GAN
创建一个生成对抗网络(GAN) !构建和训练一个GAN,使其可以生成数字(0-9)的手写图像。
学习目标:
- 从零开始构建GAN的生成器和判别器。
- 创建GAN的生成器和判别器的损失函数。
- 训练GAN并将生成的图像可视化。
Getting Started
首先,导入一些有用的包和用于构建和训练GAN的数据集,也提供了一个可视化器函数,以帮助您研究GAN将创建的图像。
import torch
from torch import nn
from tqdm.auto import tqdm
from torchvision import transforms
from torchvision.datasets import MNIST # Training dataset
from torchvision.utils import make_grid
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
torch.manual_seed(0) # Set for testing purposes, please do not change!
def show_tensor_images(image_tensor, num_images=25, size=(1, 28, 28)):
'''
Function for visualizing images: Given a tensor of images, number of images, and
size per image, plots and prints the images in a uniform grid.
'''
image_unflat = image_tensor.detach().cpu().view(-1, *size)
image_grid = make_grid(image_unflat[:num_images], nrow=5)
plt.imshow(image_grid.permute(1, 2, 0).squeeze())
plt.show()
MNIST Dataset
判别器将使用的训练图像来自一个名为MNIST的数据集。它包含6万张手写数字的图像,从0到9,如下所示:
你可能会注意到图片像素化——这是因为它们都只有28×28 !其图像的小尺寸使MNIST成为简单训练的理想选择。此外,这些图像也是黑白的,所以只需要一个维度,或“彩色通道”,就可以表示它们(这在课程的后面)。
Generator
第一步构建生成器部件:
def get_generator_block(input_dim, output_dim):
'''
Function for returning a block of the generator's neural network
given input and output dimensions.
Parameters:
input_dim: the dimension of the input vector, a scalar
output_dim: the dimension of the output vector, a scalar
Returns:
a generator neural network layer, with a linear transformation
followed by a batch normalization and then a relu activation
'''
return nn.Sequential(
# Hint: Replace all of the "None" with the appropriate dimensions.
# The documentation may be useful if you're less familiar with PyTorch:
# https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/nn.html.
#### START CODE HERE ####
nn.Linear(input_dim, output_dim),
nn.BatchNorm1d(output_dim),
#### END CODE HERE ####
nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
)
现在可以构建生成器类了。它将取3个值:
- 噪声向量维数
- 图像尺寸
- 初始隐藏维数
利用这些值,生成器将构建一个5层/块的神经网络。从噪声向量开始,发生器将通过块函数进行非线性变换,直到张量映射到要输出的图像的大小(与MNIST的真实图像相同的大小)。你需要为最后一层填写代码,因为它与其他层不同。最后一层不需要标准化或激活函数,但需要使用sigmoid函数进行缩放。
class Generator(nn.Module):
'''
Generator Class
Values:
z_dim: the dimension of the noise vector, a scalar
im_dim: the dimension of the images, fitted for the dataset used, a scalar
(MNIST images are 28 x 28 = 784 so that is your default)
hidden_dim: the inner dimension, a scalar
'''
def __init__(self, z_dim=10, im_dim=784, hidden_dim=128):
super(Generator, self).__init__()
# Build the neural network
self.gen = nn.Sequential(
get_generator_block(z_dim, hidden_dim),
get_generator_block(hidden_dim, hidden_dim * 2),
get_generator_block(hidden_dim * 2, hidden_dim * 4),
get_generator_block(hidden_dim * 4, hidden_dim * 8),
# There is a dropdown with hints if you need them!
#### START CODE HERE ####
nn.Linear(hidden_dim * 8, im_dim),
nn.Sigmoid()
#### END CODE HERE ####
)
def forward(self, noise):
'''
Function for completing a forward pass of the generator: Given a noise tensor,
returns generated images.
Parameters:
noise: a noise tensor with dimensions (n_samples, z_dim)
'''
return self.gen(noise)
# Needed for grading
def get_gen(self):
'''
Returns:
the sequential model
'''
return self.gen
Noise
为了能够使用生成器,您需要能够创建噪声向量。噪声向量z的重要作用是确保从相同类别生成的图像不都看起来一样——可以将其视为随机种子。您将使用PyTorch通过从正态分布中抽样随机数随机生成它。由于每次处理都会处理多幅图像,因此您将同时生成所有的噪声向量。
def get_noise(n_samples, z_dim, device='cpu'):
'''
Function for creating noise vectors: Given the dimensions (n_samples, z_dim),
creates a tensor of that shape filled with random numbers from the normal distribution.
Parameters:
n_samples: the number of samples to generate, a scalar
z_dim: the dimension of the noise vector, a scalar
device: the device type
'''
# NOTE: To use this on GPU with device='cuda', make sure to pass the device
# argument to the function you use to generate the noise.
#### START CODE HERE ####
return torch.randn(n_samples,z_dim).to(device)
#### END CODE HERE ####
Discriminator
需要构造的第二个组件是判别器。与生成器组件一样,您将从创建一个为鉴别器构建神经网络块的函数开始。
def get_discriminator_block(input_dim, output_dim):
'''
Discriminator Block
Function for returning a neural network of the discriminator given input and output dimensions.
Parameters:
input_dim: the dimension of the input vector, a scalar
output_dim: the dimension of the output vector, a scalar
Returns:
a discriminator neural network layer, with a linear transformation
followed by an nn.LeakyReLU activation with negative slope of 0.2
(https://pytorch.org/docs/master/generated/torch.nn.LeakyReLU.html)
'''
return nn.Sequential(
#### START CODE HERE ####
nn.Linear(input_dim,output_dim),
nn.LeakyReLU(0.2)
#### END CODE HERE ####
)
现在您可以使用这些块来制作一个鉴别器,discriminator类包含2个值:
- 图像维度 The image dimension
- 隐藏层维度 The hidden dimension
该鉴别器将构建一个4层的神经网络。它将从图像张量开始,并对其进行变换,直到它返回单个数字(一维张量)输出。这个输出将对图像的真伪进行分类。注意,在输出层之后不需要sigmoid,因为它包含在损失函数中。最后,为了使用你的鉴别器的神经网络,你会得到一个前向传递函数,它接受一个要分类的图像张量。
class Discriminator(nn.Module):
'''
Discriminator Class
Values:
im_dim: the dimension of the images, fitted for the dataset used, a scalar
(MNIST images are 28x28 = 784 so that is your default)
hidden_dim: the inner dimension, a scalar
'''
def __init__(self, im_dim=784, hidden_dim=128):
super(Discriminator, self).__init__()
self.disc = nn.Sequential(
get_discriminator_block(im_dim, hidden_dim * 4),
get_discriminator_block(hidden_dim * 4, hidden_dim * 2),
get_discriminator_block(hidden_dim * 2, hidden_dim),
# Hint: You want to transform the final output into a single value,
# so add one more linear map.
#### START CODE HERE ####
nn.Linear(hidden_dim,1)
#### END CODE HERE ####
)
def forward(self, image):
'''
Function for completing a forward pass of the discriminator: Given an image tensor,
returns a 1-dimension tensor representing fake/real.
Parameters:
image: a flattened image tensor with dimension (im_dim)
'''
return self.disc(image)
# Needed for grading
def get_disc(self):
'''
Returns:
the sequential model
'''
return self.disc
Training¶
# Set your parameters
criterion = nn.BCEWithLogitsLoss()
n_epochs = 10
z_dim = 64
display_step = 500
batch_size = 128
lr = 0.00001
# Load MNIST dataset as tensors
dataloader = DataLoader(
MNIST('.', download=False, transform=transforms.ToTensor()),
batch_size=batch_size,
shuffle=True)
### DO NOT EDIT ###
device = 'cuda'
初始化生成器、鉴别器和优化器。每个优化器只接受一个特定模型的参数,每个优化器只优化一个模型。
gen = Generator(z_dim).to(device)
gen_opt = torch.optim.Adam(gen.parameters(), lr=lr)
disc = Discriminator().to(device)
disc_opt = torch.optim.Adam(disc.parameters(), lr=lr)
在训练GAN之前,需要创建损失函数来计算判别器的损失和生成器的损失。这就是判别器和生成器如何知道他们在做什么并改进自己的方式。由于在计算判别器的损失时需要使用生成器,因此需要对生成器的结果调用.detach()以确保只有鉴别器被更新。
def get_disc_loss(gen, disc, criterion, real, num_images, z_dim, device):
'''
Return the loss of the discriminator given inputs.
Parameters:
gen: the generator model, which returns an image given z-dimensional noise
disc: the discriminator model, which returns a single-dimensional prediction of real/fake
criterion: the loss function, which should be used to compare
the discriminator's predictions to the ground truth reality of the images
(e.g. fake = 0, real = 1)
real: a batch of real images
num_images: the number of images the generator should produce,
which is also the length of the real images
z_dim: the dimension of the noise vector, a scalar
device: the device type
Returns:
disc_loss: a torch scalar loss value for the current batch
'''
# These are the steps you will need to complete:
# 1) Create noise vectors and generate a batch (num_images) of fake images.
# Make sure to pass the device argument to the noise.
# 2) Get the discriminator's prediction of the fake image
# and calculate the loss. Don't forget to detach the generator!
# (Remember the loss function you set earlier -- criterion. You need a
# 'ground truth' tensor in order to calculate the loss.
# For example, a ground truth tensor for a fake image is all zeros.)
# 3) Get the discriminator's prediction of the real image and calculate the loss.
# 4) Calculate the discriminator's loss by averaging the real and fake loss
# and set it to disc_loss.
# *Important*: You should NOT write your own loss function here - use criterion(pred, true)!
#### START CODE HERE ####
real_label = torch.ones(num_images,1, device = device)
fake_label = torch.zeros(num_images,1, device = device)
noise = get_noise(num_images, z_dim, device=device)
gen_output = gen(noise)
gen_detached = gen_output.detach()
fake_output = disc(gen_detached)
d_loss_fake = criterion(fake_output, fake_label)
real_output = disc(real)
d_loss_real = criterion(real_output, real_label)
disc_loss = torch.div(torch.add(d_loss_fake, d_loss_real), 2)
#### END CODE HERE ####
return disc_loss
def get_gen_loss(gen, disc, criterion, num_images, z_dim, device):
'''
Return the loss of the generator given inputs.
Parameters:
gen: the generator model, which returns an image given z-dimensional noise
disc: the discriminator model, which returns a single-dimensional prediction of real/fake
criterion: the loss function, which should be used to compare
the discriminator's predictions to the ground truth reality of the images
(e.g. fake = 0, real = 1)
num_images: the number of images the generator should produce,
which is also the length of the real images
z_dim: the dimension of the noise vector, a scalar
device: the device type
Returns:
gen_loss: a torch scalar loss value for the current batch
'''
# These are the steps you will need to complete:
# 1) Create noise vectors and generate a batch of fake images.
# Remember to pass the device argument to the get_noise function.
# 2) Get the discriminator's prediction of the fake image.
# 3) Calculate the generator's loss. Remember the generator wants
# the discriminator to think that its fake images are real
# *Important*: You should NOT write your own loss function here - use criterion(pred, true)!
#### START CODE HERE ####
real_label = torch.ones(num_images, 1, device = device)
noise = get_noise(num_images, z_dim, device=device)
fake_imgs = gen(noise)
disc_output = disc(fake_imgs)
gen_loss = criterion(disc_output,real_label)
#### END CODE HERE ####
return gen_loss
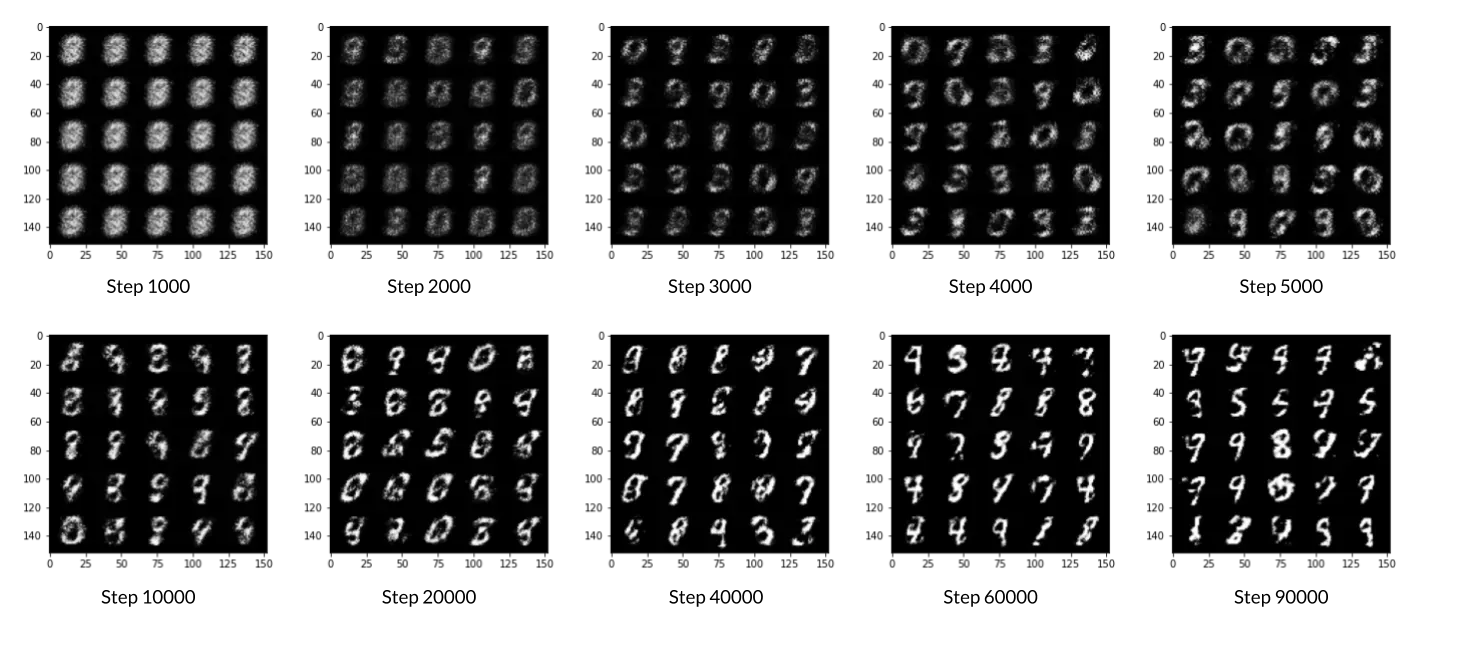
最后,可以把所有东西放在一起了!对于每个时期,将分批处理整个数据集。对于每一批,将需要更新判别器和生成器使用它们的损失。批是在计算损失函数之前进行预测的一组图像(而不是在每幅图像之后计算损失函数)。请注意,可能会看到一个损失大于1,这是可以的,因为二进制交叉熵损失可以是任何正数,对于一个足够有把握的错误猜测。
如果想了解不同的体系结构选择如何导致更好或更差的GANs,可以随意使用该体系结构。例如,考虑改变隐藏维度的大小,或者通过改变层数使网络变浅或变深。
# OPTIONAL PART
cur_step = 0
mean_generator_loss = 0
mean_discriminator_loss = 0
test_generator = True # Whether the generator should be tested
gen_loss = False
error = False
for epoch in range(n_epochs):
# Dataloader returns the batches
for real, _ in tqdm(dataloader):
cur_batch_size = len(real)
# Flatten the batch of real images from the dataset
real = real.view(cur_batch_size, -1).to(device)
### Update discriminator ###
# Zero out the gradients before backpropagation
disc_opt.zero_grad()
# Calculate discriminator loss
disc_loss = get_disc_loss(gen, disc, criterion, real, cur_batch_size, z_dim, device)
# Update gradients
disc_loss.backward(retain_graph=True)
# Update optimizer
disc_opt.step()
# For testing purposes, to keep track of the generator weights
if test_generator:
old_generator_weights = gen.gen[0][0].weight.detach().clone()
### Update generator ###
# Hint: This code will look a lot like the discriminator updates!
# These are the steps you will need to complete:
# 1) Zero out the gradients.
# 2) Calculate the generator loss, assigning it to gen_loss.
# 3) Backprop through the generator: update the gradients and optimizer.
#### START CODE HERE ####
gen_opt.zero_grad()
gen_loss = get_gen_loss(gen, disc, criterion, 10, z_dim, device)
gen_loss.backward(retain_graph=True)
gen_opt.step()
#### END CODE HERE ####
# For testing purposes, to check that your code changes the generator weights
if test_generator:
try:
assert lr > 0.0000002 or (gen.gen[0][0].weight.grad.abs().max() < 0.0005 and epoch == 0)
assert torch.any(gen.gen[0][0].weight.detach().clone() != old_generator_weights)
except:
error = True
print("Runtime tests have failed")
# Keep track of the average discriminator loss
mean_discriminator_loss += disc_loss.item() / display_step
# Keep track of the average generator loss
mean_generator_loss += gen_loss.item() / display_step
### Visualization code ###
if cur_step % display_step == 0 and cur_step > 0:
print(f"Step {cur_step}: Generator loss: {mean_generator_loss}, discriminator loss: {mean_discriminator_loss}")
fake_noise = get_noise(cur_batch_size, z_dim, device=device)
fake = gen(fake_noise)
show_tensor_images(fake)
show_tensor_images(real)
mean_generator_loss = 0
mean_discriminator_loss = 0
cur_step += 1
文章出处登录后可见!
