欢迎来到英杰社区![]() https://bbs.csdn.net/topics/617804998
https://bbs.csdn.net/topics/617804998
一、前言、
在数据分析和挖掘领域中,网络爬虫是一种常见的工具,用于从网页上收集数据。本文将介绍如何使用 Python 编写简单的网络爬虫程序,从链家网上海二手房页面获取房屋信息,并将数据保存到 Excel 文件中。
二、效果图:
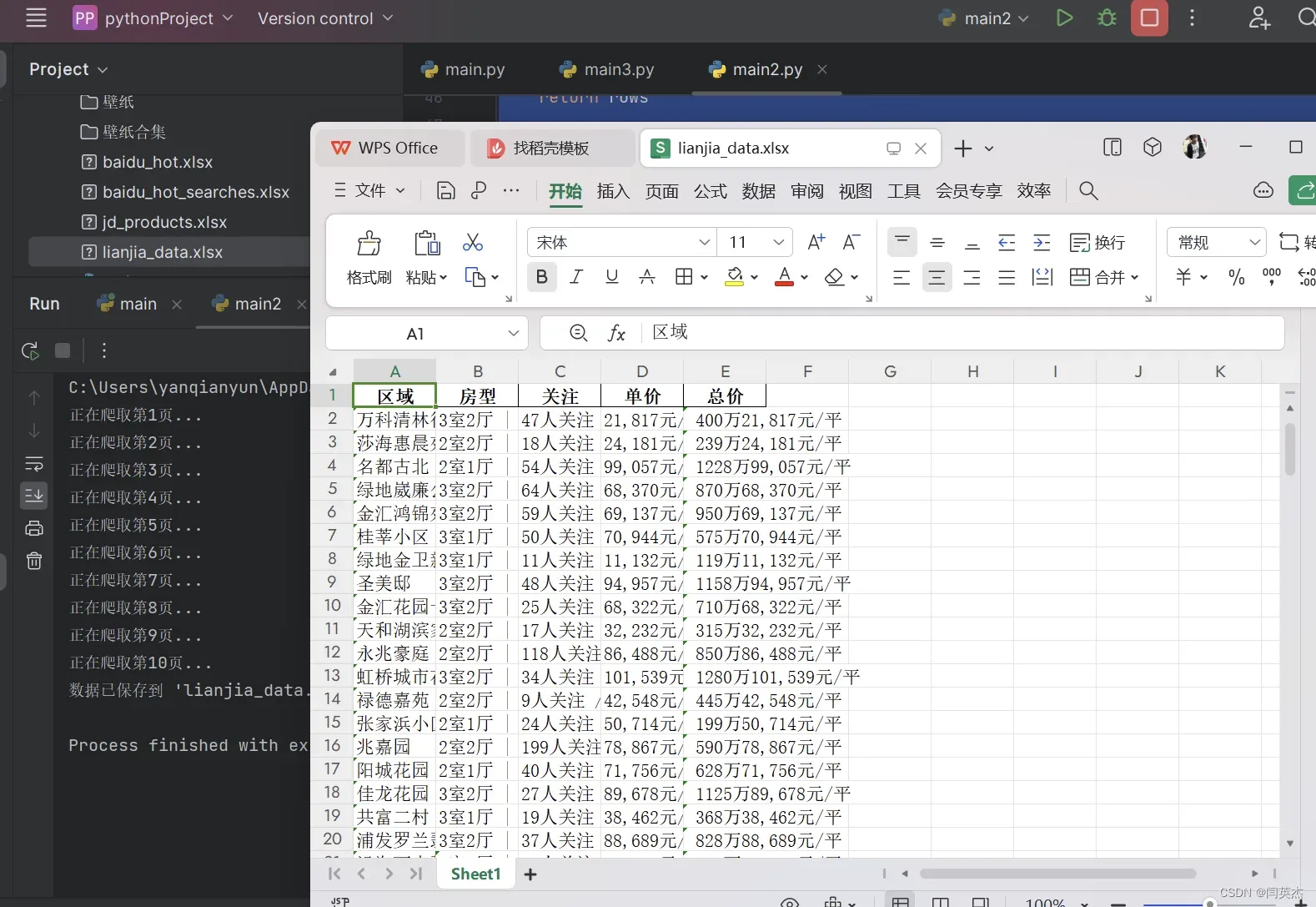
-
导入需要的库:
requests:用于发送 HTTP 请求和获取网页内容。BeautifulSoup:用于解析 HTML 内容,提取所需信息。pandas:用于数据处理和保存数据到 Excel 文件。
import requests
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
import pandas as pd如果出现模块报错
进入控制台输入:建议使用国内镜像源
pip install 模块名称 -i https://mirrors.aliyun.com/pypi/simple
我大致罗列了以下几种国内镜像源:
清华大学
https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple
阿里云
https://mirrors.aliyun.com/pypi/simple/
豆瓣
https://pypi.douban.com/simple/
百度云
https://mirror.baidu.com/pypi/simple/
中科大
https://pypi.mirrors.ustc.edu.cn/simple/
华为云
https://mirrors.huaweicloud.com/repository/pypi/simple/
腾讯云
https://mirrors.cloud.tencent.com/pypi/simple/三、代码分析
首先,我们定义了一个函数 fetch_data(page_number),用于获取指定页面的房屋信息数据。这个函数会构建对应页数的 URL,并发送 GET 请求获取页面内容。然后,使用 BeautifulSoup 解析页面内容,并提取每个房屋信息的相关数据,如区域、房型、关注人数、单价和总价。最终将提取的数据以字典形式存储在列表中,并返回该列表。
接下来,我们定义了主函数 main(),该函数控制整个爬取和保存数据的流程。在主函数中,我们循环爬取前 10 页的数据,调用 fetch_data(page_number) 函数获取每一页的数据,并将数据追加到列表中。然后,将所有爬取的数据存储在 DataFrame 中,并使用 df.to_excel('lianjia_data.xlsx', index=False) 将数据保存到 Excel 文件中。
最后,在程序的入口处,通过 if __name__ == "__main__": 来执行主函数 main()。
四、详解代码
-
定义
fetch_data(page_number)函数:- 这个函数接收一个参数
page_number,表示要爬取的页面页数。 - 构建相应页数的 URL,并发送 GET 请求获取页面内容。
- 使用 BeautifulSoup 解析页面内容,并提取每个房屋信息的相关数据,如区域、房型、关注人数、单价和总价。
- 将提取的数据以字典形式存储在
rows列表中,并返回该列表。
- 这个函数接收一个参数
# 收集单页数据 xpanx.com
def fetch_data(page_number):
url = f"https://sh.lianjia.com/ershoufang/pg{page_number}/"
response = requests.get(url)
if response.status_code != 200:
print("请求失败")
return []
soup = BeautifulSoup(response.text, 'html.parser')
rows = []
for house_info in soup.find_all("li", {"class": "clear LOGVIEWDATA LOGCLICKDATA"}):
row = {}
# 使用您提供的类名来获取数据 xpanx.com
row['区域'] = house_info.find("div", {"class": "positionInfo"}).get_text() if house_info.find("div", {
"class": "positionInfo"}) else None
row['房型'] = house_info.find("div", {"class": "houseInfo"}).get_text() if house_info.find("div", {
"class": "houseInfo"}) else None
row['关注'] = house_info.find("div", {"class": "followInfo"}).get_text() if house_info.find("div", {
"class": "followInfo"}) else None
row['单价'] = house_info.find("div", {"class": "unitPrice"}).get_text() if house_info.find("div", {
"class": "unitPrice"}) else None
row['总价'] = house_info.find("div", {"class": "priceInfo"}).get_text() if house_info.find("div", {
"class": "priceInfo"}) else None
rows.append(row)
return rows
# 主函数
def main():
all_data = []
for i in range(1, 11): # 爬取前10页数据作为示例
print(f"正在爬取第{i}页...")
all_data += fetch_data(i)
# 保存数据到Excel xpanx.com
df = pd.DataFrame(all_data)
df.to_excel('lianjia_data.xlsx', index=False)
print("数据已保存到 'lianjia_data.xlsx'")-
定义
main()函数:- 在主函数中循环爬取前 10 页的数据,调用
fetch_data(page_number)函数获取每一页的数据,并将数据追加到all_data列表中。 - 将所有爬取的数据存储在 DataFrame 中。
- 最后使用
df.to_excel('lianjia_data.xlsx', index=False)将数据保存到名为lianjia_data.xlsx的 Excel 文件中。
- 在主函数中循环爬取前 10 页的数据,调用
五、完整代码
这段代码的主要流程是通过循环遍历页面页数,调用 fetch_data(page_number) 函数爬取每一页的数据,并将数据保存到 Excel 文件中。整体上,这个程序完成了以下几个主要功能:
- 发送 HTTP 请求并获取网页内容。
- 使用 BeautifulSoup 解析 HTML 内容,提取所需信息。
- 将提取的数据存储在列表中。
- 将列表数据转换为 DataFrame。
- 将 DataFrame 数据保存到 Excel 文件中。
import requests
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
import pandas as pd
# 收集单页数据 xpanx.com
def fetch_data(page_number):
url = f"https://sh.lianjia.com/ershoufang/pg{page_number}/"
response = requests.get(url)
if response.status_code != 200:
print("请求失败")
return []
soup = BeautifulSoup(response.text, 'html.parser')
rows = []
for house_info in soup.find_all("li", {"class": "clear LOGVIEWDATA LOGCLICKDATA"}):
row = {}
# 使用您提供的类名来获取数据 xpanx.com
row['区域'] = house_info.find("div", {"class": "positionInfo"}).get_text() if house_info.find("div", {
"class": "positionInfo"}) else None
row['房型'] = house_info.find("div", {"class": "houseInfo"}).get_text() if house_info.find("div", {
"class": "houseInfo"}) else None
row['关注'] = house_info.find("div", {"class": "followInfo"}).get_text() if house_info.find("div", {
"class": "followInfo"}) else None
row['单价'] = house_info.find("div", {"class": "unitPrice"}).get_text() if house_info.find("div", {
"class": "unitPrice"}) else None
row['总价'] = house_info.find("div", {"class": "priceInfo"}).get_text() if house_info.find("div", {
"class": "priceInfo"}) else None
rows.append(row)
return rows
# 主函数
def main():
all_data = []
for i in range(1, 11): # 爬取前10页数据作为示例
print(f"正在爬取第{i}页...")
all_data += fetch_data(i)
# 保存数据到Excel xpanx.com
df = pd.DataFrame(all_data)
df.to_excel('lianjia_data.xlsx', index=False)
print("数据已保存到 'lianjia_data.xlsx'")
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()版权声明:本文为博主作者:Yan-英杰原创文章,版权归属原作者,如果侵权,请联系我们删除!
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/m0_73367097/article/details/136426621
