目录
- 0 专栏介绍
- 1 Informed RRT*原理
- 2 Informed RRT*流程
- 3 ROS C++实现
- 4 Python实现
- 5 Matlab实现
0 专栏介绍
🔥附C++/Python/Matlab全套代码🔥课程设计、毕业设计、创新竞赛必备!详细介绍全局规划(图搜索、采样法、智能算法等);局部规划(DWA、APF等);曲线优化(贝塞尔曲线、B样条曲线等)。
🚀详情:图解自动驾驶中的运动规划(Motion Planning),附几十种规划算法
1 Informed RRT*原理
传统的RRT算法存在一些局限性。在复杂的环境中,RRT算法可能会生成较长的路径,因为它主要依赖于随机采样,路径的探索性较强,而对于局部信息的利用较少,这可能导致路径搜索效率低。

Informed RRT*算法针对RRT*算法进行了采样优化,用椭圆采样代替全局均匀采样,避免了RRT*算法搜索树上产生过多冗余分支的缺陷,提高了搜索效率和收敛速度。在Informed RRT*算法中,以起点、终点为焦点,二者的直线距离为焦距;当前规划的起点、终点最佳路径长度为
,以
为长轴,
为短轴构造椭圆采样区域。
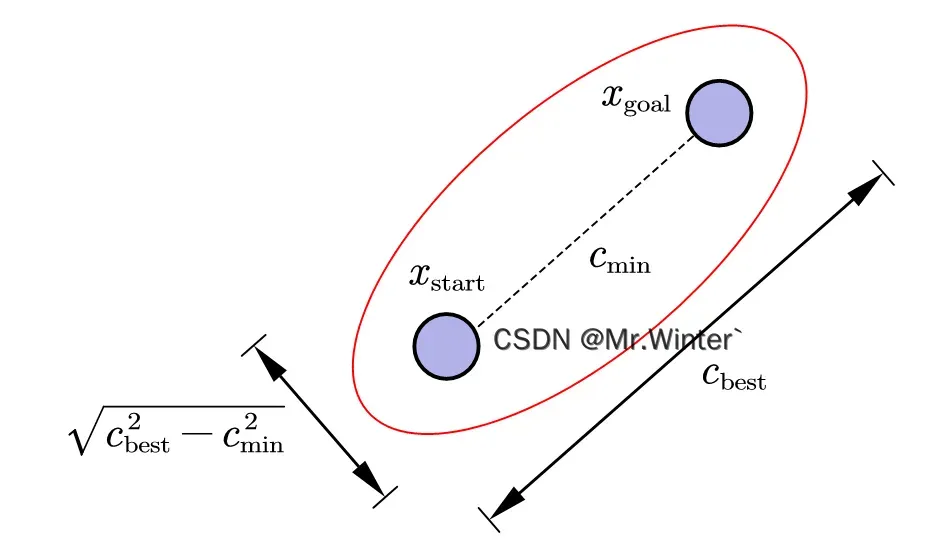
工程上一般先在标准圆内采样,再通过齐次变换
将采样点映射到地图中,其中是起点、终点连线与
轴的夹角;
是起点、终点的中点;
、
分别是长轴、短轴,
是伸缩变换和旋转变换的复合。我们通过代码来直观看看是如何实现椭圆采样的
Node InformedRRT::_transform(double x, double y)
{
// center
double center_x = (start_.x_ + goal_.x_) / 2;
double center_y = (start_.y_ + goal_.y_) / 2;
// rotation
double theta = -_angle(start_, goal_);
// ellipse
double a = c_best_ / 2.0;
double c = c_min_ / 2.0;
double b = std::sqrt(a * a - c * c);
// transform
int tx = (int)(a * cos(theta) * x + b * sin(theta) * y + center_x);
int ty = (int)(-a * sin(theta) * x + b * cos(theta) * y + center_y);
int id = grid2Index(tx, ty);
return Node(tx, ty, 0, 0, id, 0);
}
2 Informed RRT*流程
Informed RRT*算法流程如下

3 ROS C++实现
核心代码如下所示
bool InformedRRT::plan(const unsigned char* gloal_costmap, const Node& start, const Node& goal, std::vector<Node>& path,
std::vector<Node>& expand)
{
// initialization
c_best_ = std::numeric_limits<double>::max();
c_min_ = _dist(start, goal);
int best_parent = -1;
sample_list_.clear();
// copy
start_ = start, goal_ = goal;
costs_ = gloal_costmap;
sample_list_.insert(start);
expand.push_back(start);
// main loop
int iteration = 0;
while (iteration < sample_num_)
{
iteration++;
// generate a random node in the map
Node sample_node = _generateRandomNode();
// obstacle
if (gloal_costmap[sample_node.id_] >= lethal_cost_ * factor_)
continue;
// visited
if (sample_list_.find(sample_node) != sample_list_.end())
continue;
// regular the sample node
Node new_node = _findNearestPoint(sample_list_, sample_node);
if (new_node.id_ == -1)
continue;
else
{
sample_list_.insert(new_node);
expand.push_back(new_node);
}
// goal found
auto dist = _dist(new_node, goal_);
if (dist <= max_dist_ && !_isAnyObstacleInPath(new_node, goal_))
{
double cost = dist + new_node.g_;
if (cost < c_best_)
{
best_parent = new_node.id_;
c_best_ = cost;
}
}
}
if (best_parent != -1)
{
Node goal_(goal_.x_, goal_.y_, c_best_, 0, grid2Index(goal_.x_, goal_.y_),
best_parent);
sample_list_.insert(goal_);
path = _convertClosedListToPath(sample_list_, start, goal);
return true;
}
return false;
}
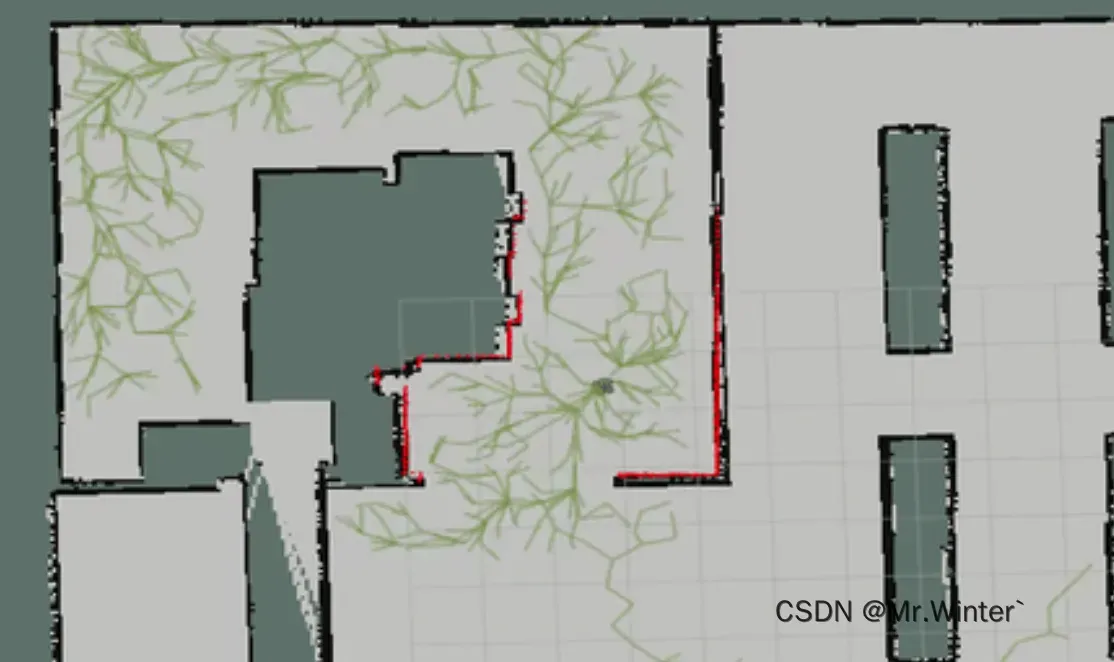
运行效果图
4 Python实现
核心代码如下所示
def plan(self):
# generate a random node in the map
node_rand = self.generateRandomNode()
# visited
if node_rand in self.sample_list:
return 0, None
# generate new node
node_new = self.getNearest(self.sample_list, node_rand)
if node_new:
self.sample_list.append(node_new)
dist = self.dist(node_new, self.goal)
# goal found
if dist <= self.max_dist and not self.isCollision(node_new, self.goal):
self.goal.parent = node_new.current
self.goal.g = node_new.g + self.dist(self.goal, node_new)
self.sample_list.append(self.goal)
return self.extractPath(self.sample_list)
return 0, None
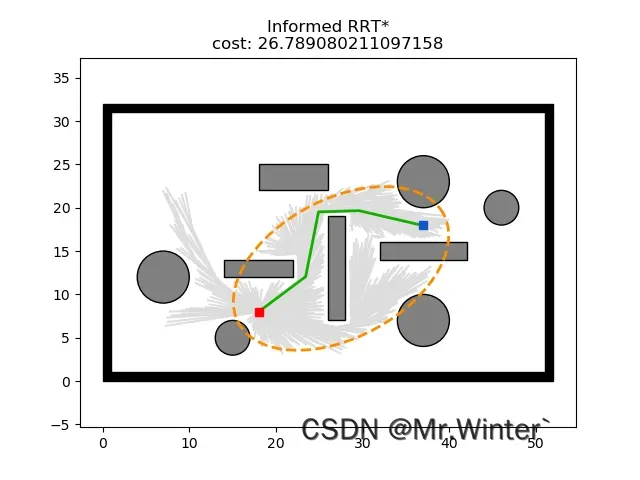
运行效果图
5 Matlab实现
核心代码如下:
function [cost, flag, node_list, path] = plan(node_list, start, goal, map, param)
cost = 0;
flag = false;
path = [];
% generate a random node in the map
node_rand = generate_node(start, goal, param);
% visited
if loc_list(node_rand, node_list, [1, 2])
return
end
% generate new node
[node_new, success] = get_nearest(node_list, node_rand, map, param);
if success
node_list = [node_new; node_list];
distance = dist(node_new(1:2), goal');
% goal found
if distance <= param.max_dist && ~is_collision(node_new(1:2), goal, map, param)
goal_ = [goal, node_new(3) + distance, node_new(1:2)];
node_list = [goal_; node_list];
flag = true;
cost = goal_(3);
path = extract_path(node_list, start);
node_list(1, :) = [];
return
end
end
end
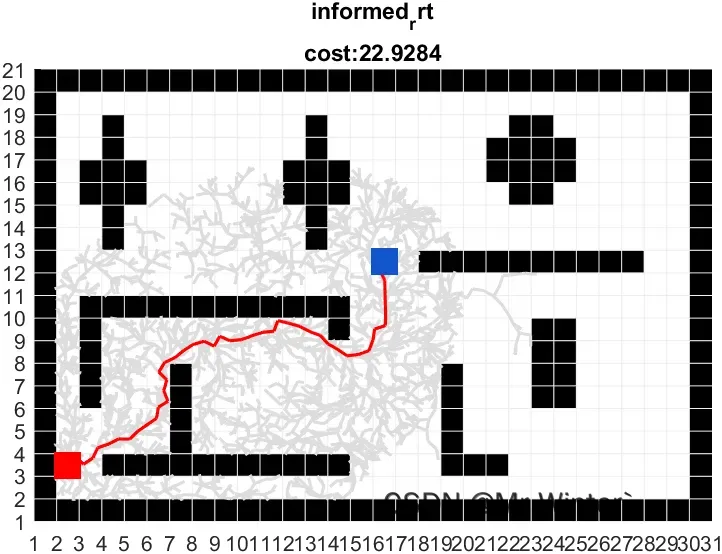
运行效果图
完整工程代码请联系下方博主名片获取
🔥 更多精彩专栏:
- 《ROS从入门到精通》
- 《Pytorch深度学习实战》
- 《机器学习强基计划》
- 《运动规划实战精讲》
- …
文章出处登录后可见!
已经登录?立即刷新
