一、BP神经网络是什么?
BP(back propagation)神经网络是一种按照误差逆向传播算法训练的多层前馈神经网络,是应用最广泛的神经网络模型之一。
从结构上讲,BP网络具有输入层、隐藏层和输出层;从本质上讲,BP算法就是以网络误差平方为目标函数、采用梯度下降法来计算目标函数的最小值。
二、神经网络的基础机制
BP神经网络的计算过程由正向计算过程和反向计算过程组成。
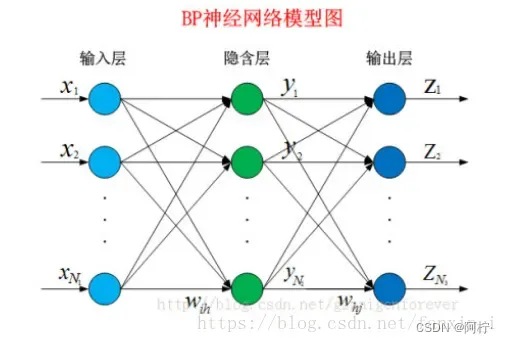
图 1. BP神经网络模型图
1. 正向传播
输入模式从输入层经隐含层逐层处理,并转向输出层,每一层神经元的状态只影响下一层神经元的状态。
1.1 神经元
神经网络的基本组成单元是神经元。神经元的通用模型如图2所示,其中常用的激活函数有阈值函数、sigmoid函数和双曲正切函数。
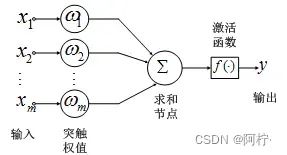
图 2. 神经元模型
神经元的输出为:
1.2 激活函数
BP神经网络采用的传递函数是非线性变换函数——Sigmoid函数(又称S函数)。其特点是函数本身及其导数都是连续的,因而在处理上十分方便。
Sigmoid函数公式为:
Sigmoid导函数公式为:
2.反向传播
反向传播将误差信号沿原来的连接通路返回,通过修改各神经元的权值,使得误差信号最小。
2.1 梯度下降
沿着梯度向量的方向,是训练误差增加最快的地方; 而沿着梯度向量相反的方向,梯度减少最快。
梯度下降法的直观理解参见下图:
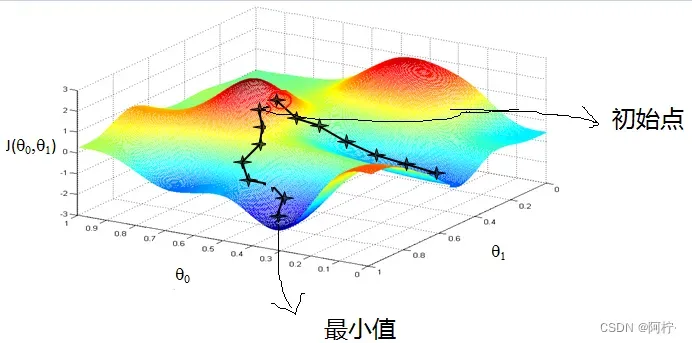
在山峰附件的某处,要一步一步走向山底,一个好的办法是求解当前位置的梯度,然后沿着梯度的负方向向下走一步,然后继续求解当前位置的梯度,继续沿着梯度的负方向走下去,这样一步一步直到山底,这其中用到的方向就是梯度下降法。
梯度下降法也有一个问题就是如果初始点的位置选择的不合适,就容易导致找到的一个局部最优解,而不是全局最优解。
三、数据读取与基本结构的实现
forward and backPropagation方法写为抽象类,在子类中实现。
package machinelearning.ann;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Random;
import weka.core.Instances;
/**
*
* @author Ling Lin E-mail:linling0.0@foxmail.com
*
* @version 创建时间:2022年5月21日 下午7:30:46
*
*/
public abstract class GeneralAnn {
/**
* The whole dataset.
*/
Instances dataset;
/**
* Number of layers. It is counted according to nodes instead of edges.
*/
int numLayers;
/**
* The number of nodes for each layer, e.g., [3, 4, 6, 2] means that there
* are 3 input nodes (conditional attributes), 2 hidden layers with 4 and 6
* nodes, respectively, and 2 class values (binary classification).
*/
int[] layerNumNodes;
/**
* Momentum coefficient.
*/
public double mobp;
/**
* Learning rate.
*/
public double learningRate;
/**
* For random number generation.
*/
Random random = new Random();
/**
********************
* The first constructor.
*
* @param paraFilename
* The arff filename.
* @param paraLayerNumNodes
* The number of nodes for each layer (may be different).
* @param paraLearningRate
* Learning rate.
* @param paraMobp
* Momentum coefficient.
********************
*/
public GeneralAnn(String paraFilename, int[] paraLayerNumNodes, double paraLearningRate, double paraMobp) {
// Step 1. Read data.
try {
FileReader tempReader = new FileReader(paraFilename);
dataset = new Instances(tempReader);
// The last attribute is the decision class.
dataset.setClassIndex(dataset.numAttributes() - 1);
tempReader.close();
} catch (Exception ee) {
System.out.println(
"Error occurred while trying to read \'" + paraFilename + "\' in GeneralAnn constructor.\r\n" + ee);
System.exit(0);
} // Of try
// Step 2. Accept parameters.
layerNumNodes = paraLayerNumNodes;
numLayers = layerNumNodes.length;
// Adjust if necessary.
layerNumNodes[0] = dataset.numAttributes() - 1;
layerNumNodes[numLayers - 1] = dataset.numClasses();
learningRate = paraLearningRate;
mobp = paraMobp;
}// Of the first constructor
/**
********************
* Forward prediction.
*
* @param paraInput
* The input data of one instance.
* @return The data at the output end.
********************
*/
public abstract double[] forward(double[] paraInput);
/**
********************
* Back propagation.
*
* @param paraTarget
* For 3-class data, it is [0, 0, 1], [0, 1, 0] or [1, 0, 0].
*
********************
*/
public abstract void backPropagation(double[] paraTarget);
/**
********************
* Train using the dataset.
********************
*/
public void train() {
double[] tempInput = new double[dataset.numAttributes() - 1];
double[] tempTarget = new double[dataset.numClasses()];
for (int i = 0; i < dataset.numInstances(); i++) {
// Fill the data.
for (int j = 0; j < tempInput.length; j++) {
tempInput[j] = dataset.instance(i).value(j);
} // Of for j
// Fill the class label.
Arrays.fill(tempTarget, 0);
tempTarget[(int) dataset.instance(i).classValue()] = 1;
// Train with this instance.
forward(tempInput);
backPropagation(tempTarget);
} // Of for i
}// Of train
/**
********************
* Get the index corresponding to the max value of the array.
*
* @return the index.
********************
*/
public static int argmax(double[] paraArray) {
int resultIndex = -1;
double tempMax = -1e10;
for (int i = 0; i < paraArray.length; i++) {
if (tempMax < paraArray[i]) {
tempMax = paraArray[i];
resultIndex = i;
} // Of if
} // Of for i
return resultIndex;
}// Of argmax
/**
********************
* Test using the dataset.
*
* @return The precision.
********************
*/
public double test() {
double[] tempInput = new double[dataset.numAttributes() - 1];
double tempNumCorrect = 0;
double[] tempPrediction;
int tempPredictedClass = -1;
for (int i = 0; i < dataset.numInstances(); i++) {
// Fill the data.
for (int j = 0; j < tempInput.length; j++) {
tempInput[j] = dataset.instance(i).value(j);
} // Of for j
// Train with this instance.
tempPrediction = forward(tempInput);
// System.out.println("prediction: " +
// Arrays.toString(tempPrediction));
tempPredictedClass = argmax(tempPrediction);
if (tempPredictedClass == (int) dataset.instance(i).classValue()) {
tempNumCorrect++;
} // Of if
} // Of for i
System.out.println("Correct: " + tempNumCorrect + " out of " + dataset.numInstances());
return tempNumCorrect / dataset.numInstances();
}// Of test
}// Of class GeneralAnn
文章出处登录后可见!
已经登录?立即刷新
