为了实现Deep Feedback Network for Recommendation 这篇文章中工业级算法,发现这篇文章的基础是Wide&Deep, 只不过增加了三个transformer 以及机器的self-attention机制, 关键在于Wide&Deep 这篇算法的实现, 当然DFN中的反馈机制与我目前的视频推荐很类似, 只不过wechat 研究的是story 推荐。整篇文章的核心内容以及公式请在网上去查找, 相应的都有很多。我尽最大程度上还原了改论文的思想,以及文中提出的特征交互,广义线性结构,多层前馈网络,以及最后的组件组合:
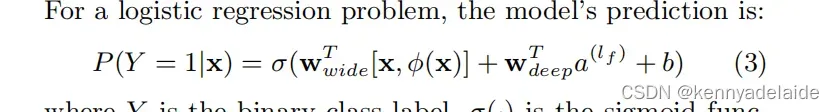
同时将总的logistic loss 返回到各个组件进行参数的更新。
两个优化器如下:
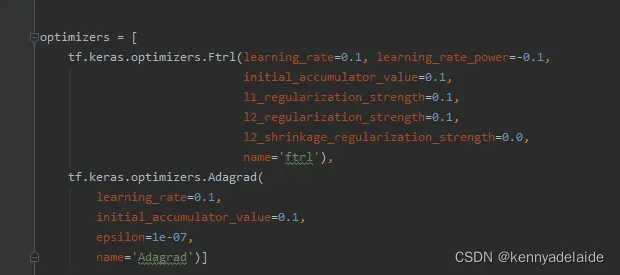
论文代码的实现全部采用tensorflow2 实现, 很容易上手。 代码中的细节就自己推敲吧,很激动全部采用手动实现。有关FTRL 优化器,建议对这部分进行详细的了解,本来想自己实现的,很简单,但是没有时间。
为了方便初学者的理解, 我构建了一个数据模拟器,采用特征工程接口做了处理,其实可以手动实现,但是肯定达不到keras 的效果,就放弃了,主要是在一些小细节的时候不容易实现。
直接上代码:
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
from tensorflow.keras.models import Sequential
'''
@name: kenny adelaide
@email: kenny13141314@163.com
@time: 2022/1/8
@description: Wide & Deep Learning for Recommender Systems implementation.
'''
class Wide(tf.keras.Model):
'''
this is a linear struct for learning some rules had defined,
it's input is a sparse matrix via as one-hot data.
'''
def __init__(self, Trained=True, **kwargs):
super().__init__(**kwargs)
self.Trained = Trained
def build(self, input_shape):
self.W = tf.Variable(initial_value=tf.random.truncated_normal([input_shape[1], 1],
dtype=tf.float32),
dtype=tf.float32, name='wide_weight')
self.b = tf.Variable(tf.zeros(shape=(1, 1),
dtype=tf.float32,
name='wide_bias').numpy(),
dtype=tf.float32)
def call(self, inputs):
return tf.transpose(tf.matmul(self.W,
inputs,
transpose_a=True,
transpose_b=True)
+ self.b)
class Deep(tf.keras.Model):
def __init__(self, **kwargs):
super().__init__(**kwargs)
# self.input_layer = tf.keras.Input(shape=(100, None))
self.hidden1 = tf.keras.layers.Dense(512,
activation='relu',
name='deep_hidden1')
self.hidden2 = tf.keras.layers.Dense(216,
activation='relu',
name='deep_hidden2')
self.hidden3 = tf.keras.layers.Dense(1,
activation='relu',
name='deep_hidden3', trainable=False)
'''
in order to update the weight via loss, hence, the last dense's weight will not changed or updated.
set trainable = False, means that the loss result will be useful for wide and deep part directly.
'''
def call(self, inputs,
training=None,
mask=None):
output1 = inputs
output2 = self.hidden1(output1)
output3 = self.hidden2(output2)
output4 = self.hidden3(output3)
return output4
class Estimate(object):
'''
this is a estimate object for machine learning.
'''
def __init__(self):
pass
def wide_deep_joint_train(self, wide_deep_input, y):
'''
joint training.
:return:
'''
result = tf.keras.layers.Dense(1, activation='sigmoid')(wide_deep_input)
# print(result)
# rows, cols = np.nonzero(y)
# pred_y = y
#
# for i in range(0, len(rows)):
# pred_y[rows[i], cols[i]] = result[rows[i]]
#
# print(result-pred_y)
class DataGenerate(object):
'''
this is a data-generation machine for training data.
'''
def __init__(self, shape):
self.embedding_weight = tf.Variable(initial_value=tf.random.truncated_normal(shape=shape,
dtype=tf.float32),
dtype=tf.float32,
name='embedding_weight')
def embedding_look(self, ids, values, shape):
ids = tf.SparseTensor(indices=ids, values=values, dense_shape=shape)
result = tf.compat.v1.nn.embedding_lookup_sparse(self.embedding_weight, ids, None,
partition_strategy="div", combiner='mean')
return result
def making_ebedding_bacpage(self, filed):
filed = np.array(filed).reshape(len(filed), 1)
filed_values = []
filed_ids = []
for i in range(0, len(filed)):
filed_ids.append([i, 0])
filed_values.append(filed[i][0])
embedding = self.embedding_look(filed_ids, filed_values, shape=filed.shape)
return embedding
def wide_input_generate_data(self):
notes = 1000000
are = np.random.randint(0, 100, notes).reshape(notes, 1)
professional = np.random.randint(0, 1000, notes).reshape(notes, 1)
isplay = np.random.randint(0, 2, notes).reshape(notes, 1)
_are = [are[i][0] for i in range(0, len(are))]
_professional = [professional[i][0] for i in range(0, len(professional))]
_isplay = [isplay[i][0] for i in range(0, len(isplay))]
are_one_hot = tf.one_hot(_are, len(set(_are)), dtype=tf.int32)
professional_one_hot = tf.one_hot(_professional, len(set(_professional)), dtype=tf.int32)
isplay_one_hot = tf.one_hot(_isplay, len(set(_isplay)), dtype=tf.int32)
_are_embedding = self.making_ebedding_bacpage(_are)
_professional_embedding = self.making_ebedding_bacpage(_professional)
_isplay_embedding = self.making_ebedding_bacpage(_isplay)
_embeddings = tf.concat([_are_embedding, _professional_embedding], axis=1)
_embeddings = tf.concat([_embeddings, _isplay_embedding], axis=1)
X = tf.concat([are_one_hot, professional_one_hot], axis=1)
X = tf.concat([X, isplay_one_hot], axis=1)
X = tf.Variable(X.numpy(), dtype=tf.float32)
Y = tf.Variable(np.random.randint(0,
1000,
X.shape[0]).reshape(X.shape[0], 1),
dtype=tf.float32)
departments = ['sport', 'sport', 'drawing', 'gardening', 'travelling']
department_indexs = np.random.randint(0, 5, notes)
_departments = []
[_departments.append(departments[department_indexs[i]]) for i in range(0, len(department_indexs))]
# 特征数据
features = {
'age': np.random.randint(18, 100, notes),
'department': _departments,
}
department = tf.feature_column.categorical_column_with_vocabulary_list('department',
['sport', 'drawing', 'gardening',
'travelling'], dtype=tf.string)
age = tf.feature_column.categorical_column_with_identity('age',
num_buckets=notes,
default_value=18)
age_department = tf.feature_column.crossed_column([department, age],
30)
age_department = tf.feature_column.indicator_column(age_department)
# 组合特征列
columns = [
age_department,
]
cross_feature_inputs = tf.compat.v1.feature_column.input_layer(features, columns)
# before contacting two data, we need pre-process data as float.
wide_X = tf.concat([X,
cross_feature_inputs.numpy()],
axis=1)
deep_X = _embeddings
return wide_X, deep_X, Y
wide_X, deep_X, Y = DataGenerate(shape=[100000, 10]).wide_input_generate_data()
wide = Wide()
deep = tf.keras.Sequential(
[
tf.keras.layers.Dense(216,
activation='relu',
name='deep_hidden1'),
tf.keras.layers.Dense(108,
activation='relu',
name='deep_hidden2'),
tf.keras.layers.Dense(1,
activation='relu',
name='deep_hidden3', trainable=False)
]
)
#
estimate = Estimate()
# estimate.train(model=wide,
# X=wide_X,
# y=Y,
# learning_rate=0.01,
# iters=10000)
# wide.Trained = False
# print(wide(X))
class_y = tf.keras.utils.to_categorical(Y, 1000)
learning_rate = 0.001
def muloss(y, y_pred):
tf.reduce_mean(
tf.add(-tf.multiply(y, tf.math.log(y_pred)), -tf.multiply(1 - y, tf.math.log(1 - y_pred))))
optimizers = [
tf.keras.optimizers.Ftrl(learning_rate=0.1, learning_rate_power=-0.1,
initial_accumulator_value=0.1,
l1_regularization_strength=0.1,
l2_regularization_strength=0.1,
l2_shrinkage_regularization_strength=0.0,
name='ftrl'),
tf.keras.optimizers.Adagrad(
learning_rate=0.1,
initial_accumulator_value=0.1,
epsilon=1e-07,
name='Adagrad')]
for i in range(1000):
# update wide
with tf.GradientTape(persistent=True) as tape:
wide_output = wide(wide_X)
deep_output = deep(deep_X)
wide_deep_output = tf.add(deep_output, wide_output)
result = tf.nn.sigmoid(wide_deep_output)
loss = tf.reduce_mean(
tf.add(-tf.multiply(class_y, tf.math.log(result)), -tf.multiply(1 - class_y, tf.math.log(1 - result))))
print(loss)
wide_variable_gradient = tape.gradient(loss, wide.trainable_variables)
optimizers[0].apply_gradients(zip(wide_variable_gradient, wide.trainable_variables))
dee_variables_gradient = tape.gradient(loss, deep.trainable_variables)
optimizers[1].apply_gradients(zip(dee_variables_gradient, deep.trainable_variables))
实验loss :


版权声明:本文为博主kennyadelaide原创文章,版权归属原作者,如果侵权,请联系我们删除!
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_17674161/article/details/122561946
