert(_size, ch);
}
void append(const char* str)
{
/* size_t len = strlen(str);
if (_size + len > _capacity)
{
reserve(_size + len);
}
strcpy(_str + _size, str);
_size += len;*/
insert(_size, str);
}
string& operator+=(char ch)
{
push_back(ch);
return *this;
}
string& operator+=(const char* str)
{
append(str);
return *this;
}
void insert(size_t pos, char ch)
{
assert(pos <= _size);
if (_size == _capacity)
{
reserve(_capacity == 0 ? 4 : 2 * _capacity);
}
//第一种写法
/*int end = _size;
while (end >= (int) pos) //需要强转,pos是size_t类型,end是int,end会被转成size_t类型,即范围小会转向范围大的。
{ //当pos等于0,即头插时。结束条件为end小于0,如果不强转,当end小于0时,又会被转成无符号的
_str[end + 1] = _str[end]; //就会死循环
--end;
}*/
//第二种
size_t end = _size+1;
while (end > pos)
{
_str[end] = _str[end-1];
--end;
}
_str[pos] = ch;
++_size;
}
void insert(size_t pos, const char* str)
{
assert(pos <= _size);
size_t len = strlen(str);
if (_size + len > _capacity)
{
reserve(_size + len);
}
size_t end = _size + len;
while (end > pos + len - 1)
{
_str[end] = _str[end - len];
end--;
}
strncpy(_str + pos, str, len);
_size += len;
}
void test_string3()
{
string s3("hello world");
s3.push_back('1');
s3.push_back('2');
cout << s3.c_str()<< endl;
s3 += 'x';
s3 += "yyyy";
cout << s3.c_str() << endl;
string s1("hello world");
s1.insert(11, 'x');
cout << s1.c_str() << endl;
s1.insert(0, 'x');
cout << s1.c_str() << endl;
}
void test_string6()
{
string s1("hello world");
cout << s1.c_str() << endl;
s1.insert(6, "xxxx");
cout << s1.c_str() << endl;
}删除、改变容量、赋值
const char* c_str() const
{
return _str;
}
void resize(size_t n, char ch = '\0')
{
if (n < _size)
{
_str[n] = '\0';
_size = n;
}
else
{
reserve(n);
for (size_t i = _size; i < n; i++)
{
_str[i] = ch;
}
_str[n] = '\0';
_size = n;
}
}
void erase(size_t pos, size_t len = npos)
{
assert(pos < _size);
if (len == npos || len >= _size - pos) //len +pos>= _size 不能这么写,会有溢出风险
{
_str[pos] = '\0';
_size = pos;
}
else
{
strcpy(_str + pos, _str + pos + len);
_size -= len;
}
}
//s2(s1)
string(const string& s)
{
_str = new char[s._capacity + 1];
strcpy(_str, s._str);
_size = s._size;
_capacity = s._capacity;
}
//s1=s3
string& operator=(const string& s)
{
char* tmp = new char[s._capacity+1];
strcpy(tmp, s._str);
delete[] _str;
_str = tmp;
_size = s._size;
_capacity = s._capacity;
return *this;
}
void test_string4()
{
string s1("hello world");
cout << s1.c_str() << endl;
s1.erase(6, 3);
cout << s1.c_str() << endl;
string s2("hello world");
cout << s2.c_str() << endl;
s2.resize(5);
cout << s2.c_str() << endl;
s2.resize(20, 'x');
cout << s2.c_str() << endl;
}
void test_string5()
{
string s1("hello world");
cout << s1.c_str() << endl;
string s2(s1);
cout << s2.c_str() << endl;
string s3("xxxxx");
s1 = s3;
cout << s1.c_str() << endl;
cout << s3.c_str() << endl;
}
交换

当我们用算法库里面的模板swap时,效率很低,它会进行3次拷贝+1次析构。我们需要自己手写一个成员函数swap提高效率。 如下图:
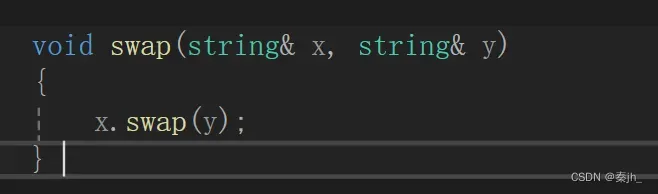
为了避免有人使用效率不高的swap,其实还有一个全局的swap,如下图:

查找
size_t find(char ch, size_t pos = 0) const
{
assert(pos < _size);
for (size_t i = pos; i < _size; i++)
{
if (_str[i] == ch)
return i;
}
return npos;
}
size_t find(const char* sub, size_t pos = 0) const
{
assert(pos < _size);
const char* p = strstr(_str+pos, sub);
if (p)
{
return p - _str;
}
else
{
return npos;
}
}
string substr(size_t pos = 0, size_t len = npos)
{
string sub;
if (len >= _size - pos)
{
for (size_t i = pos; i < _size; i++)
{
sub += _str[i];
}
}
else
{
for (size_t i = pos; i < pos+len; i++)
{
sub += _str[i];
}
}
return sub;
}
void test_string7()
{
string url1("https://legacy.cplusplus.com/reference/string/string/substr/");
string url2("https://www.baidu.com/s?ie=utf-8&f=8&rsv_bp=1&rsv_idx=1&tn=baidu&wd=%E5%90%8E%E7%BC%80%20%E8%8B%B1%E6%96%87&fenlei=256&rsv_pq=0xc61b98d100494ef5&rsv_t=b494uh2Bd6SIxMQ1XY4CwB9MZOD%2BaMk5sx8aiT0NAgUczCRAy8jK7PvP5rxt&rqlang=en&rsv_enter=1&rsv_dl=tb&rsv_sug3=23&rsv_sug1=17&rsv_sug7=100&rsv_sug2=0&rsv_btype=i&inputT=7123&rsv_sug4=8008");
string protocol, domain, uri;
size_t i1 = url1.find(':');
if (i1 != string::npos)
{
protocol = url1.substr(0, i1 - 0);//左闭右开,减去后就是个数
cout << protocol.c_str() << endl;
}
size_t i2 = url1.find('/',i1+3);
if (i2 != string::npos)
{
domain = url1.substr(i1+3, i2-(i1+3));//左闭右开,减去后就是个数
cout << domain.c_str() << endl;
uri = url1.substr(i2 + 1);
cout << uri.c_str() << endl;
}
}运算符重载
void clear()
{
_size = 0;
_str[_size] = '\0';
}
bool operator==(const string& s1, const string& s2)
{
int ret = strcmp(s1.c_str(), s2.c_str());
return ret == 0;
}
bool operator<(const string& s1, const string& s2)
{
int ret = strcmp(s1.c_str(), s2.c_str());
return ret < 0;
}
bool operator<=(const string& s1, const string& s2)
{
return s1 < s2 || s1 == s1;
}
bool operator>(const string& s1, const string& s2)
{
return !(s1 <= s2);
}
bool operator>=(const string& s1, const string& s2)
{
return !(s1 < s2);
}
bool operator!=(const string& s1, const string& s2)
{
return !(s1 == s2);
}
ostream& operator<<(ostream& out, const string& s)
{
for (auto ch : s)
{
out << ch;
}
return out;
}
istream& operator>>(istream& in, string& s)
{
s.clear();
char ch;
//in >> ch; 错误,C++规定 cin,scanf默认空格和换行是分隔符,
ch = in.get();//不会取到,get才能取到
char buff[128];
size_t i = 0;
while (ch != ' ' && ch != '\n')
{
buff[i++] = ch;
if (i == 127)
{
buff[127] = '\0';
s += buff;
i = 0;
}
ch = in.get();
}
if (i > 0)
{
buff[i] = '\0';
s += buff;
}
return in;
}
istream& getline(istream& in, string& s)
{
s.clear();
char ch;
//in >> ch; 错误,C++规定 cin,scanf默认空格和换行是分隔符,
ch = in.get();//不会取到,get才能取到
while (ch != '\n')
{
s += ch;
ch = in.get();
}
return in;
}
void test_string8()
{
string s1("hello world");
string s2("hello world");
cout << (s1 == s2) << endl;
cout << ("hello world" == s2) << endl;//因为重载成全局的函数,
cout << (s2 == "hello world") << endl;//单参数构造支持隐式类型转换。
cout << s1 << endl;
cout << s2 << endl;
cin >> s1 >> s2;
cout << s1 << endl;
cout << s2 << endl;
getline(cin, s1);
cout << s1 << endl;
}现代写法
拷贝构造

//现代写法
string(const string& s)
{
string tmp(s._str);
swap(tmp);
}赋值

string& operator=(string tmp)
{
//现代写法
swap(tmp);
return *this;
}完整代码呈现
头文件
#pragma once
#include<assert.h>
namespace bit
{
class string
{
public:
typedef char* iterator;
typedef const char* const_iterator;
const_iterator begin() const
{
return _str;
}
const_iterator end() const
{
return _str + _size;
}
iterator begin()
{
return _str;
}
iterator end()
{
return _str + _size;
}
//string()
// :_str(nullptr)
// ,_size(0)
// ,_capacity(0)
//{}
_str(str) 错误,这样的话声明部分就得加上const,加上后又会导致不能修改
//string(const char* str)
// :_str(new char[strlen(str)+1]) //必须自己开辟新的空间,
// ,_size(strlen(str)) //调用三次strlen,效率不高
// ,_capacity(strlen(str))
//{
// strcpy(_str, str);
//}
const char* c_str() const
{
return _str;
}
//string(const char* str = "\0") 里面不能写const char* str =nullptr
string(const char* str="")
: _size(strlen(str))
{
_capacity = _size;
_str = new char[_capacity + 1];
strcpy(_str, str);
}
//s2(s1) 传统写法
//string(const string& s)
//{
// _str = new char[s._capacity + 1];
// strcpy(_str, s._str);
// _size = s._size;
// _capacity = s._capacity;
//}
//现代写法
string(const string& s)
{
string tmp(s._str);
swap(tmp);
}
string& operator=(string tmp)
{
//现代写法
swap(tmp);
return *this;
}
//s1=s3 传统写法
//string& operator=(const string& s)
//{
// char* tmp = new char[s._capacity+1];
// strcpy(tmp, s._str);
// delete[] _str;
// _str = tmp;
// _size = s._size;
// _capacity = s._capacity;
//
// return *this;
//}
~string()
{
delete[] _str;
_str = nullptr;
_size = _capacity = 0;
}
//遍历
size_t size() const
{
return _size;
}
size_t capacity() const
{
return _capacity;
}
char& operator[](size_t pos)
{
assert(pos < _size);
return _str[pos]; //_str[pos]在堆上,可用引用返回,支持修改
}
const char& operator[](size_t pos) const
{
assert(pos < _size);
return _str[pos];
}
void resize(size_t n, char ch = '\0')
{
if (n < _size)
{
_str[n] = '\0';
_size = n;
}
else
{
reserve(n);
for (size_t i = _size; i < n; i++)
{
_str[i] = ch;
}
_str[n] = '\0';
_size = n;
}
}
void reserve(size_t n)
{
if (n > _capacity)
{
char* tmp = new char[n+1];
strcpy(tmp, _str);
delete[] _str;
_str = tmp;
_capacity = n;
}
}
void push_back(char ch)
{
/* if (_size == _capacity)
{
reserve(_capacity == 0 ? 4 : 2 * _capacity);
}
_str[_size] = ch;
++_size;
_str[_size] = '\0';*/
insert(_size, ch);
}
void append(const char* str)
{
/* size_t len = strlen(str);
if (_size + len > _capacity)
{
reserve(_size + len);
}
strcpy(_str + _size, str);
_size += len;*/
insert(_size, str);
}
string& operator+=(char ch)
{
push_back(ch);
return *this;
}
string& operator+=(const char* str)
{
append(str);
return *this;
}
void insert(size_t pos, char ch)
{
assert(pos <= _size);
if (_size == _capacity)
{
reserve(_capacity == 0 ? 4 : 2 * _capacity);
}
//第一种写法
/*int end = _size;
while (end >= (int) pos) //需要强转,pos是size_t类型,end是int,end会被转成size_t类型,即范围小会转向范围大的。
{ //当pos等于0,即头插时。结束条件为end小于0,如果不强转,当end小于0时,又会被转成无符号的
_str[end + 1] = _str[end]; //就会死循环
--end;
}*/
//第二种
size_t end = _size+1;
while (end > pos)
{
_str[end] = _str[end-1];
--end;
}
_str[pos] = ch;
++_size;
}
void insert(size_t pos, const char* str)
{
assert(pos <= _size);
size_t len = strlen(str);
if (_size + len > _capacity)
{
reserve(_size + len);
}
size_t end = _size + len;
while (end > pos + len - 1)
{
_str[end] = _str[end - len];
end--;
}
strncpy(_str + pos, str, len);
_size += len;
}
void erase(size_t pos, size_t len = npos)
{
assert(pos < _size);
if (len == npos || len >= _size - pos) //len +pos>= _size 不能这么写,会有溢出风险
{
_str[pos] = '\0';
_size = pos;
}
else
{
strcpy(_str + pos, _str + pos + len);
_size -= len;
}
}
void swap(string& s)
{
std::swap(_str, s._str);
std::swap(_size, s._size);
std::swap(_capacity, s._capacity);
}
size_t find(char ch, size_t pos = 0) const
{
assert(pos < _size);
for (size_t i = pos; i < _size; i++)
{
if (_str[i] == ch)
return i;
}
return npos;
}
size_t find(const char* sub, size_t pos = 0) const
{
assert(pos < _size);
const char* p = strstr(_str+pos, sub);
if (p)
{
return p - _str;
}
else
{
return npos;
}
}
string substr(size_t pos = 0, size_t len = npos)
{
string sub;
if (len >= _size - pos)
{
for (size_t i = pos; i < _size; i++)
{
sub += _str[i];
}
}
else
{
for (size_t i = pos; i < pos+len; i++)
{
sub += _str[i];
}
}
return sub;
}
void clear()
{
_size = 0;
_str[_size] = '\0';
}
private:
char* _str=nullptr;
size_t _size=0;
size_t _capacity=0;
public:
static const int npos;
};
const int string::npos = -1;
void swap(string& x, string& y)
{
x.swap(y);
}
bool operator==(const string& s1, const string& s2)
{
int ret = strcmp(s1.c_str(), s2.c_str());
return ret == 0;
}
bool operator<(const string& s1, const string& s2)
{
int ret = strcmp(s1.c_str(), s2.c_str());
return ret < 0;
}
bool operator<=(const string& s1, const string& s2)
{
return s1 < s2 || s1 == s1;
}
bool operator>(const string& s1, const string& s2)
{
return !(s1 <= s2);
}
bool operator>=(const string& s1, const string& s2)
{
return !(s1 < s2);
}
bool operator!=(const string& s1, const string& s2)
{
return !(s1 == s2);
}
ostream& operator<<(ostream& out, const string& s)
{
for (auto ch : s)
{
out << ch;
}
return out;
}
istream& operator>>(istream& in, string& s)
{
s.clear();
char ch;
//in >> ch; 错误,C++规定 cin,scanf默认空格和换行是分隔符,
ch = in.get();//不会取到,get才能取到
char buff[128];
size_t i = 0;
while (ch != ' ' && ch != '\n')
{
buff[i++] = ch;
if (i == 127)
{
buff[127] = '\0';
s += buff;
i = 0;
}
ch = in.get();
}
if (i > 0)
{
buff[i] = '\0';
s += buff;
}
return in;
}
istream& getline(istream& in, string& s)
{
s.clear();
char ch;
//in >> ch; 错误,C++规定 cin,scanf默认空格和换行是分隔符,
ch = in.get();//不会取到,get才能取到
while (ch != '\n')
{
s += ch;
ch = in.get();
}
return in;
}
void test_string1()
{
string s1("hello world");
string s2;
for (size_t i = 0; i < s1.size(); i++)
{
s1[i]++;
}
cout << endl;
for (size_t i = 0; i < s1.size(); i++)
{
cout << s1[i] << "";
}
cout << endl;
const string s3("xxxx");
for (size_t i = 0; i < s3.size(); i++)
{
//s3[i]++ 错误,可读,但不能写
cout << s3[i] << "";
}
cout << endl;
}
void test_string2()
{
string s3("hello world");
string::iterator it3 = s3.begin();
while (it3 != s3.end())
{
//*it3 -= 3;
cout << *it3 << " ";
++it3;
}
cout << endl;
for (auto ch : s3)
{
cout << ch << " ";
}
cout << endl;
const string s2("hello world");
string::const_iterator it2 = s2.begin();
while (it2 != s2.end())
{
cout << *it2 << " ";
++it2;
}
cout << endl;
}
void test_string3()
{
string s3("hello world");
s3.push_back('1');
s3.push_back('2');
cout << s3.c_str()<< endl;
s3 += 'x';
s3 += "yyyy";
cout << s3.c_str() << endl;
string s1("hello world");
s1.insert(11, 'x');
cout << s1.c_str() << endl;
s1.insert(0, 'x');
cout << s1.c_str() << endl;
}
void test_string4()
{
string s1("hello world");
cout << s1.c_str() << endl;
s1.erase(6, 3);
cout << s1.c_str() << endl;
string s2("hello world");
cout << s2.c_str() << endl;
s2.resize(5);
cout << s2.c_str() << endl;
s2.resize(20, 'x');
cout << s2.c_str() << endl;
}
void test_string5()
{
string s1("hello world");
cout << s1.c_str() << endl;
string s2(s1);
cout << s2.c_str() << endl;
string s3("xxxxx");
s1 = s3;
cout << s1.c_str() << endl;
cout << s3.c_str() << endl;
}
void test_string6()
{
string s1("hello world");
cout << s1.c_str() << endl;
s1.insert(6, "xxxx");
cout << s1.c_str() << endl;
string s2("xxxxxx");
cout << s1.c_str() << endl;
cout << s2.c_str() << endl;
//swap(s1, s2); 有了全局的swap,就会先调用全局的,
s1.swap(s2); //而不是算法库里面的模板swap
cout << s1.c_str() << endl;
cout << s2.c_str() << endl;
}
void test_string7()
{
string url1("https://legacy.cplusplus.com/reference/string/string/substr/");
string url2("https://www.baidu.com/s?ie=utf-8&f=8&rsv_bp=1&rsv_idx=1&tn=baidu&wd=%E5%90%8E%E7%BC%80%20%E8%8B%B1%E6%96%87&fenlei=256&rsv_pq=0xc61b98d100494ef5&rsv_t=b494uh2Bd6SIxMQ1XY4CwB9MZOD%2BaMk5sx8aiT0NAgUczCRAy8jK7PvP5rxt&rqlang=en&rsv_enter=1&rsv_dl=tb&rsv_sug3=23&rsv_sug1=17&rsv_sug7=100&rsv_sug2=0&rsv_btype=i&inputT=7123&rsv_sug4=8008");
string protocol, domain, uri;
size_t i1 = url1.find(':');
if (i1 != string::npos)
{
protocol = url1.substr(0, i1 - 0);//左闭右开,减去后就是个数
cout << protocol.c_str() << endl;
}
size_t i2 = url1.find('/',i1+3);
if (i2 != string::npos)
{
domain = url1.substr(i1+3, i2-(i1+3));//左闭右开,减去后就是个数
cout << domain.c_str() << endl;
uri = url1.substr(i2 + 1);
cout << uri.c_str() << endl;
}
}
void test_string8()
{
string s1("hello world");
string s2("hello world");
cout << (s1 == s2) << endl;
cout << ("hello world" == s2) << endl;//因为重载成全局的函数,
cout << (s2 == "hello world") << endl;//单参数构造支持隐式类型转换。
cout << s1 << endl;
cout << s2 << endl;
cin >> s1 >> s2;
cout << s1 << endl;
cout << s2 << endl;
getline(cin, s1);
cout << s1 << endl;
}
void test_string10()
{
string s1("hello world");
string s2(s1);
cout << s1 << endl;
cout << s2 << endl;
}
}
测试代码
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
#include"string.h"
int main()
{
bit::test_string10();
return 0;
}版权声明:本文为博主作者:秦jh_原创文章,版权归属原作者,如果侵权,请联系我们删除!